AP Chemistry 2.3 Structure of Ionic Solids- MCQs - Exam Style Questions
Question
(B) Determining the density of the substance
(C) Testing the electrical conductivity of the crystals
(D) Testing the electrical conductivity of an aqueous solution of the substance
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Characteristic Property of Ionic Compounds:
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water (ions are mobile) but not as solids (ions are fixed).
2. Evaluate Options:
(A) Crystal shape is not definitive for ionic vs covalent.
(B) Density varies widely for both ionic and covalent compounds.
(C) Most solids don’t conduct electricity, including ionic solids.
(D) Correct – Aqueous solutions of ionic compounds conduct electricity.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
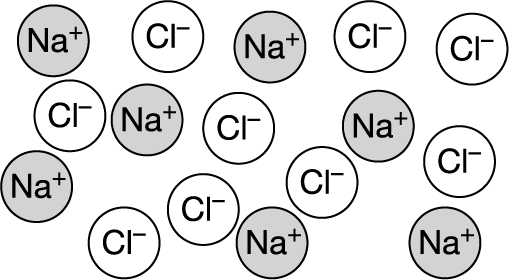
Molten (liquid) NaCl is represented by the particulate diagram shown above. Which of the following indicates whether NaCl(l) conducts electricity and best explains why or why not?
A It conducts electricity because Na is a metal.
B It conducts electricity because ions are free to move.
C It does not conduct electricity because Cl is a nonmetal.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B For a substance to conduct electricity, it must contain charged particles that are mobile. In molten salts such as NaCl , those charged particles are ions. (Metals conduct electricity via mobile electrons within a lattice of metal atoms.)
Question
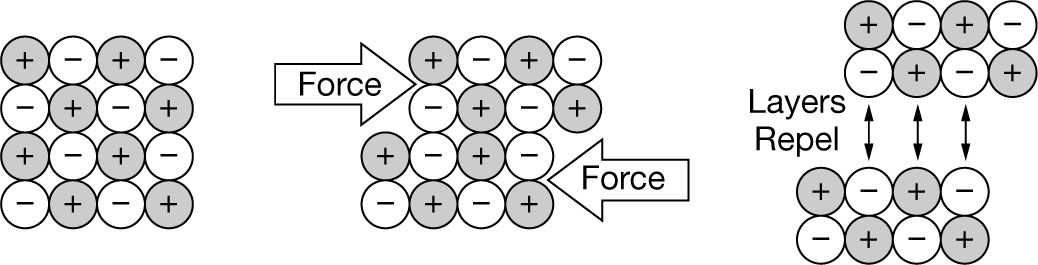
The particulate-level diagram shown above best helps to explain which of the following properties of ionic solids?
A Density
B Brittleness
C Malleability
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B The brittleness of ionic solids is due to the internal repulsion of ion layers within the crystal lattice that occurs when the layers are displaced by an outside force parallel to the layers and they move relative to adjacent layers.
Question
The particles in solid KI, a stable ionic compound, are arranged to maximize coulombic attractions while minimizing coulombic repulsions among the particles. Which of the following diagrams best represents the structure of solid KI?
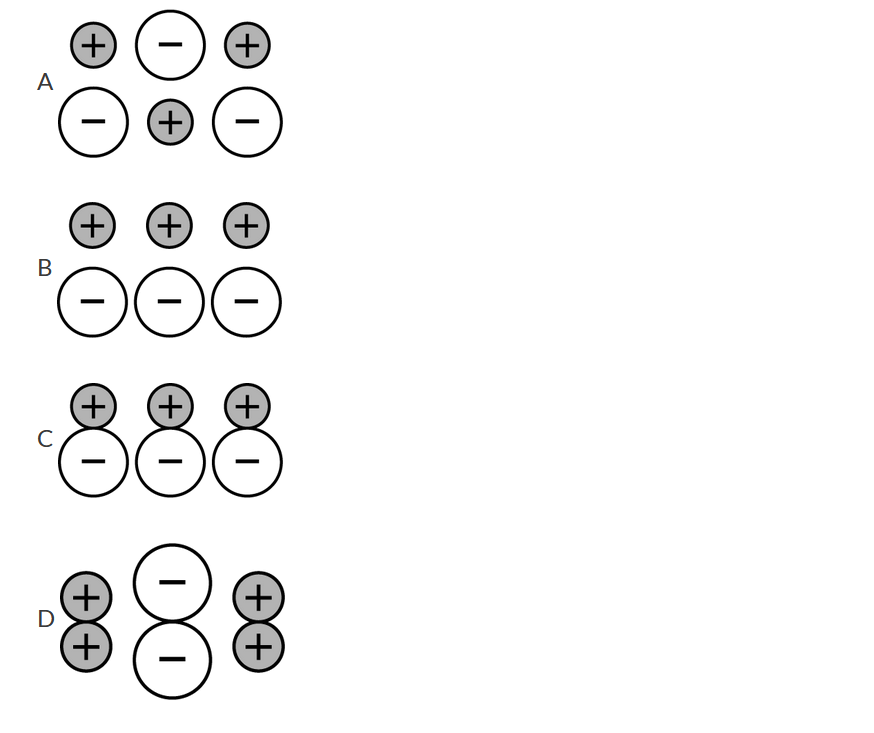
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A This diagram shows both types of charged ions being surrounded by ions of the opposite charge, thus maximizing attraction and minimizing repulsion.
