Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonds
- Electrons are transferred from one atom to another creating ions
- Metal + nonmetal
- Metals form cations (lose e- bcuz low IE) and nonmetals form anions (gain e- bcuz high IE)
- Cations are attracted to anions; (+) & (-) attract
- Nonmetal achieves electron configuration of next noble gas and valence orbitals of metal are emptied
- Ions are usually more stable than atoms but still unstable because are electrically charged
- Before losing/gaining electrons, atoms are neutral (no charge)
- All elements with more than one charge are metals and give away e- (+)
Types of Ions
- Ions: electrically charged particle
Monatomic = one type of atom (same element)
- H+, \(Ca^2+, N^3-\)
Polyatomic = many types of atoms (different elements) with a charge; small charged molecules
- Held by covalent bonds and net charge is not zero
- Elements are in imperfect bonding → slightly more stable than by itself
- So they are ready to react with a better bond
Lewis Dot Structures 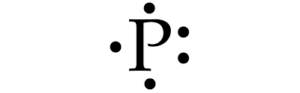
- Valence electrons represented by dots, no more than two per side
- Can show rearrangement of electrons during chemical reactions
- Note: CH3+→ has lost an e- so C will have only 6 ve-
Binary Ionic Compounds
- Contains ions of only two elements
- Formula: cation first, then anion
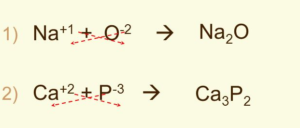
- Charges of atoms written as superscript (on top)
- Number of atoms written as subscripts (on bottom)
- Cation has positive charge while anion has negative
- The total (net) charge on the compound should be zero
Naming Types of Ionic Compounds
- If cation has more than one valence (can have different charges) indicate the charge using roman numerals in parentheses after the cation name
- FeO = iron (II) Oxide
Binary Ionic Compounds
- Name cation using its element name
- Some have common names (ex. Water, sodium)
- Name anion by dropping ending of the element name and adding -ide
- Ex: Calcium Phosphide → -ide shows that there is one anion
Polyatomic Ionic Compounds
- If anion is polyatomic, name it using the ions name
- Will be polyatomic if ends in -ate or -ite
- -ate = has more oxygen ions
- -ite = has less oxygen ions
- Treat as one whole unit
- Always use parenthesis () unless there is only one
- Fe(OH)₂
- 3 ions
- 5 atoms: two subscript belongs to hydrogen AND oxygen
Covalent Bonding 
- Covalent Bonds: formed by a share of a pair of electrons between two atoms that completes electron configuration of both atoms
- Between nonmetals (gasses)
- Shared electrons give a lower energy state because they are simultaneously attracted by two nuclei
Types of Covalent Bonds
- Polar covalent bonds = unequal sharing; charges indicated using small delta
- Due to electronegativity difference: electrons pulled to more electroneg. atom
- More electroneg. atom becomes slightly (-) (higher e- density)
- Less electroneg. atom becomes slightly (+)
- Soluble in water (hydrophilic) cuz of charge
- Due to electronegativity difference: electrons pulled to more electroneg. atom
- Nonpolar covalent bonds = atoms of the same element or with similar electronegativity so have equal sharing of e-
- Ex: O₂, N₂, Cl₂
- Even though is bonded to itself, is more stable BUT is a strained bond so is ready to react with a better bond
- No charge
Properties of Covalent Bonds
- Low melting points
- Bcuz attraction between e- are easy to overcome
- Soft, flexible
- Many won’t dissolve/be disrupted in water (nonpolar)
- Cannot conduct electricity even when dissolved bcuz no charges (+ or -) are present
- Polar covalent can dissolve cuz of charges
- Many are liquids at room temperature
- Flow of electricity:
- NO for nonpolar covalent bonds bcuz e- are tightly held & no charges are present
- YES for polar covalent bonds in molten form bcuz of charges
Naming Covalent Bonds
- Rule 1: Element with lower group number (more left) goes first
- Rule 2: If elements in same group then greater period number (more down) goes first
- Rule 3: 2nd element in compound ends in -ide
- Use greek prefixes to determine number of atoms
| Mono: one | Di: 2 | Tri: 3 | Tetra: 4 | Penta: 5 |
| Hexa: 6 | Hepta: 7 | Octo: 8 | Nona: 9 | Deca: 10 |
- If there is only one atom of first element, them NO prefix → just elemental name
- Ex CO: Carbon monoxide
- NO CRISS CROSS METHOD
