Question
Equimolar samples of \(CH_4\)(g) and \(C_2H_6\)(g) are in identical containers at the same temperature. The \(C_2H_6\)(g) deviates much more from ideal behavior than the \(CH_4\)(g) does.
Which of the following best helps explain this deviation?
A The \(C_2H_6\)(g) molecules have more hydrogen bonding than \(CH_4\)(g) molecules do.
B The \(C_2H_6\)(g) molecules have a larger, more polarizable electron cloud than \(CH_4\)(g) molecules do.
C The \(C_2H_6\)(g) molecules have a greater average kinetic energy than the \(CH_4\)(g) molecules have.
D The \(C_2H_6\)(g) molecules have a greater average speed than the \(CH_4\)(g) molecules have.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The ideal gas law assumes that attractions between gas particles are negligible. Since \(C_2H_6\)(g)
molecules have a larger, more polarizable electron cloud than \(CH_4\)(g) molecules do, their intermolecular forces are greater. Gas pressure is due to collisions of gas particles with the walls of the container. If gas particles about to hit the walls of a container are attracted to nearby gas particles, they will hit the walls of the container with less force than expected.
Question
The gases \(CO_2~(g)\) and \(NH_3~(g)\) can be liquefied at 20°C by compressing them to sufficiently high pressures. A student claims that \(NH_3~(g)\) can be liquefied at a lower pressure than \(CO_2~(g)\) can be liquefied. Which of the following is the best justification for this claim?
A At 20°C , the average speed of \(NH_3~(g)\) molecules is greater than that of \(CO_2~(g)\) molecules because \(NH_3~(g)\) molecules have less mass than \(CO_2~(g)\) molecules have.
B \(CO_2~(g)\) is a nonpolar molecule that has no significant intermolecular forces, whereas \(NH_3~(g)\) has strong London dispersion intermolecular forces.
C Both \(CO_2~(g)\) and \(NH_3~(g)\) are nonpolar molecules that have only London dispersion intermolecular forces, but the larger electron cloud of \(CO_2~(g)\) molecules causes it to have stronger intermolecular forces.
D \(CO_2~(g)\) is a nonpolar molecule that has London dispersion intermolecular forces that are weaker than the dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces between the polar \(NH_3~(g)\) molecules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Because polar \(NH_3\) molecules have stronger intermolecular forces than \(CO_2\), its molecules can condense to a liquid at a lower pressure than \(CO_2\).
Question
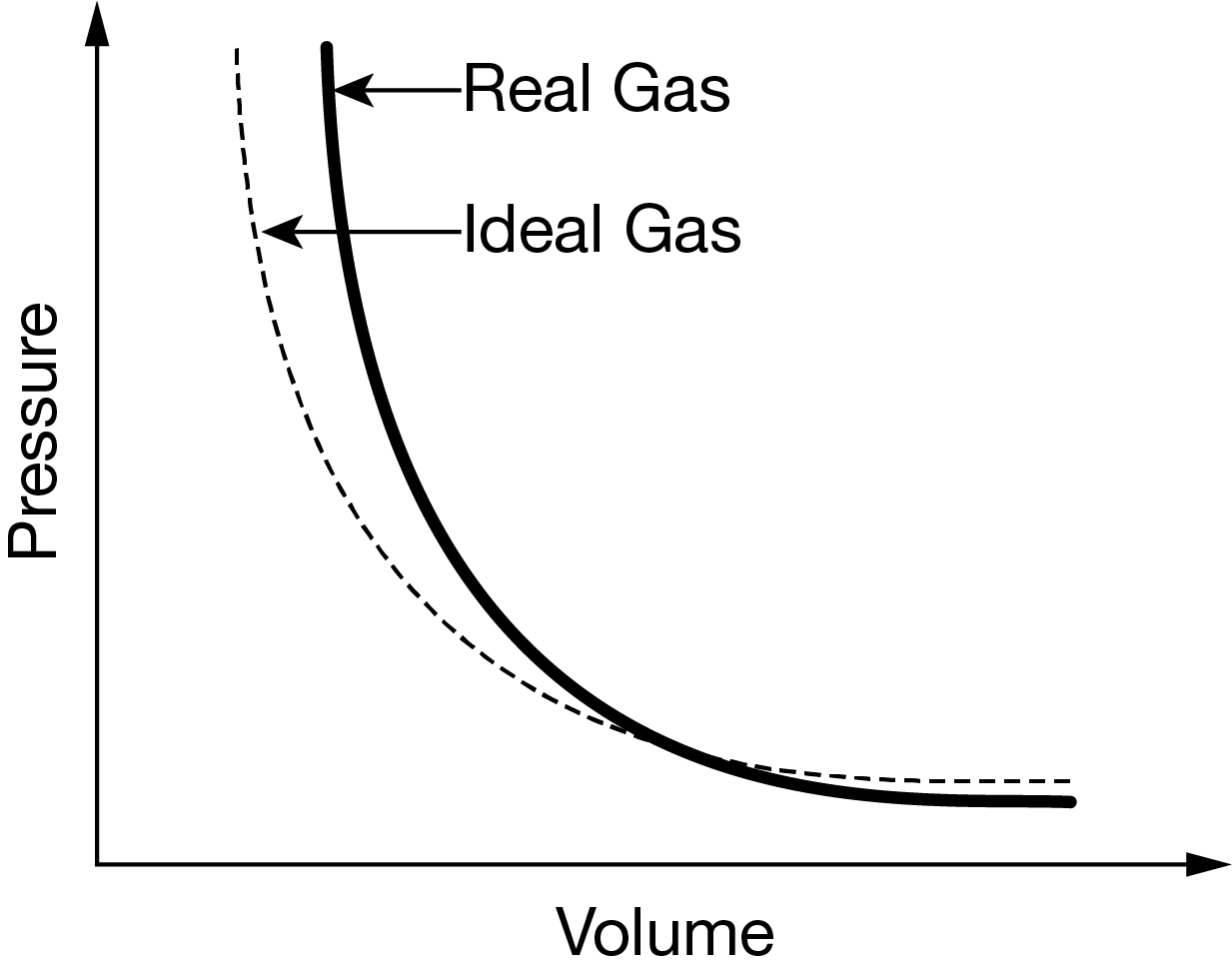
The graph above shows how a particular real gas deviates from ideal behavior at very high pressures. Based on this information, which of the following is most likely the gas and gives the reason based on kinetic molecular theory?
A \(H_2\) , because it has the smallest mass.
B \(N_2\) , because its molecules have a triple bond.
C \(Ne\) , because it has a completely filled valence shell.
D \( SO_2\) , because it has the largest molecular volume.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
\( SO_2\)has the largest molecular volume. At very high pressures, the space occupied by the molecules is more significant and will result in the largest deviation from the volume predicted by the ideal gas law. According to kinetic molecular theory, ideal gas molecules have negligible volumes, so the larger its molecules are, the more the behavior of the gas will deviate from that of an ideal gas.
Question
A 1.0 L sample of a pure gas is found to have a lower pressure than that predicted by the ideal gas law. The best explanation for the observation is that the molecules of the gas
(A) have a combined volume that is too large to be considered negligible when compared to the volume of the container
(B) have a low molecular mass and therefore do not strike the container walls with as much force as expected
(C) are attracted to each other and do not exert as much force on the container walls as they would if they had no mutual attractions
(D) are attracted to the sides of the container and strike the container walls with more force than expected
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A vessel contains Ar(g) at a high pressure. Which of the following statements best helps to explain why the measured pressure is significantly greater than the pressure calculated using the ideal gas law?
(A) The molar mass of Ar is relatively large.
(B) A significant number of \(Ar_{2}\) molecules form.
(C) The attractive forces among Ar atoms cause them to collide with the walls of the container with less force.
(D) The combined volume of the Ar atoms is too large to be negligible compared with the total volume of the container.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
