AP Physics 1- 2.5 Newton’s Second Law- Study Notes- New Syllabus
AP Physics 1-2.5 Newton’s Second Law – Study Notes
AP Physics 1-2.5 Newton’s Second Law – Study Notes -AP Physics 1 – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Newton’s Second Law
Newton’s Second Law
Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of a system’s center of mass has a magnitude proportional to the magnitude of the net force exerted on the system and is in the same direction as that net force. This explains how and when a system’s velocity changes.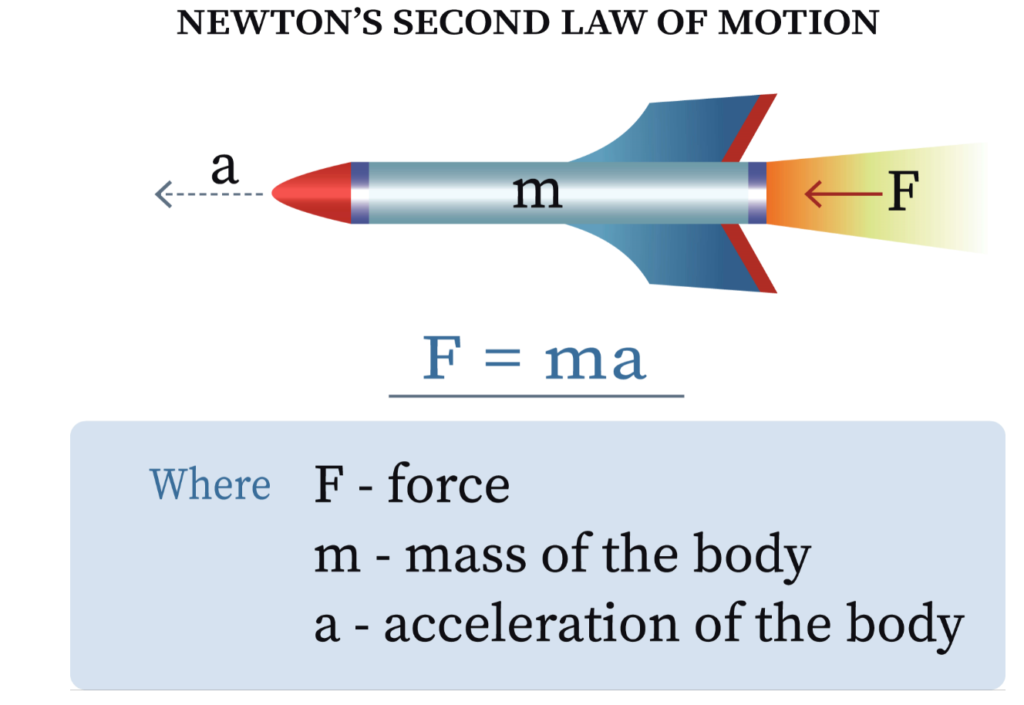
\( \vec{F}_{\text{net}} = m \vec{a} \)
- A system’s velocity changes when there is a nonzero net external force acting on it.
- The velocity of a system’s center of mass will only change if a nonzero net external force is exerted on that system.
- If the net force is zero, the system maintains constant velocity (Newton’s First Law).
- The direction of acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force.
Conditions under which velocity changes:
| Condition | Effect on Velocity | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Nonzero Net Force | System accelerates | Car speeding up when engine force exceeds friction |
| Force Opposes Motion | System decelerates | Ball rolling to stop due to friction |
| Unbalanced Forces at Angle | Velocity changes in magnitude and/or direction | Satellite orbiting Earth (direction changes) |
Example :
A 5 kg object experiences a net force of 20 N to the right. Find its acceleration.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Using \( F = ma \):
\( a = \dfrac{F}{m} = \dfrac{20}{5} = 4 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
Answer: Acceleration = 4 m/s² to the right.
Example :
A car of mass 1000 kg moving at 20 m/s applies brakes, exerting a constant retarding force of 5000 N. Find its deceleration.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Using \( F = ma \):
\( a = \dfrac{F}{m} = \dfrac{5000}{1000} = 5 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
The acceleration is opposite to motion, so it’s a deceleration.
Answer: Deceleration = 5 m/s².
Example :
A block of mass 10 kg is pulled on a horizontal surface by a 40 N force at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. If friction is negligible, find the block’s acceleration.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Only the horizontal component of force causes acceleration:
\( F_x = F \cos \theta = 40 \cos 30^\circ = 40 \times 0.866 \approx 34.6 \, \text{N} \).
\( a = \dfrac{F_x}{m} = \dfrac{34.6}{10} \approx 3.46 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
Answer: Acceleration ≈ 3.46 m/s² to the right.
