Introduction to Structures and Types of Solids
- Crystalline solids: have highly regular arrangement of their components (NaCl)
- Amorphous solids: have considerable disorder in their structures (glass)
- Lattice: represents the positions of the components in a crystalline solid
- Unit Cell: the smallest repeating unit of the lattice
Types of Crystalline Solids
- Classify solids according to what type of component occupies the lattice point
Atomic Solids (have atoms at lattice points)

Network Solids
- Network solids:
- Examples to know: C (diamond), C (graphite), most silicon and boron compounds
Carbon-a Special Network Solid
- 3 allotropes of Carbon: Are all network solids but differences are due to the way they are connected
- Coal: amorphous
- Diamond: hardest natural substance on earth bcuz network is very strong
- Insulator bcuz diamond has electrons are locked into lattice with little space to move; large energy gap between the filled and empty molecular orbitals → prevents excitation of e- to empty orbitals
- Graphite: slippery (sheets formed can slide past each other; the pi bonds extend above and below plane
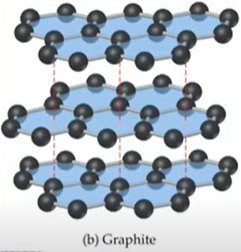
- Graphite held together by weak dispersion forces so is why is much weaker
- The delocalization of pi bonds accounts for the electrical conductivity of graphite bcuz network not as tightly bound (electrons can move around)
