AP® Calculus BC Memorization Sheet - New Syllabus
AP® Calculus BC Memorization Sheet
Ace AP Calculus BC Exam with AP® Calculus BC Memorization Sheet at IITian Academy
BC Calc Memorization Sheet
Derivatives
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}x^{n}=n\,x^{\,n-1}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}x = 1\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\ln x=\frac{1}{x}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\log_a x=\frac{1}{x\ln a}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}e^{x}=e^{x}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}a^{x}=a^{x}\ln a\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\sin x=\cos x\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\cos x=-\sin x\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\tan x=\sec^{2}x\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\sec x=\sec x\tan x\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\arcsin x=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\arccos x=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\arctan x=\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}\)
Integrals
\(\displaystyle \int x^{n}\,dx=\frac{x^{\,n+1}}{n+1}+C,\; n\neq -1\)
\(\displaystyle \int \frac{1}{x}\,dx=\ln|x|+C\)
Integration Rules
U-Substitution: \(\displaystyle \int f(g(x))\,g'(x)\,dx\), let \(\,u=g(x)\).
Integration by Parts: \(\displaystyle \int u\,dv=uv-\int v\,du\).
Partial Fractions: \(\displaystyle \frac{1}{(cx+a)(dx+b)}=\frac{A}{cx+a}+\frac{B}{dx+b}\).
Trig Identities
\(\displaystyle \tan x=\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}\)
\(\displaystyle \sin^{2}x+\cos^{2}x=1\)
L’Hospital’s Rule
\(\displaystyle \text{If }\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\ \text{is }0/0\text{ or }\infty/\infty,\)
\(\displaystyle \qquad \lim_{x\to a}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f'(x)}{g'(x)}\) (when the latter exists).
First Fundamental Theorem
\(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\!\left(\int_{a}^{\,g(x)}\! f(t)\,dt\right)=f(g(x))\cdot g'(x)\)
Second Fundamental Theorem
\(\displaystyle \int_{a}^{b} f(x)\,dx = F(b)-F(a),\quad F'(x)=f(x).\)
Volume
Disc: \(\displaystyle V=\pi\int r(x)^{2}\,dx\)
Washer: \(\displaystyle V=\pi\int\!\big(R(x)^{2}-r(x)^{2}\big)\,dx\)
Shell: \(\displaystyle V=2\pi\int r(x)\,h(x)\,dx\)
Cross Section: \(\displaystyle V=\int A(x)\,dx\)
Differentiation Rules
Product: \(\displaystyle (fg)’=f’g+fg’\)
Quotient: \(\displaystyle \left(\frac{f}{g}\right)’=\frac{f’g-fg’}{g^{2}}\)
Chain: \(\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}f(g(x))=f'(g(x))\,g'(x)\)
Definition of Derivative
\(\displaystyle f'(x)=\lim_{h\to 0}\frac{f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}\)
Inverse Function (slope)
\(\displaystyle f(a)=b,\ \text{slope }=m \Rightarrow (f^{-1})'(b)=\frac{1}{m}\)
Position, Velocity, Acceleration
\(\displaystyle v(t)=\frac{d}{dt}\,\text{(position)}\), \(\ a(t)=\frac{d}{dt}v(t)\)
\(\displaystyle \text{displacement}=\int v(t)\,dt\)
\(\displaystyle \text{T.D.T.}=\int |v(t)|\,dt\)
\(\displaystyle \text{speed}=|v|\)
Series Error Bounds
Alternating Series: \(\displaystyle |\text{error}|\le |a_{n+1}|\)
Lagrange Error (Taylor)
\(\displaystyle |R_{n}(x)|\le \frac{M\,(b-a)^{\,n+1}}{(n+1)!}\)
\(\displaystyle M=\max_{c\in[a,b]}\big|f^{(n+1)}(c)\big|\)
Logistic & Line
\(\displaystyle \frac{dP}{dt}=kP\!\left(1-\frac{P}{M}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle P(t)=\frac{M}{1+Ce^{-kt}}\)
\(\displaystyle \text{(}M\text{ = carrying capacity)}\)
Point–Slope: \(\displaystyle y-y_{1}=m(x-x_{1})\)
Taylor & Maclaurin
Taylor about \(a\): \(\displaystyle f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{f^{(n)}(a)}{n!}\,(x-a)^{n}\)
Maclaurin (\(a=0\)): \(\displaystyle f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{f^{(n)}(0)}{n!}\,x^{n}\)
Common Maclaurin Series
\(\displaystyle e^{x}=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{x^{n}}{n!}\)
\(\displaystyle \sin x=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{(-1)^{n}x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}\)
\(\displaystyle \cos x=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{(-1)^{n}x^{2n}}{(2n)!}\)
\(\displaystyle \frac{1}{1-x}=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}x^{n}\quad(|x|<1)\)
Euler’s Method
| \((x,y)\) | \(\dfrac{dy}{dx}\) | \(\Delta y=\dfrac{dy}{dx}\,\Delta x\) | \((x,y)\) |
Average Rate of Change: AROC \(=\displaystyle \frac{f(b)-f(a)}{\,b-a\,}\) (slope between two points)
Inst. Rate of Change: IROC \(= f'(c)\) (slope at a single point)
Mean Value Thm Part 1: \(\displaystyle f'(c)=\frac{f(b)-f(a)}{\,b-a\,}\) Rolles Thm.: if \(f(a)=f(b)\), then \(f'(c)=0\)
Average Value of a Function: \(\displaystyle f_{\text{avg}}=\frac{1}{b-a}\int_{a}^{b} f(x)\,dx\) Mean Value Thm Part 2: \(\displaystyle \int_{a}^{b} f(x)\,dx=f(c)(b-a)\)
Intermediate Value Thm. A function \(f(x)\) that is continuous on \([a,b]\) takes on every \(y\)-value between \(f(a)\) and \(f(b)\).
Extreme Value Thm: If \(f(x)\) is continuous on \([a,b]\), then \(f(x)\) must have both an absolute min and absolute max on the interval \([a,b]\).
Arc Length
cartesian
\(\displaystyle L=\int_{a}^{b}\sqrt{1+\Big(\frac{dy}{dx}\Big)^{2}}\,dx\)Arc Length
parametric
\(\displaystyle L=\int_{t=a}^{t=b}\sqrt{\Big(\frac{dx}{dt}\Big)^{2}+\Big(\frac{dy}{dt}\Big)^{2}}\,dt\)Speed
\(\displaystyle \sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^{2}}\)
T.D.T.
\(\displaystyle \int |v(t)|\,dt\)
Polar Area
\(\displaystyle \tfrac12\int r^{2}\,d\theta\)
Parametric Derivatives:
\(\displaystyle \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{dy/dt}{dx/dt},\qquad \frac{d^{2}y}{dx^{2}}=\frac{d}{dt}\!\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)\Big/\frac{dx}{dt}\)
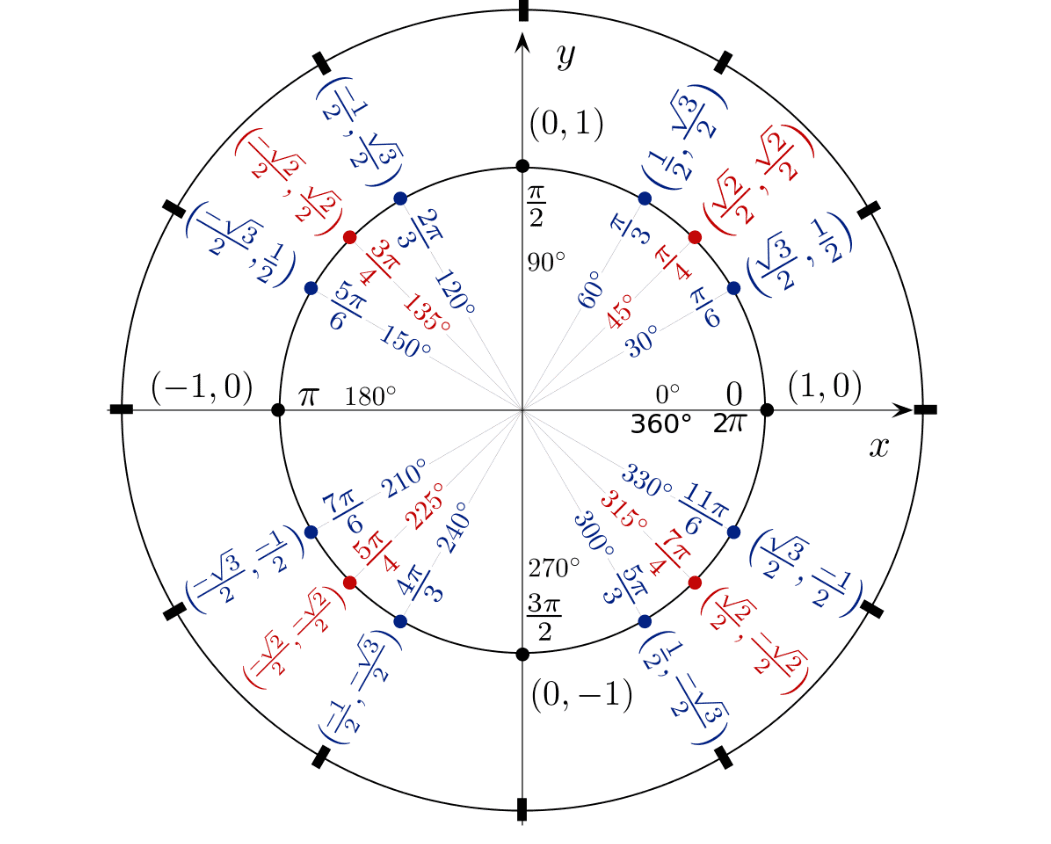
Polar Conversions:
\(\displaystyle r^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2},\; x=r\cos\theta,\; y=r\sin\theta,\; \theta=\arctan\!\Big(\frac{y}{x}\Big)\)
Area of Trapezoid
\(A=\tfrac12 h(b_{1}+b_{2})\)
Tests for Convergence/Divergence
| \(n^{\text{th}}\) term test | div. if \(\displaystyle \lim_{n\to\infty} a_{n}\ne 0\) (cannot be used to show convergence) | |
| Geom. series test | \(\displaystyle \sum a r^{n}\) \(|r|<1\Rightarrow\) conv., \(|r|\ge 1\Rightarrow\) div., \(S_{\infty}=\dfrac{a}{1-r}\) | |
| \(p\)-series | \(\displaystyle \sum \frac{1}{n^{p}}\) \(p>1\Rightarrow\) conv., \(p\le 1\Rightarrow\) div. | |
| Alternating series | decr. terms and \(\displaystyle \lim a_{n}=0 \Rightarrow\) conv. | |
| Integral test | \(a_{n}=f(x)\) \(\sum a_{n}\) conv. if \(\int f(x)\,dx\) conv., \(\sum a_{n}\) div. if \(\int f(x)\,dx\) div. | |
| Ratio test | \(\displaystyle \lim \left|\frac{a_{n+1}}{a_{n}}\right|<1 \Rightarrow\) conv., \(\displaystyle \lim \left|\frac{a_{n+1}}{a_{n}}\right|>1 \Rightarrow\) div., (inconclusive if \(\displaystyle \lim \left|\frac{a_{n+1}}{a_{n}}\right|=1\)) (works well for factorials and exponentials) | |
| Direct Comparison | a series with terms smaller than a known convergent series also converges a series with terms larger than a known divergent series also diverges | |
| Limit Comparison | if \(\displaystyle \lim \frac{a_{n}}{b_{n}}=c\), is finite and positive both series converge or both diverge | (use with “messy” algebraic series, usually compared to a \(p\)-series) |
