AP Physics 1- 2.4 Newton’s First Law- Study Notes- New Syllabus
AP Physics 1-2.4 Newton’s First Law – Study Notes
AP Physics 1-2.4 Newton’s First Law – Study Notes -AP Physics 1 – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Newton’s First Law
Newton’s First Law
Newton’s First Law states that an object continues in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a net external force.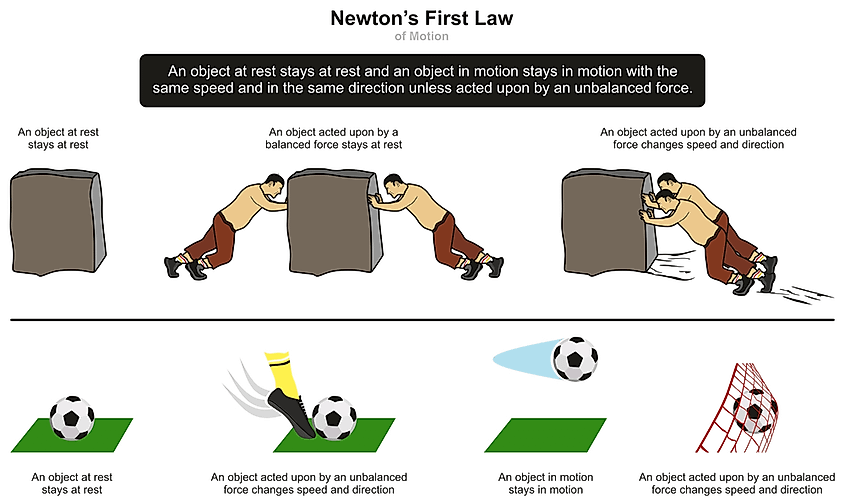
Conditions for Constant Velocity:
- The net external force acting on the system is zero.
- All forces acting on the system are balanced (e.g., friction = applied force).
- No unbalanced force exists to change the system’s velocity (magnitude or direction).
Relevant Equation:
\( \sum F = 0 \implies v = \text{constant} \)
Example:
A hockey puck slides on frictionless ice with a velocity of 5 m/s. Since no external horizontal force acts on it, the puck continues moving at 5 m/s indefinitely.
Example :
A car moves on a straight road at 20 m/s with the engine force exactly balancing the air resistance and friction. Net external force is zero, so velocity remains constant at 20 m/s.
Example :
A box of mass 10 kg is pushed on a horizontal floor with a constant velocity of 2 m/s. The frictional force acting on the box is 20 N. Find the applied force.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Since the velocity is constant, net force = 0.
Thus, \( F_{\text{applied}} = F_{\text{friction}} \).
\( F_{\text{applied}} = 20 \, \text{N} \).
Answer: The applied force = 20 N.
Example :
A 1500 kg car is moving at a constant velocity of 25 m/s on a straight road. The resistive force due to air and friction is 600 N. Find the forward driving force exerted by the engine.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
For constant velocity: Net force = 0.
Thus, Driving force = Resistive force = 600 N.
Answer: Engine force = 600 N.
