Question
HCOOH(aq ) + H2O(l) ⇔ H2O+(aq) + HCOO– (aq) Ka = 1.8 × 10-4
Methanoic acid, HCOOH, ionizes according to the equation above.
(a) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, Ka, for the reaction.
(b) Calculate the pH of a 0.25 M solution of HCOOH.
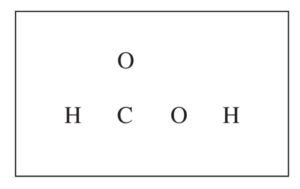
(c) In the box below, complete the Lewis electron-dot diagram for HCOOH. Show all bonding and nonbonding valence electrons.
H2NNH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇔ H2NNH3+ (aq) + OH –(aq) Kb = 1.3 × 10-6
(d) In aqueous solution, the compound H2NNH2 reacts according to the equation above. A 50.0 mL sample of 0.25 M H2NNH2(aq) is combined with a 50.0 mL sample of 0.25 M HCOOH(aq).
(i) Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when H2NNH2 is combined with HCOOH.
(ii) Is the resulting solution acidic, basic, or neutral? Justify your answer.
When a catalyst is added to a solution of HCOOH(aq), the reaction represented by the following equation occurs.
HCOOH(aq) → H2 (g) + CO2 (g)
(e) Is the reaction a redox reaction? Justify your answer.
(f) The reaction occurs inarigid 4.3 L vessel at 25°C, and the total pressure is monitored, as shown in the graph above. The vessel originally did not contain any gas. Calculate the number of moles of CO2(g) produced in the reaction. (Assume that the amount of CO2(g) dissolved in the solution is negligible.)
(g) After the reaction has proceeded for several minutes, does the amount of catalyst increase, decrease, or remain the same? Justify your answer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
For the correct expression:
\(K_{a}=\frac{[H_{3}O^{+}][HCOO^{-}]}{[HCOOH]}\)
(b) For the correct calculated concentration of H3O+ :
HCOOH + H2O ⇔ H3O+ + HCOO–
I 0.25 0 0
C –x +x +x
E 0.25 – x x x
Let [H3 O+ ] = x, then 1.8 × 10-4 \(\frac{x^{2}}{(0.25-x)}\)
Assume x << 0.25, then 1.8 × 10-4 \(\frac{x^{2}}{(0.25)}\) ⇒ x = 0.0067 M
For the correct calculated value of pH:
pH = -log[H3 O + ] = – log(0.0067) = 2.17
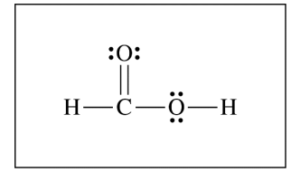
(c) For the correct diagram:
(d) (i) For the correct balanced equation (state symbols not required):
H2NNH2 (aq) + HCOOH(aq) → H2NNH3+ (aq) + HCOO– (aq)
(ii) For the correct answer and a valid justification:
Acidic. The Ka of H2NNH3+ is greater than the Kb of HCOO−, so the production of H3O+(aq) occurs to a greater extent than the production of OH−(aq).
(e) For the correct answer and a valid justification:
Accept one of the following:
• Yes. The oxidation number of hydrogen changes from +1 in HCOOH to zero in H2.
• Yes. The oxidation number of carbon changes from +2 in HCOOH to +4 in CO2.
(f) For the correct calculated value of the pressure of CO2 (may be implicit):
24 atm total × 1 atm CO2 / 2 atm of product = 12 atm CO2
For the correct calculated number of moles of CO2:
PV = nRT
\(n = \frac{PV}{RT}=\frac{(12 atm)(4.3 L)}{(0.08206 L atm mol^{-1}K^{-})(298 K)}=2.1 mol CO_{2}\)
(g) For the correct answer and a valid justification:
It would remain the same. In a catalyzed reaction the net amount of catalyst is constant.
