Question
For each of the following three reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are extensively ionized. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by the reaction. You may use the empty space at the bottom of the next page for scratch work, but only equations that are written in the answer boxes provided will be graded.

(a) Equal volumes of 0.1 M hydrofluoric acid and 0.1 M potassium hydroxide are combined.
(i) Balanced equation: |
(ii) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for the reactant that is the Brønsted-Lowry base in the forward reaction.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
(b) Solid calcium metal burns in air.
| (i) Balanced equation: |
(ii) Predict the algebraic sign of ΔH° for the reaction. Explain your prediction.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
(c) Samples of nitrogen monoxide gas and oxygen gas are combined.
| (i) Balanced equation: |
(ii) If the reaction is second order with respect to nitrogen monoxide and first order with respect to oxygen, what is the rate law for the reaction?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(i) Balanced equation: HF + OH− → F − + H2O
(a)(ii) 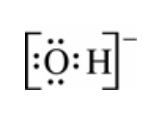
(b) (i) Balanced equation: 2 Ca + O2 → 2 CaO
(b)(ii) The sign of ΔH° will be negative because ΔG° is negative (the reaction occurs) and ΔS° is negative (a solid and a gas react to form a solid). According to the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, ΔH° = ΔG° + TΔS°. Therefore ΔH° is the sum of two negative quantities and as such must be negative.
(c) (i) Balanced equation: 2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2
(c)(ii) rate = k[NO]2[O2]_
