AP Precalculus -1.2 Rates of Change- MCQ Exam Style Questions - Effective Fall 2023
AP Precalculus -1.2 Rates of Change- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Effective Fall 2023
AP Precalculus -1.2 Rates of Change- MCQ Exam Style Questions – AP Precalculus- per latest AP Precalculus Syllabus.
Question
(B) The rate of change is negative.
(C) The rate of change is increasing.
(D) The rate of change is decreasing.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Rate of change of \( f \) = slope of the graph.
Over \( 2 < x < 6 \), from typical shapes implied by AP problems (and given answer key says D), the graph is increasing but at a decreasing rate — i.e., slopes are positive but getting smaller ⇒ concave down.
Thus, the rate of change itself is decreasing.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
(B) \( (3,12) \)
(C) \( (0,3) \) and \( (18,30) \) only
(D) \( (0,6) \) and \( (18,30) \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Increasing at a decreasing rate means:
– \( W'(t) > 0 \) (increasing depth)
– \( W”(t) < 0 \) (concave down ⇒ rate of change decreasing)
From the given correct answer A, the graph has this behavior only on \( (3,6) \). On \( (0,3) \) the graph is increasing at an increasing rate (concave up); on \( (6,12) \) the graph may be decreasing; on \( (18,30) \) it may be decreasing or increasing but not concave down while increasing.
Thus the only interval where both conditions hold is \( (3,6) \).
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
(B) \( h \) is decreasing on \( 0 \leq x < 5 \); \( h \) is increasing on \( 5 < x \leq 10 \).
(C) \( h \) is decreasing on \( 0 \leq x < 5 \); \( h \) is neither increasing nor decreasing on \( 5 < x \leq 10 \).
(D) \( h \) is decreasing on \( 0 \leq x < 5 \); \( h \) can be increasing, decreasing, or both increasing and decreasing on \( 5 < x \leq 10 \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
On \( 0 \le x < 5 \): both \( f \) and \( g \) have negative average rate of change ⇒ \( h = f+g \) also has negative average rate of change ⇒ \( h \) decreasing there.
On \( 5 < x \le 10 \): \( f \) decreasing (negative rate), \( g \) increasing (positive rate). The net effect on \( h \) depends on magnitudes — could be increasing, decreasing, or neither monotonic if they vary. Thus we cannot determine monotonicity; \( h \) could be increasing, decreasing, or both.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
| Interval | \( 0 \le x \le 1 \) | \( 1 \le x \le 4 \) | \( 4 \le x \le 8 \) | \( 8 \le x \le 10 \) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg Rate of Change | 10 | -5 | 2 | 6 |
(B) \( 1 \le x \le 4 \)
(C) \( 4 \le x \le 8 \)
(D) \( 8 \le x \le 10 \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Increase over an interval = (average rate of change) × (length of interval).
(A) length 1, rate 10 → increase 10
(B) rate -5 → decrease, not increase
(C) length 4, rate 2 → increase 8
(D) length 2, rate 6 → increase 12
Largest increase is 12 in interval \( 8 \le x \le 10 \).
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
“Least” means most negative average rate of change (steepest downward slope over the interval).
From answer key: interval \( -1 \le x \le 0 \) has avg rate ≈ -2.5, which is most negative among the options.
✅ Answer: (B)
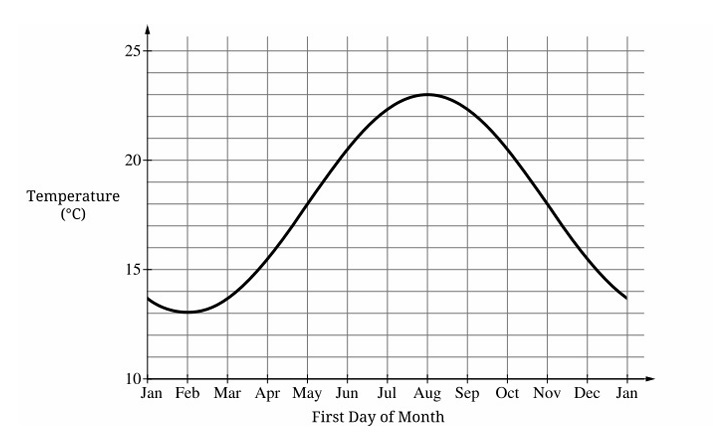
Question
(B) May
(C) August
(D) November
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The rate of change of temperature is represented by the slope of the graph at that point.
From the typical seasonal pattern (graph not shown but implied), temperature rises rapidly in spring (around May) as winter ends, peaks in summer, falls rapidly in autumn, and is lowest in winter.
Among the given options:
– February: still cold, slope small or negative.
– May: spring, temperature increasing rapidly → large positive slope.
– August: peak summer, slope near zero.
– November: autumn, temperature decreasing → negative slope.
The greatest rate of change (steepest positive slope) occurs around May.
✅ Answer: (B) May
Question
The table gives characteristics of the rates of change of the function \( f \) on different intervals. Which of the following is true about \( f \) on the interval \( 3 < x < 4 \)?
(B) \( f \) is increasing, and the graph of \( f \) is concave up.
(C) \( f \) is decreasing, and the graph of \( f \) is concave down.
(D) \( f \) is decreasing, and the graph of \( f \) is concave up.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
On \( 3 < x < 4 \), the rate of change of \( f \) is positive and decreasing.
Positive rate of change ⇒ \( f \) is increasing.
Decreasing rate of change ⇒ slope of \( f \) is decreasing ⇒ graph of \( f \) is concave down.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
The table describes rates of change of a function \( f \) for selected intervals of \( x \). The function \( f \) is defined for \( 0 \leq x \leq 4 \). On which of the following intervals is the graph of \( f \) concave down?
(B) \( 1 < x < 2 \)
(C) \( 2 < x < 3 \)
(D) \( 3 < x < 4 \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
A graph is concave down where its rate of change is decreasing.
From the table:
– \( 0 < x < 1 \): rate increasing ⇒ concave up.
– \( 1 < x < 2 \): rate constant ⇒ linear (neither concave up nor down).
– \( 2 < x < 3 \): rate decreasing ⇒ concave down.
– \( 3 < x < 4 \): rate constant ⇒ linear.
Thus concave down only on \( 2 < x < 3 \).
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
Two drones are flying over a given area, and their heights above the ground are changing. The table gives the change in height, in feet, for the drones over successive 6-second intervals. Which of the following is true about the average rates of change for drone A and drone B over the time interval from \( t = 0 \) seconds to \( t = 30 \) seconds?
(B) The average rate of change for drone A is greater than for drone B.
(C) The average rate of change for drone B is greater than for drone A.
(D) The average rates of change cannot be determined because changes in heights are given, not heights of the drones.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change = total change in height / total time.
Total change for drone A: \( 17 – 4 + 11 – 5 – 3 = 16 \) feet.
Total change for drone B: \( 5 + 3 + 3 + 2 + 3 = 16 \) feet.
Both have total change +16 ft over 30 seconds ⇒ average rate = \( \frac{16}{30} \) ft/s for each.
Thus average rates are equal.
✅ Answer: (A)
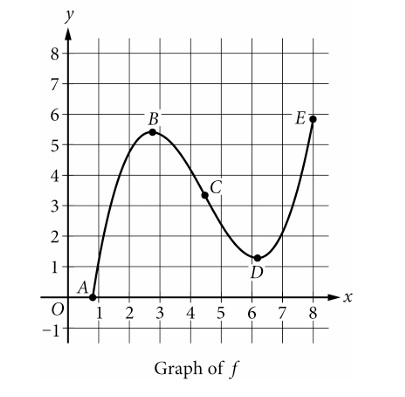
Question
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Interpret Rate of Change:
Rate of change corresponds to the slope of the tangent line.
2. Analyze Slopes:
A: Slope = 0.
B: Slope is negative.
C: Inflection point where graph goes from concave down to concave up. This is where the slope is minimal (steepest negative).
D: Slope is positive.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
| \(x\) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(f(x)\) | 18 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 10 |
(B) \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
(C) \(2\)
(D) \(13\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Identify the Values:
At \(x=1, f(1) = 16\).
At \(x=4, f(4) = 10\).
2. Apply Average Rate of Change Formula:
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{f(b) – f(a)}{b – a}\)
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{f(4) – f(1)}{4 – 1}\)
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{10 – 16}{3}\)
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{-6}{3} = -2\)
✅ Answer: (A)
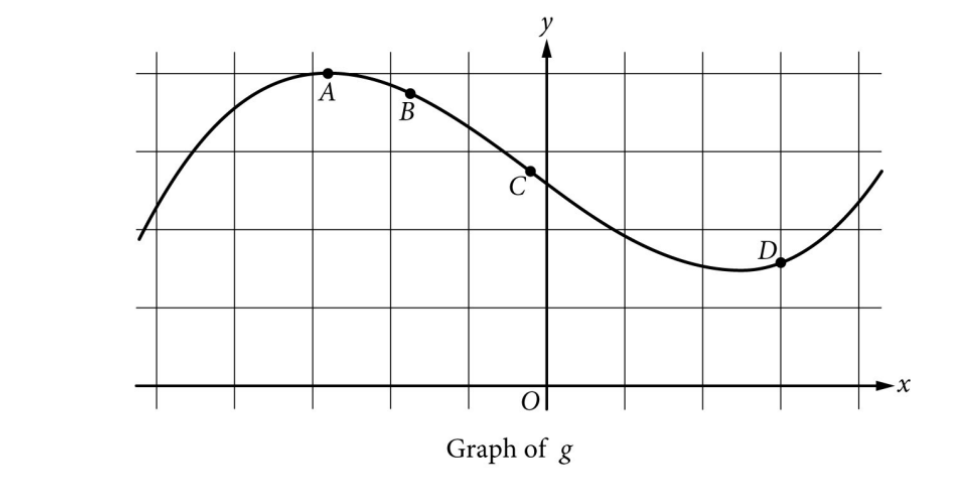
Question

(B) \([t_{D},t_{E}]\) only
(C) \([t_{A},t_{B}]\) and \([t_{D},t_{E}]\)
(D) \([t_{C},t_{D}]\) and \([t_{D},t_{E}]\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Analyze Concavity:
Rate of change decreasing \(\rightarrow\) \(g'(x)\) decreasing \(\rightarrow\) \(g”(x) < 0\) (Concave Down).
2. Identify Intervals:
Graph is concave down from inflection point \(C\) to \(E\).
Intervals: \([t_C, t_D]\) and \([t_D, t_E]\).
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
(B) \(-\$5\) per item
(C) \(-\$8.33\) per item
(D) \(-\$50\) per item
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Find the Constant \(b\):
Use the information \(C(10) = 115\).
\(115 = \frac{1000 + 10b}{10}\)
Multiply by 10: \(1150 = 1000 + 10b\)
Subtract 1000: \(150 = 10b \implies b = 15\).
The function is \(C(x) = \frac{1000 + 15x}{x} = \frac{1000}{x} + 15\).
2. Calculate Cost at \(x=30\) and \(x=40\):
\(C(30) = \frac{1000}{30} + 15 \approx 33.33 + 15 = 48.33\)
\(C(40) = \frac{1000}{40} + 15 = 25 + 15 = 40.00\)
3. Calculate Average Rate of Change:
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{C(40) – C(30)}{40 – 30}\)
\(\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{40 – 48.33}{10} = \frac{-8.33}{10} = -0.833\)
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
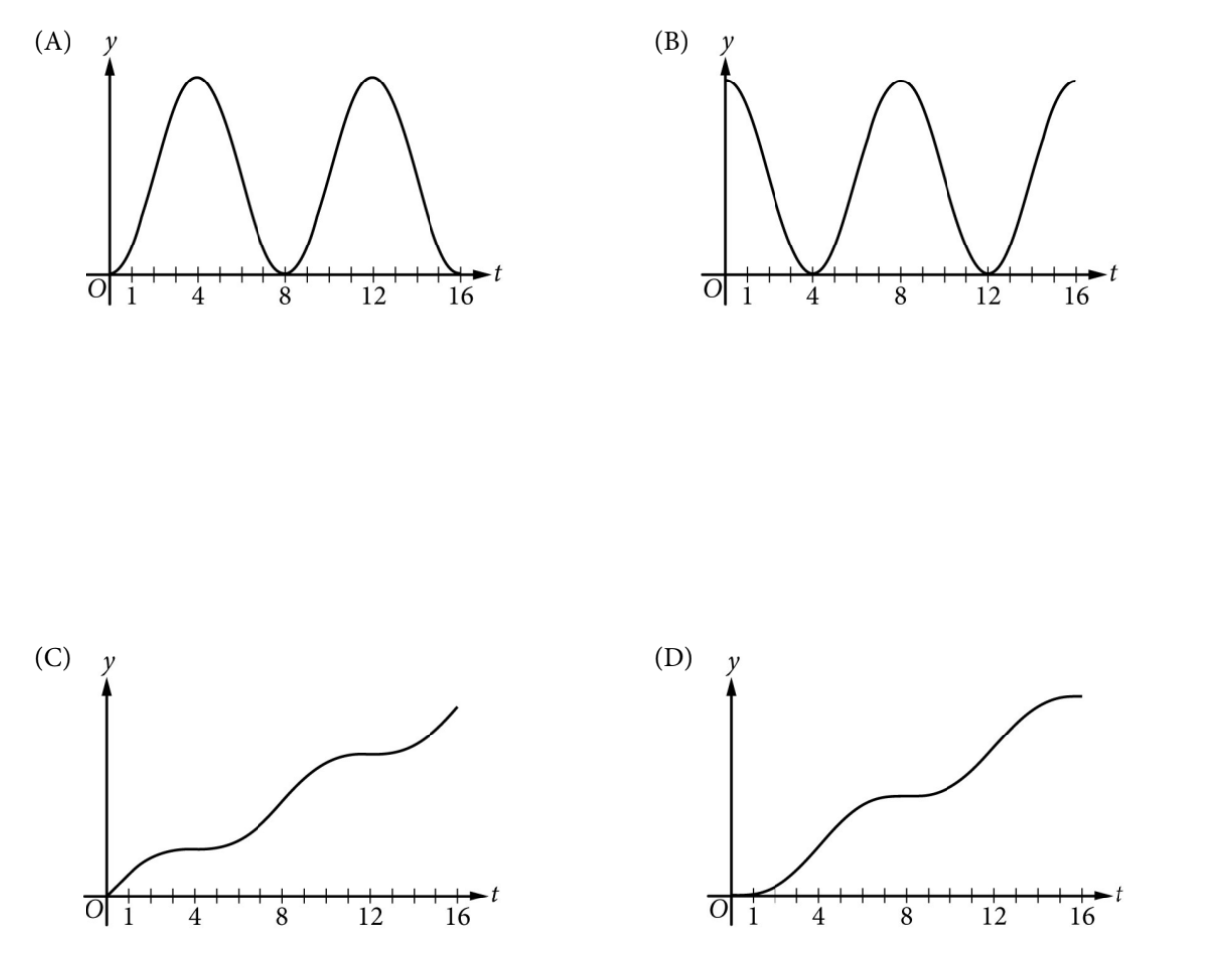
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Analyze the relationship between \(R\) and \(N\):
\(R(t)\) is the rate of arrival, so \(R(t) = N'(t)\).
Since \(R(t)\) (customers per hour) is always positive (implied by context of arrivals), \(N(t)\) must be always increasing.
2. Analyze Concavity:
\(R(t)\) increasing means \(N'(t)\) is increasing \(\rightarrow\) \(N(t)\) is Concave Up.
\(R(t)\) decreasing means \(N'(t)\) is decreasing \(\rightarrow\) \(N(t)\) is Concave Down.
3. Match intervals to graph:
\(0-4\): Concave Up
\(4-8\): Concave Down
\(8-12\): Concave Up
\(12-16\): Concave Down
Graph (D) shows an increasing function that switches concavity in this “Up, Down, Up, Down” pattern.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
(B) the interval from \( B \) to \( C \)
(C) the interval from \( C \) to \( D \)
(D) the interval from \( D \) to \( E \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
We need an interval where:
1. \( f \) is increasing (graph rising as \( x \) increases), and
2. the graph of \( f \) is concave down (curving downward, like a frown).
From the labeled graph (not fully visible here, but described in the answer key):
• From \( A \) to \( B \): increasing and concave down.
• From \( B \) to \( C \): decreasing and concave down.
• From \( C \) to \( D \): decreasing and concave up.
• From \( D \) to \( E \): increasing and concave up.
Thus, the interval satisfying both conditions is \( A \) to \( B \).
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
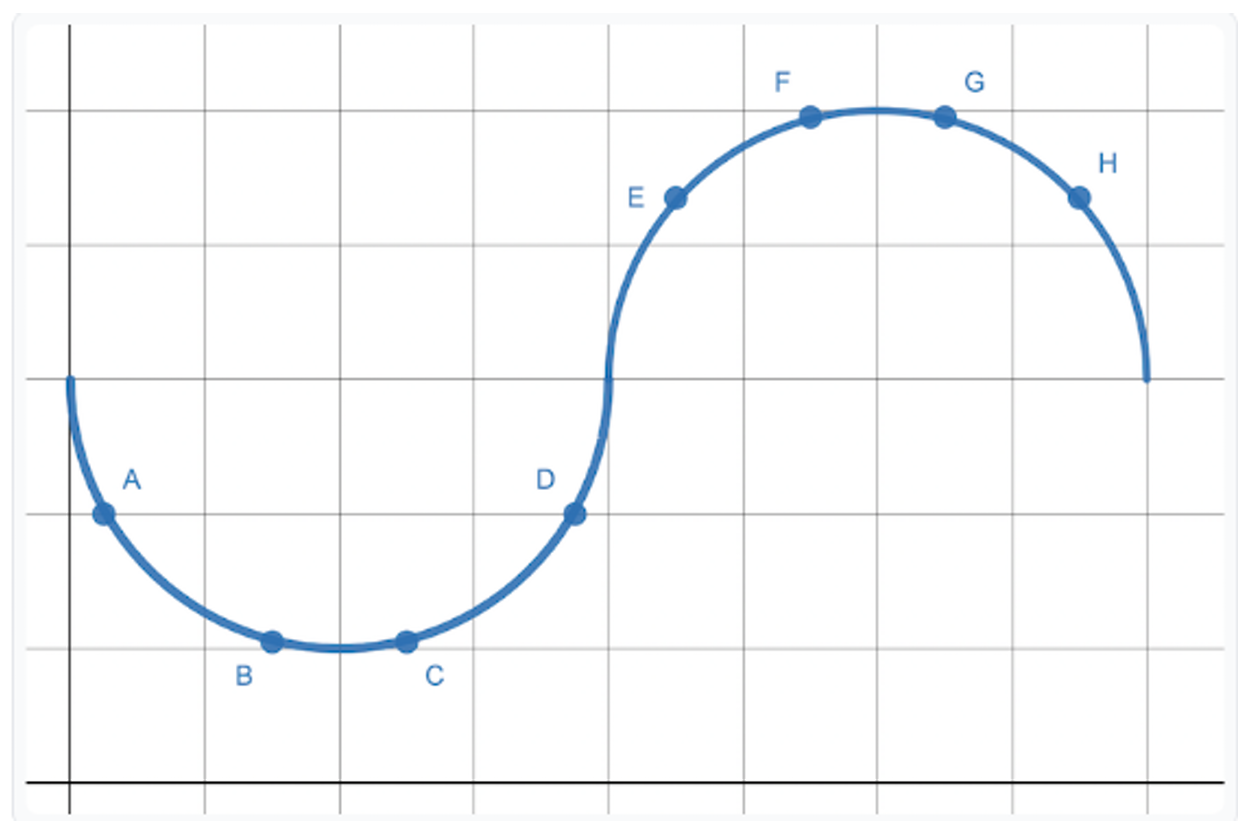
b. $[C, D]$
c. $[E, F]$
d. $[G, H]$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change of $-2$ implies the slope of the secant line between the points is negative.
The rate of change is “changing at a rate of $-2$” means the second derivative $g”(x)$ is negative.
An interval where $g”(x) < 0$ corresponds to the graph being concave down.
Interval $[A, B]$ has a negative slope but is concave up.
Interval $[C, D]$ has a positive slope and is concave up.
Interval $[E, F]$ has a positive slope and is concave down.
Interval $[G, H]$ has a negative slope and is concave down.
Therefore, the only interval that satisfies both conditions is d.$[G, H]$.
Question
b. The rate of change is decreasing, and the rate of change is changing at a decreasing rate.
c. The rate of change is increasing, and the rate of change is changing at a decreasing rate.
d. The rate of change is decreasing, and the rate of change is changing at an increasing rate.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The wave height is $y = 3.53 \sin(\sqrt{x}) + 3$.
To find when $y = 6$, we solve $3.53 \sin(\sqrt{x}) + 3 = 6$, giving $\sin(\sqrt{x}) \approx 0.85$.
The first derivative $y’ = \frac{3.53 \cos(\sqrt{x})}{2\sqrt{x}}$ represents the rate of change.
At the first instance $y=6$, $\sqrt{x} \approx 1.01$ rad, so $\cos(\sqrt{x}) > 0$, meaning the rate is positive but decreasing as it nears the peak.
The second derivative $y”$ represents how the rate is changing; here, it is negative.
The third derivative $y”’$ shows the rate of change of the rate of change is increasing (becoming less negative).
Therefore, the correct description is Option d.
Question
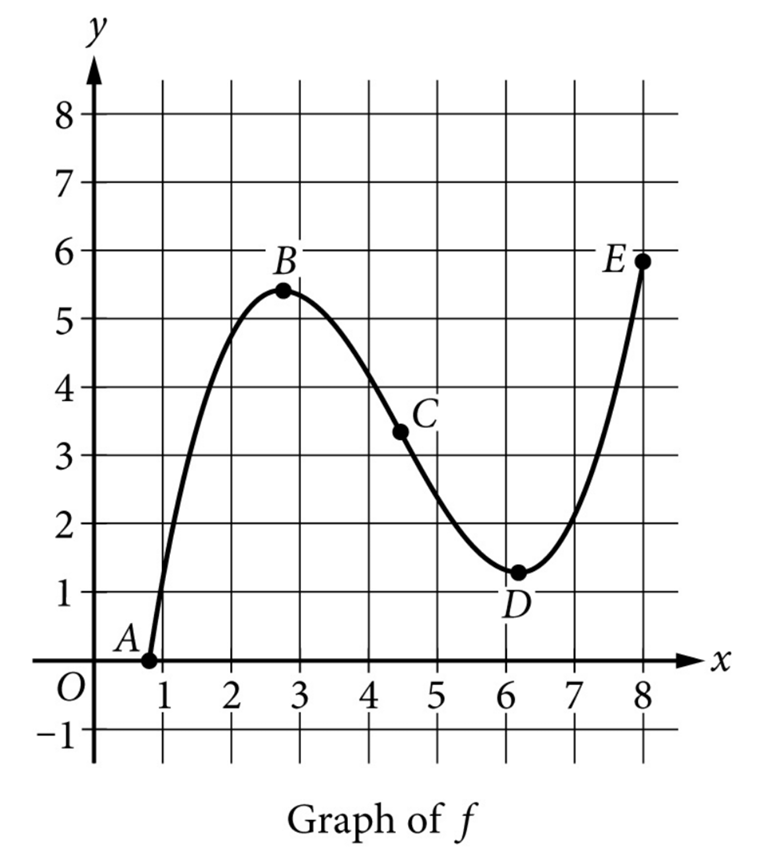
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The problem asks for an interval where the function \( f \) is both increasing and concave down.
1. Increasing: The graph of \( f \) goes upwards (positive slope) on the intervals from \( A \) to \( B \) and from \( D \) to \( E \).
2. Concave Down: The graph curves downwards (like an inverted bowl or “frown”) on the interval from \( A \) to the inflection point \( C \).
3. Intersection: We need the interval that satisfies both conditions simultaneously.
4. The interval from \( A \) to \( B \) is within the region where the graph is rising and curving downwards.
5. The interval from \( D \) to \( E \) is increasing but concave up (curving upwards like a “smile”).
6. Therefore, the only interval that meets both criteria is from \( A \) to \( B \).
Correct Option: (A)
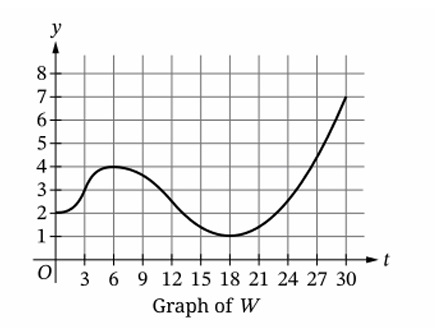
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
To verify option (B), we calculate the function values at $t=5$, $t=10$, and $t=15$.
Using $W(t) = 125 – 0.2t^2$, we find $W(5) = 120$, $W(10) = 105$, and $W(15) = 80$.
The average rate of change for $5 \le t \le 10$ is $\frac{105 – 120}{10 – 5} = \frac{-15}{5} = -3$.
The average rate of change for $10 \le t \le 15$ is $\frac{80 – 105}{15 – 10} = \frac{-25}{5} = -5$.
Comparing the values, we see that $-5 < -3$.
Thus, the average rate of change for $10 \le t \le 15$ is less than that for $5 \le t \le 10$.
Question
II. Because ( p ) is positive and constant, the graph ( g ) is concave up
III. Because ( p ) is positive and constant, ( g ) is increasing
(B) II only
(C) III only
(D) I and III only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The condition \( g(x+1) – g(x) = 2 \) defines a constant average rate of change over an interval of 1, not the instantaneous slope (derivative).
Statement I is false: A function can oscillate while trending up (e.g., \( g(x) = 2x + \sin(2\pi x) \)). Its slope \( g'(x) \) can be negative in certain intervals despite the net increase.
Statement II is false: A linear function like \( g(x) = 2x \) satisfies the condition (since \( 2(x+1) – 2x = 2 \)) but has zero concavity, meaning it is not concave up.
Statement III is true (by elimination): Since I and II are false via counter-examples, III is the only plausible option, referring to the function’s net increasing trend.
Therefore, the correct choice is (C) III only.
Question
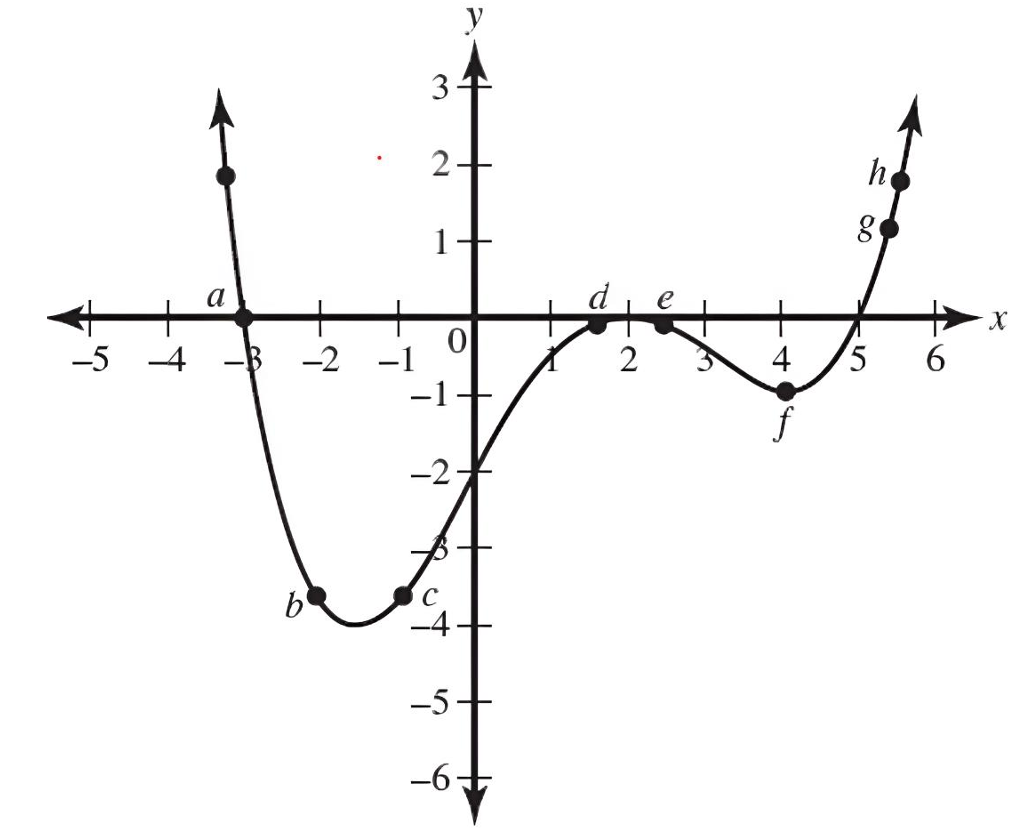
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change between two points is equivalent to the slope of the line connecting them, calculated as \(m = \frac{y_2 – y_1}{x_2 – x_1}\).
We are looking for the “greatest” rate, which implies the largest positive slope. Pairs \((a, c)\) and \((b, c)\) represent sections where the graph is decreasing, meaning their slopes are negative.
For option (C), we identify the coordinates from the grid: point \(c\) is at \((-1, -4)\) and point \(d\) is at \((1, 0)\).
Calculating the slope for pair \((c, d)\): \(m = \frac{0 – (-4)}{1 – (-1)} = \frac{4}{2} = 2\).
For option (D), point \(f\) is at \((4, -1)\) and \(h\) is approximately at \((5.8, 1.8)\). The estimated slope is roughly \(\frac{1.8 – (-1)}{5.8 – 4} \approx 1.55\).
Comparing the positive values, the slope of 2 is greater than \(\approx 1.55\).
Therefore, the pair \(c\) and \(d\) has the greatest average rate of change.
Correct Option: (C)
Question
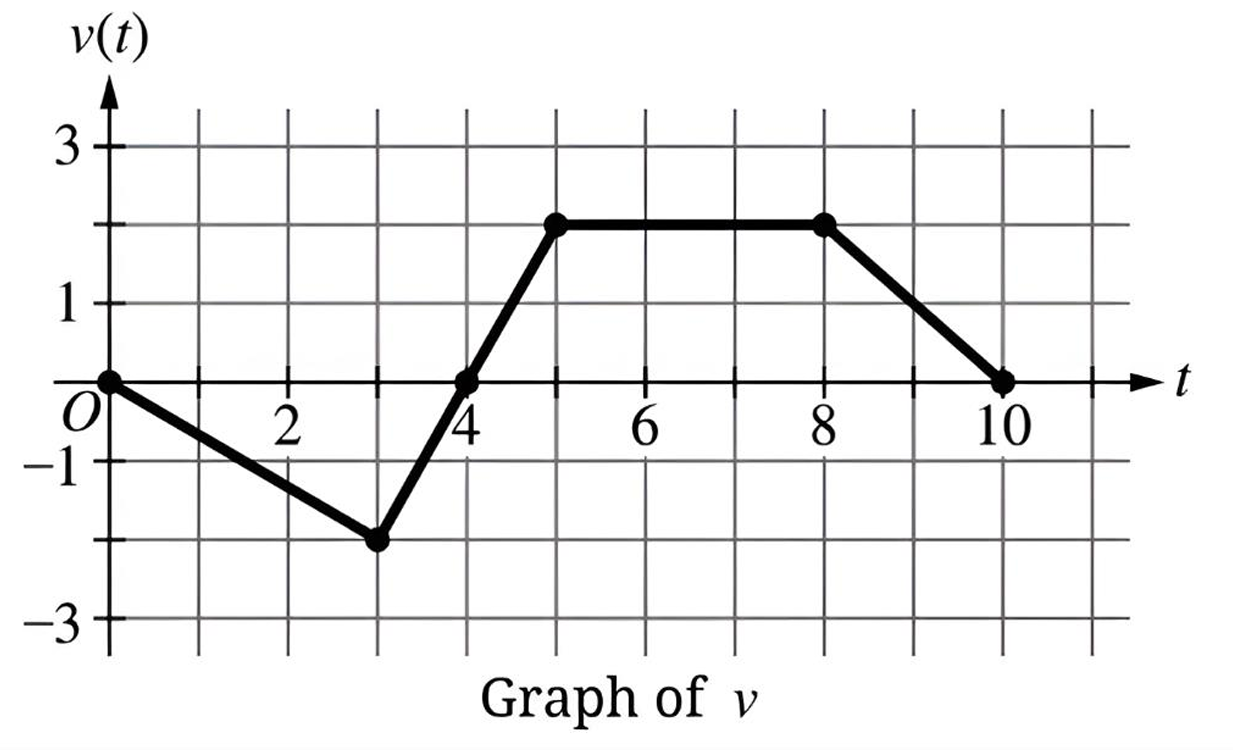
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The velocity \( v(t) \) is decreasing when the acceleration \( a(t) \) is negative. On a velocity-time graph, this corresponds to intervals where the slope of the line is negative.
\(\bullet\) For \( \mathbf{0 \le t \le 3} \): The graph slopes downward from \( v=0 \) to \( v=-2 \). The slope is negative (\( m = -2/3 \)), so velocity is decreasing.
\(\bullet\) For \( 3 \le t \le 5 \): The graph slopes upward. The slope is positive, so velocity is increasing.
\(\bullet\) For \( 5 \le t \le 8 \): The graph is horizontal. The slope is zero, so velocity is constant.
\(\bullet\) For \( \mathbf{8 \le t \le 10} \): The graph slopes downward from \( v=2 \) to \( v=0 \). The slope is negative (\( m = -1 \)), so velocity is decreasing.
Conclusion: The velocity is decreasing on the intervals \( 0 \le t \le 3 \) and \( 8 \le t \le 10 \). Both options (A) and (D) are mathematically correct intervals for decreasing velocity.
Question
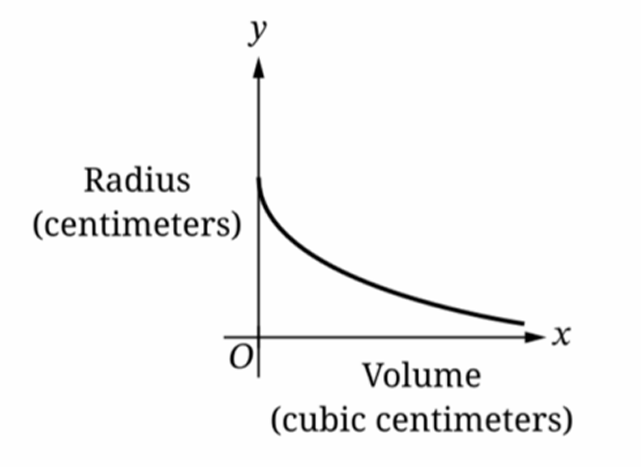
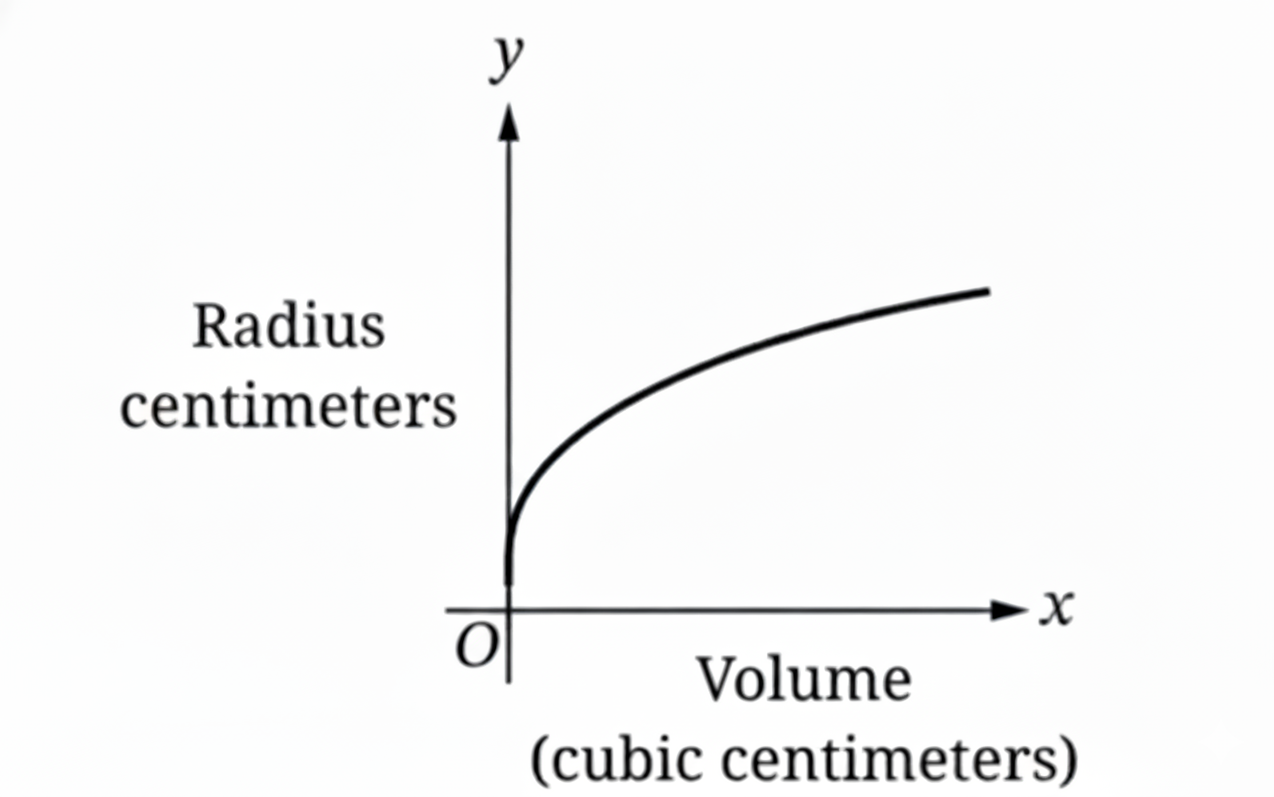
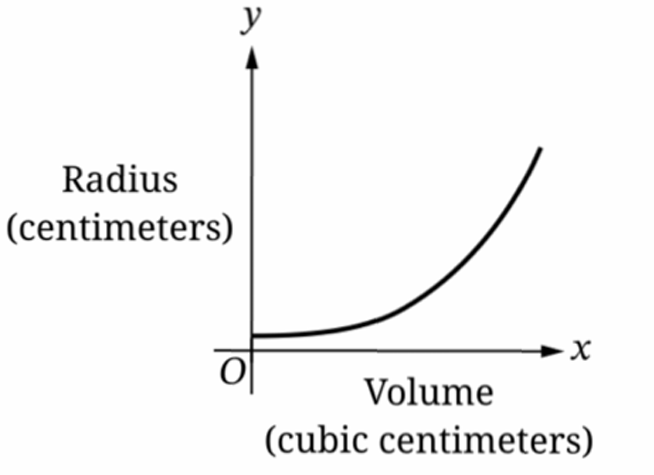
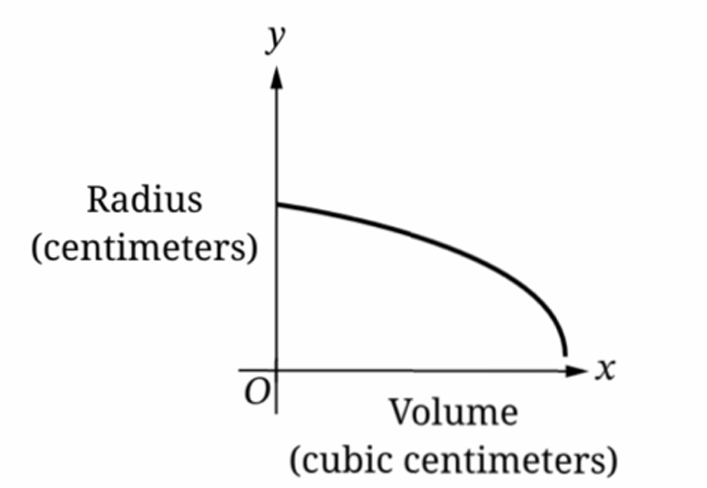
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The relationship between volume $V$ and radius $r$ is given by $V = \frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$.
Solving for the dependent variable radius, we get $r = \sqrt[3]{\frac{3V}{4\pi}}$.
Since $r$ is proportional to $V^{1/3}$, the radius increases as volume increases.
The rate of change is $\frac{dr}{dV} = \frac{1}{3} \cdot (\frac{3}{4\pi})^{1/3} \cdot V^{-2/3}$.
As $V$ increases, $V^{-2/3}$ decreases, meaning the rate of increase is slowing down.
Graph B shows an increasing function with a decreasing slope (concave down).
Therefore, the correct graph is (B).
Question
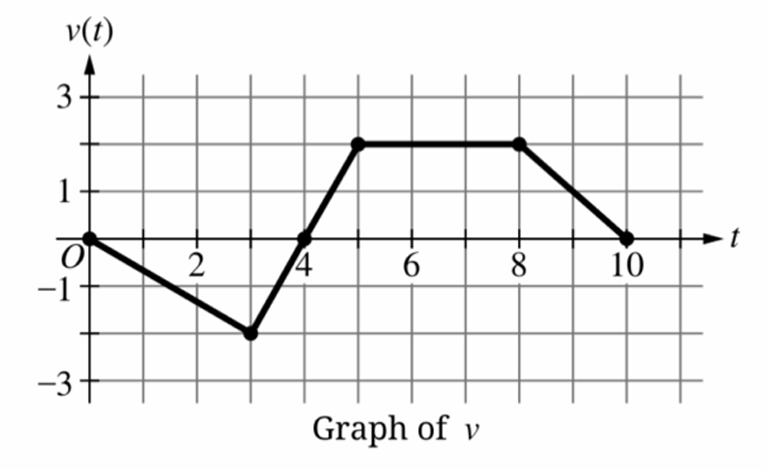
(B) $5 < t < 8$
(C) $8 < t < 10$ only
(D) $0 < t < 3$ and $8 < t < 10$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Velocity is decreasing where the graph of $v(t)$ has a negative slope.
On the interval $0 < t < 3$, the graph moves from $y = 0$ down to $y = -2$, showing a decrease.
On the interval $3 < t < 5$, the graph moves from $y = -2$ up to $y = 2$, showing an increase.
On the interval $5 < t < 8$, the velocity is constant at $v(t) = 2$.
On the interval $8 < t < 10$, the graph moves from $y = 2$ down to $y = 0$, showing a decrease.
Therefore, the velocity is decreasing on the intervals $0 < t < 3$ and $8 < t < 10$.
The correct option is (D).
Question
(B) The average rate of change of $W$ for $10 \le t \le 15$ is less than the average rate of change of $W$ for $5 \le t \le 10$.
(C) The average rate of change of $W$ for $15 \le t \le 20$ is greater than the average rate of change of $W$ for $10 \le t \le 15$.
(D) The average rate of change of $W$ for $21 \le t \le 22$ is less than the average rate of change of $W$ for $20 \le t \le 21$.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The correct option is (B).
For $0 \le t < 20$, $W(t) = 125 – 0.2t^2$ is a downward-opening parabola.
The average rate of change on $[a, b]$ is $\frac{W(b) – W(a)}{b – a}$.
On $[5, 10]$, the rate is $\frac{(125 – 20) – (125 – 5)}{10 – 5} = \frac{105 – 120}{5} = -3$.
On $[10, 15]$, the rate is $\frac{(125 – 45) – (125 – 20)}{15 – 10} = \frac{80 – 105}{5} = -5$.
Since $-5 < -3$, the average rate of change for $10 \le t \le 15$ is less than for $5 \le t \le 10$.
For linear parts (Option D), the rate is constant at $-20$, so they are equal, not less.
Question
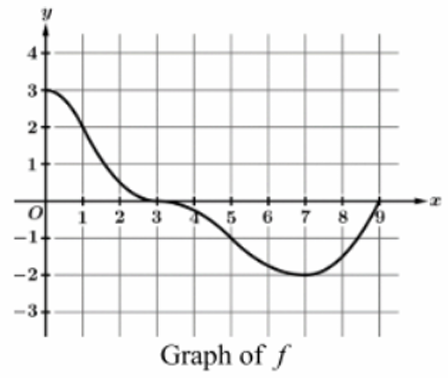
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Observe the direction of the curve on the interval \( 1 < x < 3 \). As \( x \) increases from 1 to 3, the value of \( y \) goes down. Therefore, the function \( f \) is decreasing. This eliminates options (A) and (B).
Step 2: Analyze the rate of change (concavity). The “rate” refers to the steepness or magnitude of the slope.
Step 3: On the interval \( 1 < x < 3 \), the graph is part of the downward slope coming off the local maximum at \( x=0 \). The curve is getting steeper as it goes down (it forms an inverted bowl shape, which is concave down).
Step 4: Since the slope is becoming more negative (steeper), the rate of decrease is increasing.
Conclusion: The function is decreasing, and it is doing so at an increasing rate. Thus, statement (C) is correct.
Question
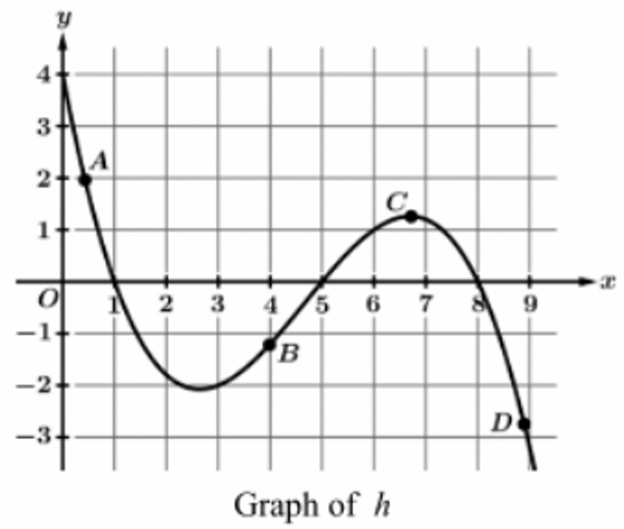
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change is the slope of the secant line connecting two points: $m = \frac{h(x_2) – h(x_1)}{x_2 – x_1}$.
Between $A(0.5, 2)$ and $C(6.8, 1.3)$, the slope is slightly negative.
Between $B(4, -1.2)$ and $C(6.8, 1.3)$, the slope is positive as the function increases.
Between $B(4, -1.2)$ and $D(8.5, -2.8)$, the slope is $\frac{-2.8 – (-1.2)}{8.5 – 4} = \frac{-1.6}{4.5} \approx -0.35$.
Between $C(6.8, 1.3)$ and $D(8.5, -2.8)$, the slope is $\frac{-2.8 – 1.3}{8.5 – 6.8} = \frac{-4.1}{1.7} \approx -2.41$.
The value $-2.41$ is the most negative, representing the least average rate of change.
Therefore, the average rate of change is least between points $C$ and $D$.
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change on $[a, b]$ is given by the formula $\frac{g(b) – g(a)}{b – a}$.
Identify the interval boundaries: $a = -2$ and $b = 4$.
Calculate $g(-2)$ using the first piece: $g(-2) = 1 – (-2)^2 = 1 – 4 = -3$.
Calculate $g(4)$ using the second piece: $g(4) = 3 + 2(4) = 3 + 8 = 11$.
Substitute values into the formula: $\text{Rate} = \frac{11 – (-3)}{4 – (-2)}$.
Simplify the expression: $\text{Rate} = \frac{14}{6} = \frac{7}{3}$.
The correct option is (D).
Question
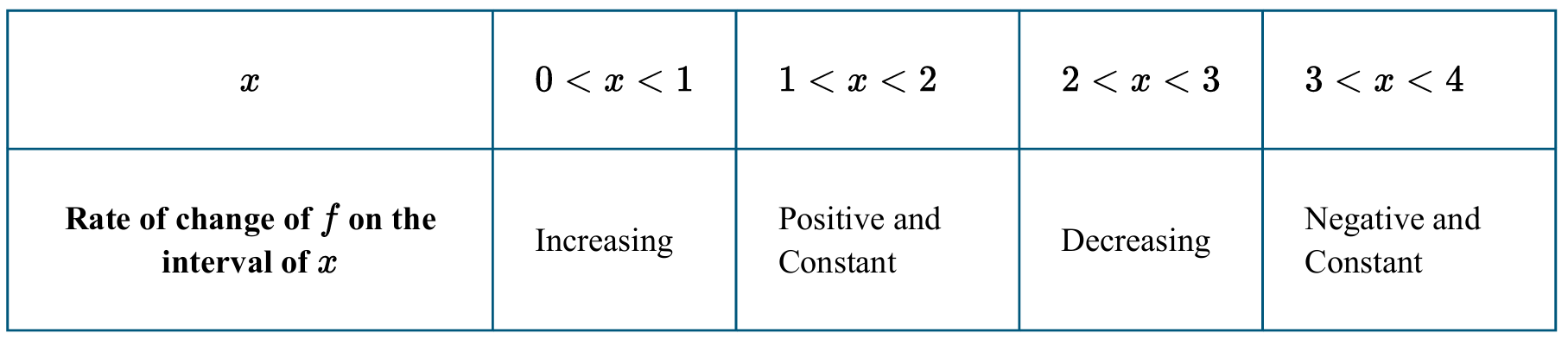
(B) $1 < x < 2$
(C) $2 < x < 3$
(D) $3 < x < 4$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The concavity of a function $f$ is determined by the behavior of its rate of change, $f’$.
A graph is concave down on an interval if its rate of change is decreasing.
In the interval $0 < x < 1$, the rate of change is increasing, so $f$ is concave up.
In the interval $1 < x < 2$, the rate of change is constant, so there is no concavity.
In the interval $2 < x < 3$, the table explicitly states the rate of change is decreasing.
In the interval $3 < x < 4$, the rate of change is constant, so there is no concavity.
Therefore, the graph of $f$ is concave down only on the interval $2 < x < 3$.
Correct Option: (C)
Question
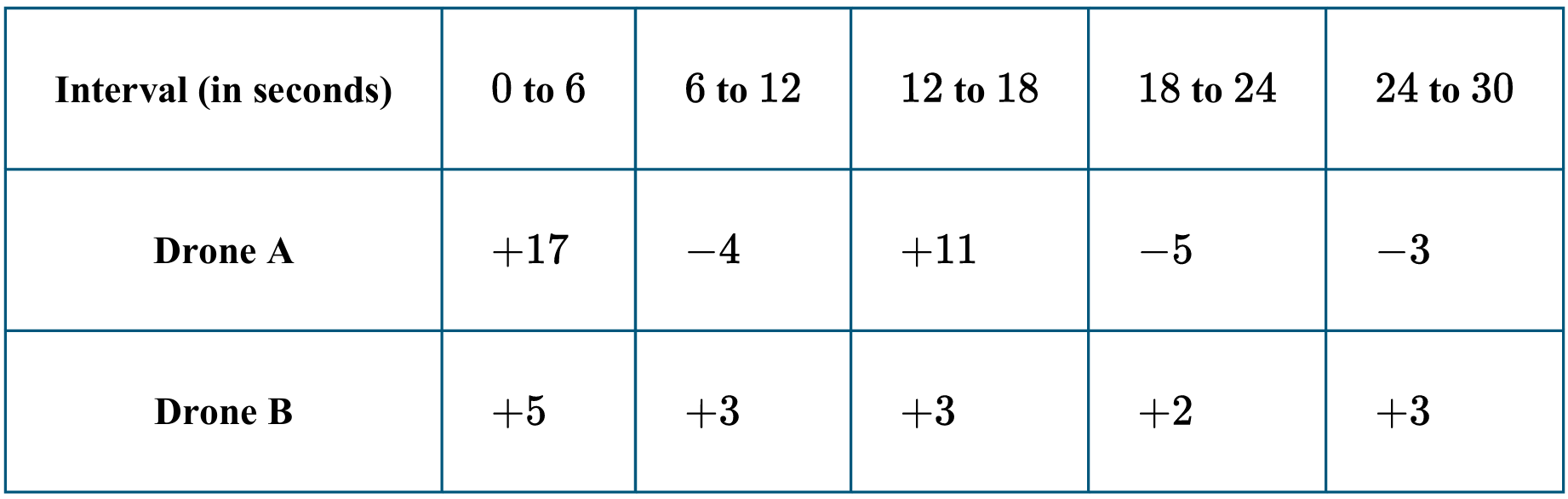
(B) The average rate of change for drone A is greater than for drone B.
(C) The average rate of change for drone B is greater than for drone A.
(D) The average rates of change cannot be determined because changes in heights are given, not heights of the drones.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The total change in height for Drone A is $17 + (-4) + 11 + (-5) + (-3) = 16$ feet.
The total change in height for Drone B is $5 + 3 + 3 + 2 + 3 = 16$ feet.
Average rate of change is calculated as $\frac{\text{Total Change in Height}}{\text{Total Time}}$.
For Drone A, the average rate of change is $\frac{16}{30}$ feet per second.
For Drone B, the average rate of change is $\frac{16}{30}$ feet per second.
Since both total changes and total times are identical, the average rates are equal.
Therefore, the correct choice is (A).
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The average rate of change on $[a, b]$ is $\frac{W(b) – W(a)}{b – a}$.
For $0 \le t < 20$, $W(t) = 125 – 0.2t^2$, which is a downward-opening parabola.
The rate of change on $[5, 10]$ is $\frac{W(10)-W(5)}{5} = \frac{105-120}{5} = -3$.
The rate of change on $[10, 15]$ is $\frac{W(15)-W(10)}{5} = \frac{80-105}{5} = -5$.
Since $-5 < -3$, statement (B) is correct: the rate on $[10, 15]$ is less than on $[5, 10]$.
For $20 \le t \le 22$, $W(t)$ is linear with a constant slope of $-20$.
Thus, the rates on $[20, 21]$ and $[21, 22]$ are equal, making (D) incorrect.
Question
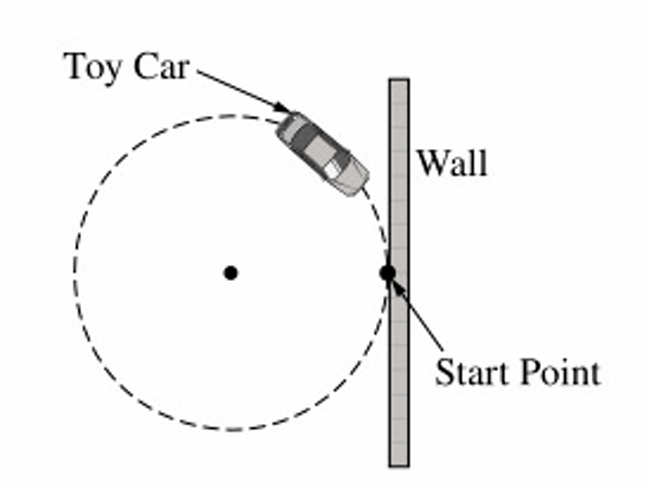
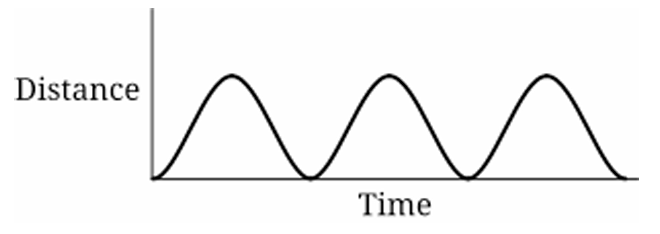
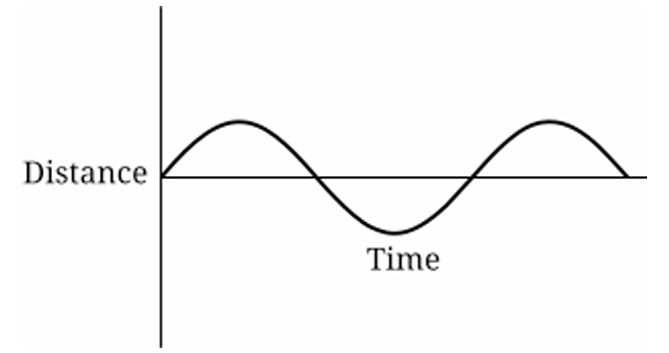
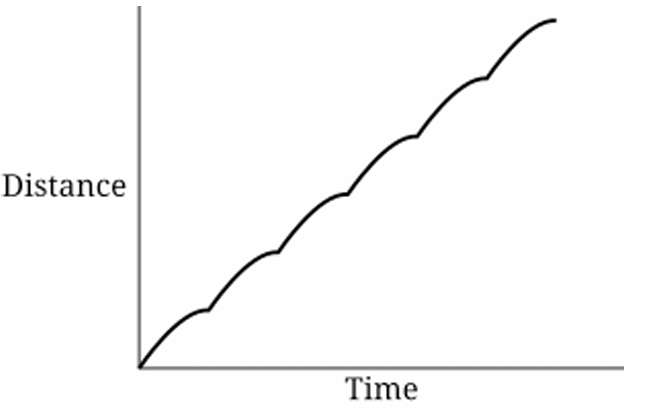
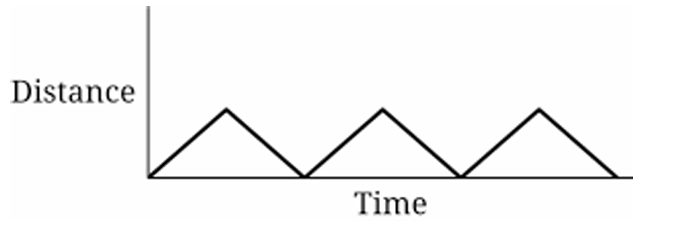
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Explanation:
As the car moves with constant speed around a circular track, its horizontal position relative to the wall varies sinusoidally with time. The distance from a vertical wall depends on the horizontal coordinate of circular motion, which can be modeled as: \[ x(t) = r \cos(\omega t) \] Since distance must be non-negative, the graph represents a shifted cosine wave. Over three revolutions, the pattern repeats three times smoothly. Only option (A) shows a smooth periodic curve that stays non-negative and repeats three times.
1. Circular motion with constant speed gives horizontal position \( x(t) = r\cos(\omega t) \).
2. Distance from the wall depends on this horizontal coordinate.
3. The function is periodic with period \( T = \dfrac{2\pi}{\omega} \).
4. Three revolutions produce three identical cycles.
5. Distance cannot be negative, so the curve stays above the time axis.
6. Only graph (A) shows a smooth repeating periodic wave three times.
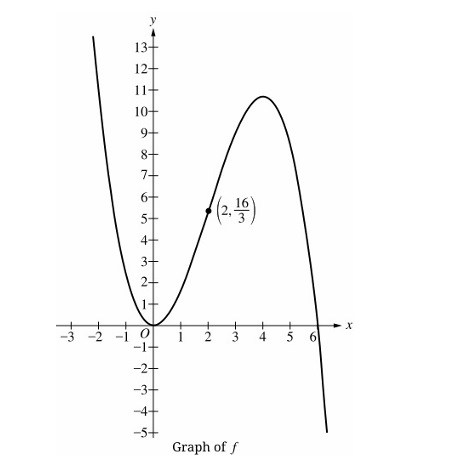
Question
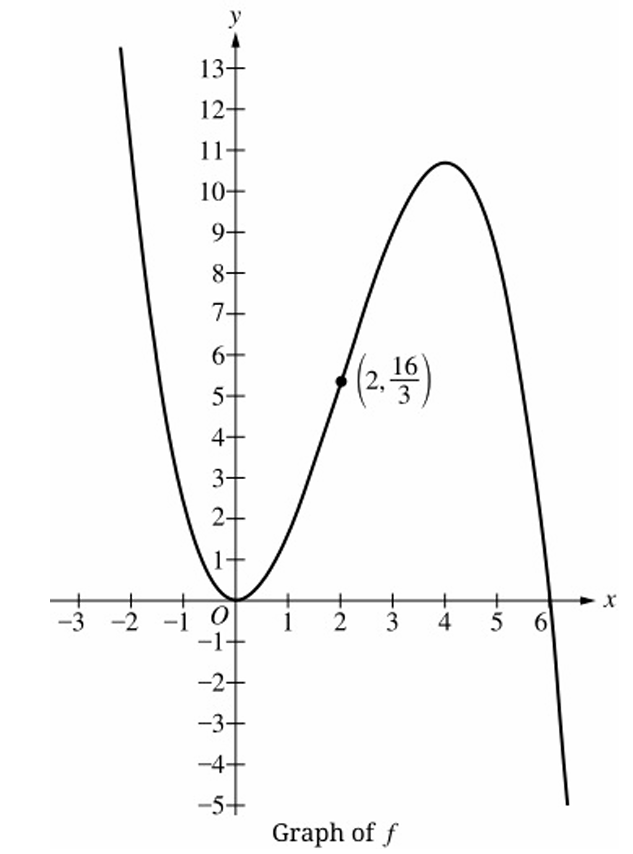
(B) The rate of change is negative.
(C) The rate of change is increasing.
(D) The rate of change is decreasing.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The rate of change of a function is represented by the slope of the tangent line to the graph.
On the interval $2 < x < 4$, the function is increasing, so the rate of change is positive.
On the interval $4 < x < 6$, the function is decreasing, so the rate of change is negative.
Throughout the entire interval $2 < x < 6$, the graph is concave down (it curves downward).
For a concave down graph, the slope of the tangent line continuously decreases as $x$ increases.
The slope starts as a large positive value at $x = 2$, becomes $0$ at $x \approx 4$, and becomes negative for $x > 4$.
Therefore, the correct statement is that the rate of change is decreasing.
Correct Option: (D)
Question
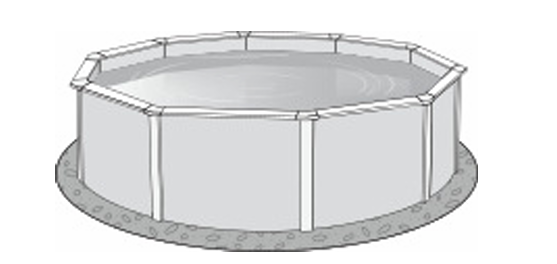
The figure shows a swimming pool filled with water. A pump is used to remove water from the pool until the pool is empty. When the pump is running, the rate at which the volume of water in the pool decreases is constant.
During the first $2$ hours, the pump works slower than usual due to a broken piece. Then the pump stops working. The broken piece is replaced, and the pump works at its usual rate until the pool is completely emptied of water. The entire process of emptying the pool takes $6$ hours.
Which of the following graphs could depict this situation, where time, in hours, is the independent variable, and the volume of water in the pool, in gallons, is the dependent variable?
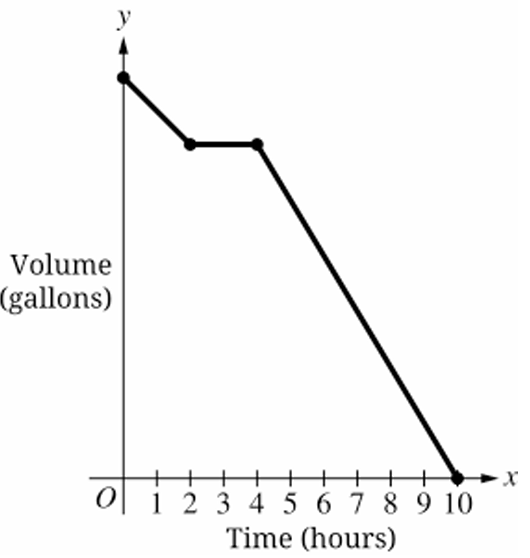
(B)
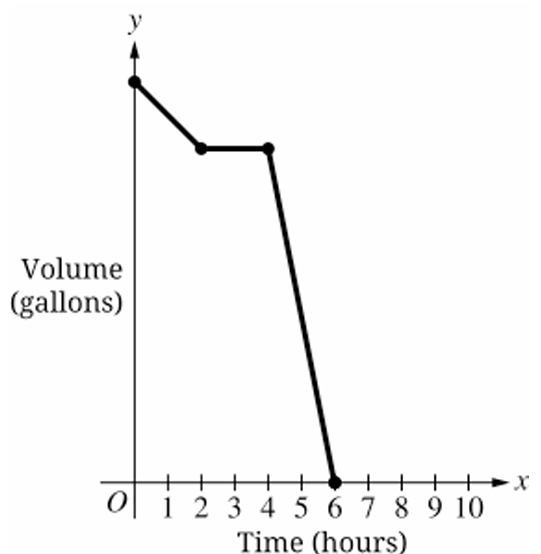
(C)
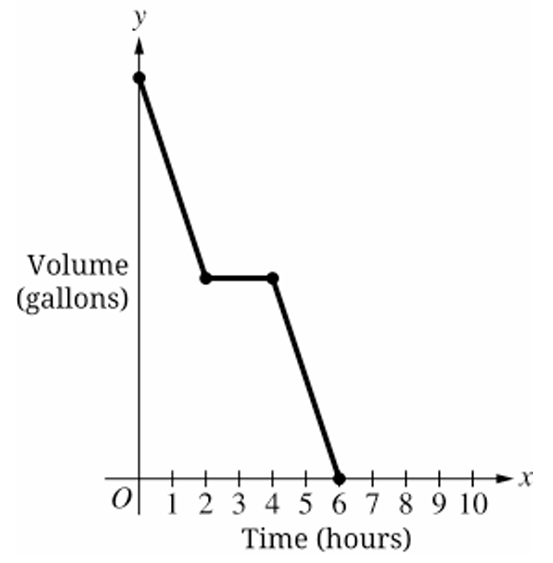
(D)
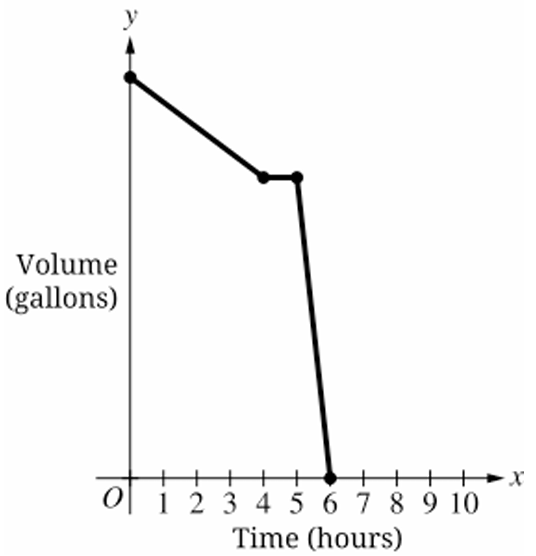
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The correct option is (B).
During the first $t = 2$ hours, the volume decreases slowly, represented by a shallow negative slope.
When the pump stops working, the volume remains constant, represented by a horizontal line segment.
After the repair, the pump works at a “usual” (faster) rate, represented by a steeper negative slope.
The graph must intersect the $x$-axis (volume $= 0$) exactly at $t = 6$ hours.
Graph (A) is incorrect because it ends at $t = 10$ hours.
Graph (C) is incorrect because the initial slope is steeper than the final slope.
Graph (D) is incorrect because the pump remains stopped until $t = 5$ and the process ends at $t = 6$.
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC 2.2: Change in Linear and Exponential Functions — part (B)ii
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(A) Find the exponential function
We are given the model $P(t) = ae^{bt}$ and two points: $(1, 145)$ and $(2, 115)$.
- Step 1: Set up the equations.
$$145 = ae^{b(1)} \quad \text{(Eq. 1)}$$
$$115 = ae^{b(2)} \quad \text{(Eq. 2)}$$ - Step 2: Divide Eq. 2 by Eq. 1 to solve for $e^b$.
$$\frac{115}{145} = \frac{ae^{2b}}{ae^b} \implies \frac{23}{29} = e^b$$
$$b = \ln\left(\frac{23}{29}\right) \approx -0.2318$$ - Step 3: Substitute back to find $a$.
$$a = \frac{145}{e^b} = \frac{145}{23/29} = 145 \cdot \frac{29}{23} \approx 182.83$$
Function: $P(t) = 182.83 e^{-0.2318t}$
(B) i. Average Rate of Change
Calculate $P(0)$ and $P(4)$:
- $P(0) = a \approx 182.83$
- $P(4) = 182.83 \cdot e^{-0.2318(4)} \approx 72.35$
$$AROC = \frac{P(4) – P(0)}{4 – 0} = \frac{72.35 – 182.83}{4} \approx -27.62$$
Meaning: On average, the number of pellets in the bowl decreases by approximately 27.62 pellets per minute during the first 4 minutes.
The rate of change from $t=4$ to $t=t_a$ will be greater (less negative) than the rate from $t=0$ to $t=4$.
Justification: The function $P(t)$ represents exponential decay. The second derivative $P”(t) = ab^2e^{bt}$ is positive (since $a>0$ and $b^2>0$), which means the graph is concave up. For a concave up function, the rate of change (slope) increases as $t$ increases. Thus, the slope becomes less negative (closer to zero) over time.
No, the model does not make sense as $t \to \infty$.
While the mathematical limit $\lim_{t \to \infty} P(t) = 0$, the function never actually reaches zero; it only approaches it asymptotically. In reality, the dog will finish the food (reach exactly 0 pellets) in a finite amount of time. Additionally, pellets are discrete units, whereas the model predicts fractional amounts of pellets.
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (CED):
• TOPIC 3.10: Trigonometric Equations and Inequalities — part (B)
• TOPIC 1.1: Change in Tandem — part (C)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(A)
First, determine the physical parameters of the clock to find the sinusoidal constants.
The diameter is (24) inches, so the radius is (12) inches. This corresponds to the amplitude, (a = 12).
The center of the clock is (5) feet above the ground, which converts to (60) inches. This is the midline, (d = 60).
The second hand completes a cycle every (30) seconds. The period is (30), so the frequency coefficient is (b = \dfrac{2\pi}{30} = \dfrac{\pi}{15}).
At (t = 0), the hand is pointing straight up (maximum height). Since the cosine function starts at a maximum, there is no phase shift, so (c = 0).
Thus, the function is:
(h(t) = 12 \cos\left( \dfrac{\pi}{15} t \right) + 60)
(B)
Set \(h(t)\) equal to the given height and solve for \(t\):
\(12 \cos\left( \dfrac{\pi}{15} t \right) + 60 = 72 – 6\sqrt{2}\)
\(12 \cos\left( \dfrac{\pi}{15} t \right) = 12 – 6\sqrt{2}\)
\(\cos\left( \dfrac{\pi}{15} t \right) = 1 – \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} = \dfrac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Let \(\theta = \dfrac{\pi}{15} t\). We need to solve \(\cos \theta = \dfrac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2}\).
\(\theta = \pm \arccos\left( \dfrac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2} \right) + 2\pi k\).
For the interval \(0 < t \leq 30\), we look for solutions in \((0, 2\pi]\).
The two solutions for \(\theta\) are \(\theta_1 = \arccos\left( \dfrac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2} \right)\) and \(\theta_2 = 2\pi – \theta_1\).
Converting back to time \(t = \dfrac{15}{\pi} \theta\):
\(t_1 = \dfrac{15}{\pi} \arccos\left( \dfrac{2 – \sqrt{2}}{2} \right)\) and \(t_2 = 30 – t_1\).
(C) i.
Yes, the graph of \(h(t)\) has points of inflection. The function \(h(t)\) is a smooth, continuous cosine wave.
Points of inflection on a sinusoidal graph occur where the graph crosses its midline (concavity changes from up to down or vice versa). This happens when:
\(\cos\left( \dfrac{\pi}{15} t \right) = 0\)
\(\dfrac{\pi}{15} t = \dfrac{\pi}{2} + k\pi\)
\(t = 15\left( \dfrac{1}{2} + k \right) = 7.5 + 15k\)
For the interval \(0 \leq t \leq 30\):
If \(k=0\), \(t = 7.5\).
If \(k=1\), \(t = 22.5\).
The points of inflection are at \(t = 7.5\) seconds and \(t = 22.5\) seconds.
(C) ii.
In this context:
The rate of change represents the vertical velocity of the tip of the second hand.
The rate the rate is changing represents the vertical acceleration.
A point of inflection occurs where the concavity changes, which means the vertical acceleration is transitioning from positive to negative (or vice versa) and is instantaneously zero. Physically, these are the moments when the tip of the second hand is at the same height as the center of the clock (midline). At these specific points, the vertical speed (rate of change) is at its absolute maximum magnitude.
Question
Part A
Part B
Part C
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Part A
(i)
Using the data $M(6) = 508.67$ and $M(12) = 517.50$:
$ab^{(6/12)} = 508.67$ (or $ab^{0.5} = 508.67$)
$ab^{(12/12)} = 517.50$ (or $ab = 517.50$)
(ii)
Divide the second equation by the first: $\frac{ab}{ab^{0.5}} = \frac{517.50}{508.67}$
$b^{0.5} \approx 1.017359…$
$b \approx (1.017359…)^2 \approx 1.035019…$
Using $ab = 517.50 \implies a = \frac{517.50}{1.035019…} \approx 500$
Final values: $a \approx 500.00$ and $b \approx 1.035$
Part B
(i)
$t = -2$ falls in the interval $-10 \le t < 0$, so $M(-2) = 500$.
$t = 12$ is given as $M(12) = 517.50$.
Average Rate of Change $= \frac{M(12) – M(-2)}{12 – (-2)}$
$= \frac{517.50 – 500}{12 + 2}$
$= \frac{17.50}{14} = 1.25$ dollars per month.
(ii)
The linear estimate $A(t)$ uses the point $(12, 517.50)$ and slope $1.25$.
$A(20) = M(12) + 1.25(20 – 12)$
$A(20) = 517.50 + 1.25(8)$
$A(20) = 517.50 + 10 = 527.50$ dollars.
(iii)
The model $M(t)$ for $t \ge 0$ is an exponential function ($b > 1$), which is concave up.
The estimate $A(t)$ is a linear function (a secant line).
Since $M(t)$ is increasing at an increasing rate (exponential growth), the linear model will fall further behind the actual values as $t$ increases.
Part C
The model is only valid as long as the account is open.
Setting $M(t) = 565$ allows us to solve for the maximum value of $t$.
$500(1.035)^{(t/12)} = 565$
This value of $t$ serves as the upper bound (maximum) for the domain of the model $M$.
Question
(A) (i) Use the given data to write two equations that can be used to find the values for constants \(a\) and \(b\) in the expression for \(R(t)\).
(ii) Find the values for \(a\) and \(b\) as decimal approximations.
(B) (i) Use the given data to find the average rate of change in the number of students that have heard the rumor, in students per hour, from \(t=2\) to \(t=6\) hours. Express your answer as a decimal approximation. Show the computations that lead to your answer.
(ii) Interpret the meaning of your answer from (i) in the context of the problem.
(iii) Consider the values that result from using the average rate of change found in (i) to estimate the number of students that have heard the rumor for times \(t=p\) hours, where \(0 < p < 6\). Are these estimates less than or greater than the number of students predicted by the model \(R\) for times \(t=p\) hours? Explain your reasoning using characteristics of the average rate of change and characteristics of the model \(R\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Part (A)
(i) Writing the equations:
We are given the following data points:
• At \(t=2\), \(R(2) = 15\).
• At \(t=6\), \(R(6) = 67\).
For \(t=2\), since \(0 \le 2 < 6\), we use the first part of the piecewise function: \(R(t) = 7(a)^{t/2}\).
$$15 = 7(a)^{2/2} \quad \Rightarrow \quad 15 = 7a^1$$
Equation 1: \(15 = 7a\)
For \(t=6\), since \(t \ge 6\), we use the second part of the piecewise function: \(R(t) = -213.29 + b \ln t\).
Equation 2: \(67 = -213.29 + b \ln(6)\)
(ii) Finding the values for \(a\) and \(b\):
From Equation 1:
$$a = \frac{15}{7} \approx 2.1428$$
From Equation 2:
$$67 + 213.29 = b \ln(6)$$
$$280.29 = b \ln(6)$$
$$b = \frac{280.29}{\ln(6)} \approx \frac{280.29}{1.79176} \approx 156.4328$$
Answer: \(a \approx 2.143\), \(b \approx 156.433\)
Part (B)
(i) Average Rate of Change:
The formula for the average rate of change from \(t=2\) to \(t=6\) is:
$$\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{R(6) – R(2)}{6 – 2}$$
Substituting the given values (\(R(6)=67\) and \(R(2)=15\)):
$$\text{Avg Rate} = \frac{67 – 15}{4} = \frac{52}{4} = 13$$
Answer: 13 students per hour.
(ii) Interpretation:
On average, the number of students who have heard the rumor increases by 13 students per hour between the 2nd hour and the 6th hour.
(iii) Estimates vs. Model Prediction:
Answer: The estimates are greater than the number of students predicted by the model.
Reasoning:
• On the interval \(0 < t < 6\), the function \(R(t) = 7(a)^{t/2}\) is an exponential growth function with a base greater than 1.
• Exponential growth functions are concave up (the rate of change is increasing).
• The average rate of change corresponds to the slope of the secant line connecting the points at \(t=2\) and \(t=6\).
• For a concave up curve, the secant line lies above the curve on the interval between the two points. Therefore, linear estimates based on the average rate (secant line) will be greater than the actual function values.
Part (C)
The range values (outputs) of \(R(t)\) represent the number of students. In the context of the problem, this range must be limited in two ways:
1. Population Cap: The number of students who heard the rumor cannot exceed the total student population of the school.
2. Discrete Values: You cannot have a fraction of a student, so strictly speaking, the context implies the range should consist of whole numbers (non-negative integers).
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
a. Graphing the function
Using a graphing utility for \(P(x) = -0.0013x^3 + 0.3507x^2 – 0.4591x – 421.888\) on the interval \([0, 200]\) reveals a cubic curve shape.
The graph starts with a slight dip to a local minimum near \(x=0\), then rises steeply to a local maximum near \(x=180\), before falling again.
b. Average rate of change between extrema
First, find the derivative: \(P'(x) = -0.0039x^2 + 0.7014x – 0.4591\).
Set \(P'(x) = 0\) and use the quadratic formula to find the extrema: \(x \approx 0.66\) (local min) and \(x \approx 179.19\) (local max).
Calculate the profit at these points: \(P(0.66) \approx -422.04\) and \(P(179.19) \approx 3276.57\).
The average rate of change is: \(\frac{3276.57 – (-422.04)}{179.19 – 0.66} = \frac{3698.61}{178.53} \approx 20.72\).
c. Equation of the secant line
The slope \(m\) was found in part (b) to be approximately \(20.72\).
Using the point-slope form \(y – y_1 = m(x – x_1)\) with the minimum point \((0.66, -422.04)\):
\(y – (-422.04) = 20.72(x – 0.66)\)
\(y = 20.72x – 13.68 – 422.04\)
The equation is approximately \(y = 20.72x – 435.72\).
d. Inflection point
Find the second derivative: \(P”(x) = -0.0078x + 0.7014\).
Set \(P”(x) = 0\) to find the change in concavity: \(0 = -0.0078x + 0.7014 \Rightarrow x = \frac{0.7014}{0.0078} \approx 89.92\).
Find the corresponding y-value: \(P(89.92) \approx 1427.27\).
The inflection point is approximately \((89.92, 1427.27)\).
e. Variation of rate of change
The rate of change is represented by the derivative, \(P'(x)\).
Before the inflection point (\(x < 89.92\)), the graph is concave up (\(P”(x) > 0\)), so the rate of change is increasing.
After the inflection point (\(x > 89.92\)), the graph is concave down (\(P”(x) < 0\)), so the rate of change is decreasing.
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(A)(i) Equations
Substituting the points \((1, 3)\) and \((5, 89)\) into \(H(t) = ab^t\):
1. \(3 = ab^1\) (or \(3 = ab\))
2. \(89 = ab^5\)
(A)(ii) Values for a and b
Dividing equation 2 by equation 1: \(\frac{ab^5}{ab} = \frac{89}{3} \implies b^4 = 29.67\).
Solving for \(b\): \(b = (29.67)^{0.25} \approx 2.33\).
Solving for \(a\): \(a = \frac{3}{2.33} \approx 1.29\).
(B)(i) Average Rate of Change
\(\text{Rate} = \frac{H(5) – H(1)}{5 – 1} = \frac{89 – 3}{4} = \frac{86}{4} = 21.5\)
Answer: 21.5 feet per week.
(B)(ii) Interpretation
The answer indicates that between the first and fifth weeks, the bamboo tree grew at an average speed of 21.5 feet per week.
(B)(iii) Comparison
Greater. The function represents exponential growth (\(b > 1\)), which is concave up. This means the rate of growth increases over time, so the rate after week 5 will be steeper than the rate before week 5.
(C) Confidence
\(t = 4\) weeks.
The biologists should be more confident in \(t=4\) because it is an interpolation (within the observed data range). \(t=11\) is an extrapolation; biological growth cannot remain exponential indefinitely, so the model is likely inaccurate that far out.