Ionic Solids
- Ionic solids: stable substances held together by opposite charges (electrostatic attraction)
- Will not conduct electricity in solid form → only when ions are mobile (melted (molten) or dissolved)
- In order to conduct electricity need charged particles that must be free to flow
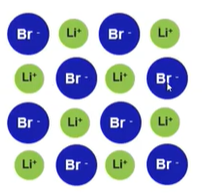
- Ions pack themselves to maximize attractions between opposite charges and to minimize repulsion between like ions → like charges will be far away from each other → cations and anions should alternate within a row and column to avoid them repelling each other
- As the size of ions decrease and charges increase, lattice energy increases → compound more stable and MP higher
- Why are ionic solids hard and brittle?
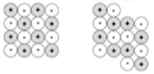
- Hard: the cations and anions are locked tightly into place because of the very strong electrostatic attraction (ionic bonds)
- Brittle: ionic bonds as result of electrostatic attraction create crystals in rigid, lattice structures that, when pressured, causes one layer to slide past another and break
