Question
The half-life (t1/2) of the catalyzed isomerization of cis-2-butene gas to produce trans-2-butene gas, represented above, was measured under various conditions, as shown in the table below.
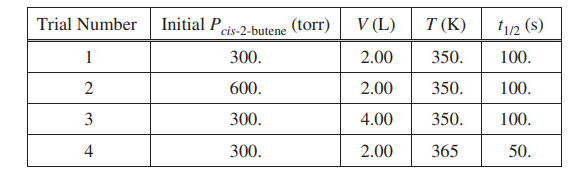
(a) The reaction is first order. Explain how the data in the table are consistent with a first-order reaction.
(b) Calculate the rate constant, k, for the reaction at 350. K. Include appropriate units with your answer.
(c) Is the initial rate of the reaction in trial 1 greater than, less than, or equal to the initial rate in trial 2? Justify your answer.
(d) The half-life of the reaction in trial 4 is less than the half-life in trial 1. Explain why, in terms of activation energy.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
| For a first-order reaction, the half-life is independent of reactant concentration (or pressure) at constant T, as shown in trials 1, 2, and 3. |
(b)
| \(k = \frac{0.693}{t_{1/2}}=\frac{0.693}{100.s}=0.00693 s^{-1}\) |
(c)
| The initial rate in trial 1 is less than that in trial 2 because rate = k [cis-2-butene] or rate = kPcis-2-butene (with reference to values from both trials). OR because the initial concentration of cis-2-butene in trial 1 is less than that in trial 2 and k is constant |
(d)
| The temperature is higher in trial 4, meaning that the KEavg of the molecules is greater. Consequently, in this trial a greater fraction of collisions have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier, thus the rate is greater. |
