Question
A student wants to determine the concentration of H2O2 in a solution of H2O2(aq). The student can use one of two titrants, either dichromate ion, Cr2O72–(aq), or cobalt(II) ion, Co2+(aq). The balanced chemical equations for the two titration reactions are shown below.
Dichromate as titrant: Cr2O72–(aq) + 3 H2O2(aq) + 8 H+(aq) → 2 Cr3+(aq) + 3 O2(g) + 7 H2O(l)
Cobalt(II) as titrant: 2 Co2+(aq) + H2O2(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → 2 Co3+(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
The half-reactions and the E° values for the systems related to the titrations above are given in the following table.
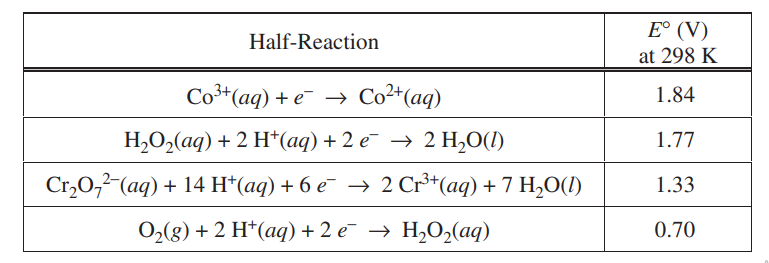
(a) Use the information in the table to calculate the following.
(i) E° for the reaction between Cr2O72–(aq) and H2O2(aq) at 298 K
(ii) E° for the reaction between Co2+(aq) and H2O2(aq) at 298 K
(b) Based on the calculated values of E°, the student must choose the titrant for which the titration reaction is thermodynamically favorable at 298 K.
(i) Which titrant should the student choose? Explain your reasoning.
(ii) Calculate the value of ΔG°, in kJ/molrxn, for the reaction between the chosen titrant and H2O2(aq).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i)
| E0 = 1.33 – 0.70 = 0.63 V |
(ii)
| E0 = -1.84 + 1.77 = -0.07 V |
(b) (i)
| The student should be the dichromate ion for the titration because, for the reaction, the value of E0 is positive, which means that the reaction is thermodynamically favorable. OR ΔG0 = -n FE0 and n, F, and E0 are all positive numbers, therefore ΔG0 < 0, which means that the reaction is thermodynamically favorable. |
(ii)
| \(\Delta G^{0}= – nFE^{0}= – 6(96,485\frac{C}{mol})(0.63\frac{J}{C})(\frac{1 kJ}{1000 J})=-360 kJ/mol_{rxn}\) |
