Question
\(XY_{2} → X + Y_{2}\) The equation above represents the decomposition of a compound \(XY_{2}\). The diagram below shows two reaction profiles (path one and path two) for the decomposition of\( XY_{2}\).
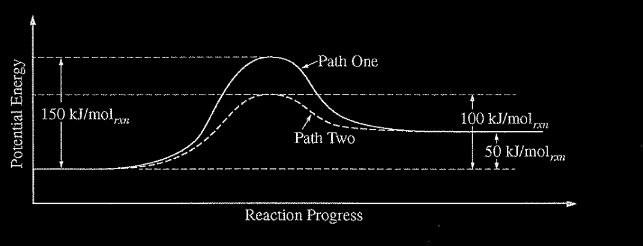
Which of the following most likely accounts for the difference between reaction path one and reaction path two?
(A) A higher temperature in path one
(B) A higher temperature in path two
(C) The presence of a catalyst in path one
(D) The presence of a catalyst in path two
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Which energy difference in the energy profile below corresponds to the activation energy for the forward
reaction?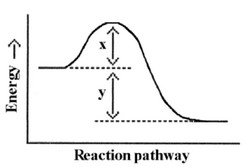
A) x B) y C) x + y D) y – x E) x – y
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
In the energy profile of a reaction, the species that exists at the maximum on the curve is called the __________.
A) product
B) enthalpy of reaction
C) atomic state
D) activated complex
E) activation energy
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
In the Arrhenius equation,
\(k = Ae^{-Ea/RT}\)
__________ is the frequency factor.
A) k B) A C) e D) R E) \(E_a\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The energy diagram for the reaction X + Y → Z is shown above. The addition of a catalyst to this reaction would cause a change in which of the indicated energy differences?
(A) 1 only
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and II only
(E) I, II, and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
