2.2E Molecular Geometry (VSEPR Theory)- Pre AP Chemistry Study Notes - New Syllabus.
2.2E Molecular Geometry (VSEPR Theory)- Pre AP Chemistry Study Notes
2.2E Molecular Geometry (VSEPR Theory)- Pre AP Chemistry Study Notes – New Syllabus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
2.2.E.1 Determine molecular geometry from a Lewis diagram using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Key Concepts:
- 2.2.E Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory predicts molecular geometry from a Lewis diagram. Molecular geometries include linear, bent, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, and tetrahedral arrangements of atoms.
2.2.E.1 — Molecular Geometry Using VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is used to determine molecular geometry by predicting how electron groups arrange themselves around a central atom. VSEPR models are built directly from a Lewis diagram.
According to VSEPR theory, electron groups repel each other and adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsion, resulting in a predictable three-dimensional shape.
Key Ideas of VSEPR Theory
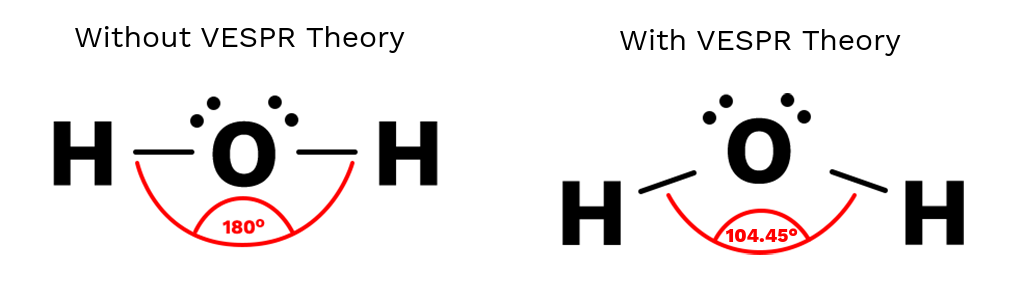
- Electron groups repel each other
- Electron groups arrange as far apart as possible
- Molecular geometry depends on electron arrangement around the central atom
Electron groups include:
- Single bonds
- Double bonds (count as one group)
- Triple bonds (count as one group)
- Lone pairs
Steps to Determine Molecular Geometry
- Draw a correct Lewis diagram
- Identify the central atom
- Count the total number of electron groups around the central atom
- Determine the molecular geometry using VSEPR theory
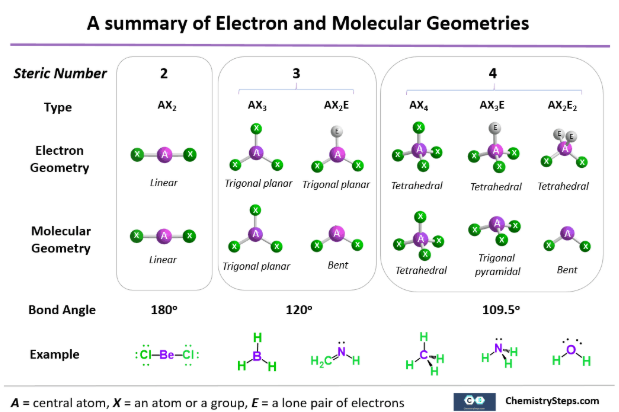
Common Molecular Geometries (Pre-AP)
| Electron Groups | Lone Pairs | Molecular Geometry | General Shape Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | Linear | 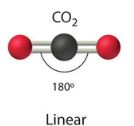 |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | 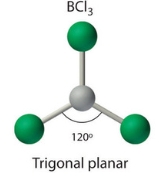 |
| 3 | 1 | Bent | 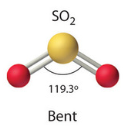 |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | |
| 4 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | 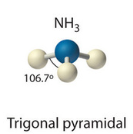 |
Effect of Lone Pairs on Geometry
Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs. As a result:
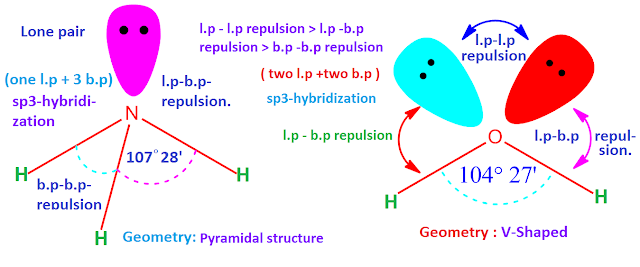
- Lone pairs compress bond angles
- The molecular geometry may differ from the electron geometry
VSEPR focuses on the positions of atoms, not lone pairs, when naming molecular geometry.
Evaluating VSEPR Models
A correct VSEPR-based model must:
- Start with a valid Lewis diagram
- Correctly count electron groups
- Account for lone pairs
- Use the correct geometry name
Incorrect electron counting leads to incorrect geometry.
Exam Tip (Pre-AP)
Always count electron groups, not atoms. Double and triple bonds count as one electron group in VSEPR theory.
Example
A molecule has a central atom bonded to three other atoms and contains no lone pairs on the central atom. Determine the molecular geometry using VSEPR theory.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
There are three electron groups around the central atom.
With no lone pairs, the electron groups arrange themselves evenly in a plane, resulting in a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
Example
A Lewis diagram shows a central atom with four electron groups, one of which is a lone pair. Use VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry and justify your answer.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Four electron groups produce a tetrahedral electron arrangement.
Because one of the electron groups is a lone pair, the positions of only the bonded atoms are considered. This results in a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry.
