Reaction Quotient and Equilibrium Constant
- For
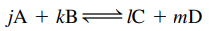 the Equilibrium Constant Expression relates the concentrations of reactants and products once the reaction has reached equilibrium.
the Equilibrium Constant Expression relates the concentrations of reactants and products once the reaction has reached equilibrium.- Equilibrium Constant Expression:
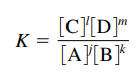 (on RFS)
(on RFS)- In some tests K is written as Kc
- Equilibrium Constant Expression:
- If asked to find Kc expression only include gasses and (aq), NOT solids (s) or liquids (l)
Equilibrium Expressions with Pressure
- For reactions that occur all in the gas phase, the equilibrium expression can be written in terms of partial pressures
- Only include gases in the Kp expression
Reaction Quotient: Q
- Calculated the same as the equilibrium constant, but for a system not at equilibrium (usually initial conditions)
- Ex:
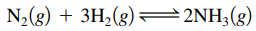 →
→ 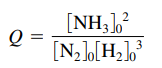
- The subscript zeros indicate initial concentrations
- To determine in which direction a system will shift to reach equilibrium, we compare the values of Q and K. There are three possible cases
- Q = K. The system is at equilibrium; no shift will occur.
- Q > K → too many products, will shift to consume products and produce more reactants (shift reverse reaction/left)
- Q < K → not enough products; will shift to consume reactants and produce more products (shift forward reaction/right )
- Do not say shift right/left on AP exam (won’t receive credit)
