Question:
Consider the differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dx}=2x – y.\)
(a) On the axes provided, sketch a slope field for the given differential equation at the six points indicated.
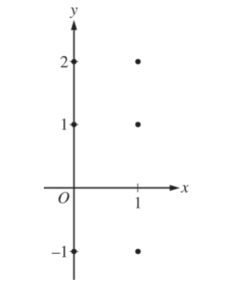
(b) Find \(\frac{d^{2}y}{dx^{2}}\) in terms of x and y. Determine the concavity of all solution curves for the given differential equation in Quadrant II. Give a reason for your answer.
(c) Let y = f(x) be the particular solution to the differential equation with the initial condition f (2) = 3.
Does f have a relative minimum, a relative maximum, or neither at x = 2 ? Justify your answer.
(d) Find the values of the constants m and b for which y = mx + b is a solution to the differential equation.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
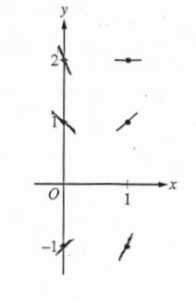
(b)
\(\frac{dy}{dx}= 2x – y\)
\(\frac{d^{2}y}{dx^{2}}= 2-\frac{dy}{dx}=2-(2x-y)\)
\(\frac{d^{2}y}{dx^{2}}= 2-2x+y\)
In Quadrant II, x < 0 and y > 0, So \(\frac{d^{2}y}{dx^{2}}= 2-2x+y>0,\)
Thus all solution curves in Quadrant II are concave up.
(c)
\(\frac{dy}{dx}= 2x-y=2.2-3 =1\)
Neither, as \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) ≠ 0 at x = 2.
(d)
\(\frac{dy}{dx}= 2x-y\), y = mx + b
\(\frac{dy}{dx}= m = 2x – y\)
m = 2x – (mx + b)
m = (2-m)x – b, equate coefficients
2 – m = 0
m = 2
-b = m
b = -m = -2.
m = 2, b = -2
Question:
At time t = 0, a boiled potato is taken from a pot on a stove and left to cool in a kitchen. The internal temperature of the potato is 91 degrees Celsius (°C) at time t = 0, and the internal temperature of the potato is greater than 27 C° for all times t > 0. The internal temperature of the potato at time t minutes can be modeled by the function H that satisfies the differential equation \(\frac{dH}{dt}=-\frac{1}{4}(H-27)\), where H(t) is measured in degrees Celsius and H( 0) = 91 .
(a) Write an equation for the line tangent to the graph of H at t = 0. Use this equation to approximate the internal temperature of the potato at time t = 3.
(b) Use \(\frac{d^{2}H}{dt^{2}}\) to determine whether your answer in part (a) is an underestimate or an overestimate of the internal temperature of the potato at time t = 3.
(c) For t < 10, an alternate model for the internal temperature of the potato at time t minutes is the function G that satisfies the differential equation \(\frac{dG}{dt} = -(G-27)^{2/3},\) where G(t) is measured in degrees Celsius and G(0) = 91. Find an expression for G (t). Based on this model, what is the internal temperature of the potato at time t = 3 ?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
\(\frac{dH}{dt}_{H=91} = -\frac{1}{4}(91-27)=\left ( -\frac{1}{4} \right )(64)=-16\)
A(t) = -16 (t-0) + 91
A(t) = -16t + 91
A(3) = – 16(3) + 91
= -48 + 91
430C
at t = 3 minutes
(b)
\(\frac{dH}{dt} = -\frac{1}{4}(H-27)\) H > 27 for all t > 0
\(\frac{d^{2}H}{dt^{2}} = -\frac{1}{4}\left ( \frac{dH}{dt} \right )\) \(\frac{d^{2}H}{dt^{2}}\) is always positive,
\(-\frac{1}{4}\left ( -\frac{1}{4} \right )(H-24)\) So part (a) is an underestimate.
\(\frac{d^{2}H}{dt^{2}} = \frac{1}{16}(H-24)\)
(c)
\(\frac{dG}{dt} = -(G-27)^{2/3}\)
\(\int \frac{dG}{(G-27)^{2/3}}=\int -1dt\)
\(\int (G-27)^{-2/3}dt = -t+c\)
3 (G-27) 1/3 = -t + c1
\((G-27)^{-2/3} = -\frac{t}{3}+c_{2}\)
\(G-27 = \left ( -\frac{t}{3}+c_{2} \right )^{3}\)
\(G = \left ( -\frac{t}{3}+c_{2} \right )^{3}+27\)
at (0, 91)
\(91= (0+c_{2})^{3}+27\)
91 = (c2)3 + 27
64 = (c2)3 →c2 = 4
\(G(t)= \left ( -\frac{t}{3}+4 \right )^{3}+27\)
\(G(3)= \left ( \frac{-3}{3}+4 \right )^{3}+27\)
= (3)3 + 27
= 27 + 27
G(3) = 540C
