Pre AP Chemistry -1.1A Particle Motion, Arrangement, and Energy- MCQ Exam Style Questions -New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.1A Particle Motion, Arrangement, and Energy- MCQ Exam Style Questions – New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.1A Particle Motion, Arrangement, and Energy- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Pre AP Chemistry – per latest Pre AP Chemistry Syllabus.
A compound, X, has a melting point of 71°C and a boiling point of 375°C.
Which statement about X is correct?
A) It is a liquid at 52°C and a gas at 175°C.
B) It is a liquid at 69°C and a gas at 380°C.
C) It is a liquid at 75°C and a gas at 350°C.
D) It is a liquid at 80°C and a gas at 400°C.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To determine the state of a substance at different temperatures, we compare the given temperature to its melting and boiling points:
- Below melting point: solid
- Between melting and boiling points: liquid
- Above boiling point: gas
Analyzing each option:
A) 52°C is below melting point (should be solid), 175°C is below boiling point (should be liquid). Incorrect.
B) 69°C is below melting point (should be solid), 380°C is just above boiling point (correct for gas). Partially correct but not fully.
C) 75°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), but 350°C is below boiling point (should be liquid, not gas). Incorrect.
D) 80°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), 400°C is above boiling point (correct for gas). Fully correct.
Which statement describes a liquid at room temperature?
A) A sample of a liquid has a fixed volume and shape.
B) A sample of a liquid does not have a fixed volume or shape.
C) The particles are touching but can move by sliding over each other.
D) The particles spread out and fill all available space.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Incorrect – Liquids have fixed volume but not fixed shape (they take the shape of their container).
B) Incorrect – Liquids do have fixed volume, though they don’t have fixed shape.
C) Correct – This accurately describes the particle arrangement and movement in liquids. The particles are close together (touching) but can move past one another.
D) Incorrect – This describes gas particles, not liquid particles.
Which conditions cause gas particles to move the fastest and the furthest apart?
| temperature | pressure | |
|---|---|---|
| A | high | high |
| B | low | high |
| C | high | low |
| D | low | low |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Gas particles move fastest at high temperatures because temperature is directly related to the kinetic energy of particles. At higher temperatures, particles have more energy and move faster.
Particles move furthest apart at low pressures because there’s more space between them when the pressure is reduced. High pressure forces particles closer together.
Therefore, the combination that causes gas particles to move fastest and furthest apart is high temperature and low pressure.
The table shows some information about the three states of matter.
| particle separation | particle arrangement | type of motion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | touching with some particles having spaces between them | random | slide past each other at low speed |
| 2 | particles are far apart | random | rapid motion in straight lines |
| 3 | touching with very little space between the particles | regular | vibration only |
Which row is correct?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | gas | liquid | solid |
| B | liquid | solid | gas |
| C | liquid | gas | solid |
| D | solid | gas | liquid |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each state:
State 1: Particles touching with some spaces, random arrangement, sliding past each other – these are characteristics of a liquid.
State 2: Particles far apart, random arrangement, rapid motion – these are characteristics of a gas.
State 3: Particles touching with little space, regular arrangement, vibrating only – these are characteristics of a solid.
Therefore, the correct matching is: 1 = liquid, 2 = gas, 3 = solid, which corresponds to option C.
Four statements about the arrangement or movement of particles are given.
- Particles are packed in a regular arrangement.
- Particles are randomly arranged.
- Particles move over each other.
- Particles vibrate about fixed points.
Which statements describe the particles in a pure solid?
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In a pure solid:
- Particles are packed in a regular, fixed arrangement (statement 1 is correct, 2 is incorrect as that describes liquids/gases)
- Particles vibrate about fixed positions but don’t move freely (statement 4 is correct, 3 is incorrect as that describes liquid behavior)
Therefore, the correct combination is 1 and 4.
The table shows the melting and boiling points of four elements.
Which element is a gas at room temperature and pressure?
| melting point/°C | boiling point/°C | |
|---|---|---|
| A | −101 | −35 |
| B | −7 | 59 |
| C | 10 | 100 |
| D | 113 | 445 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Room temperature is typically around 20-25°C. For an element to be a gas at room temperature, its boiling point must be below this range.
Option A has a boiling point of -35°C, which is below room temperature, so it would be a gas. The melting point (-101°C) tells us it’s not a solid at room temperature.
Option B boils at 59°C (liquid at room temp), C at 100°C (liquid), and D at 445°C (solid at room temp).
Which two processes are required to change ice into steam?
A) boiling and melting
B) boiling and freezing
C) condensing and melting
D) condensing and freezing
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To change ice into steam, two phase transitions must occur:
1. Melting – Ice (solid) turns into water (liquid).
2. Boiling – Water (liquid) turns into steam (gas).
Freezing and condensing are reverse processes, so options B, C, and D are incorrect. Thus, the correct answer is A (boiling and melting).
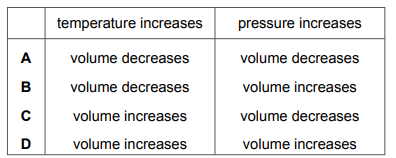
Which row describes how the volume of a gas changes when the temperature increases, or when the pressure increases?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
From the ideal gas law (\(PV = nRT\)):
1. When temperature increases (at constant pressure), volume increases (row must say “increases” for temperature).
2. When pressure increases (at constant temperature), volume decreases (row must say “decreases” for pressure).
Only option C matches both conditions correctly.
Which statement about gases is correct?
- Gases are difficult to compress when pressure is applied.
- The particles in gases are close together.
- The particles in gases have a random arrangement.
- The particles in gases move slowly past each other.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Key properties of gases:
1. Gases are easy to compress (statement 1 is wrong).
2. Gas particles are far apart (statement 2 is wrong).
3. Gas particles move randomly (statement 3 is correct).
4. Gas particles move rapidly, not slowly (statement 4 is wrong).
Thus, only statement 3 is correct.
A sample of argon gas is heated in a closed container. Which row describes what happens to the pressure and the size of the argon atoms?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When argon gas is heated in a closed container:
1. The pressure increases because the gas molecules move faster and collide more frequently and forcefully with the container walls (Gay-Lussac’s Law).
2. The size of the argon atoms remains unchanged because heating affects molecular motion but not the atomic radius.
Thus, the correct row is D (Pressure increases, Size stays the same).
Which row shows the conditions for the particles of a gas colliding most frequently?
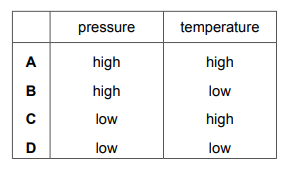
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The frequency of gas particle collisions depends on both temperature and pressure. Higher temperature increases particle speed, while higher pressure means more particles are confined in a given volume. In the table, Row A combines high temperature (50°C) and high pressure (5 atm), which maximizes collision frequency. The other options either have lower temperature or lower pressure, resulting in fewer collisions.
Which statement about a solid, a liquid or a gas is correct?
A A solid has a fixed shape and can be compressed.
B A liquid takes the shape of the container it is in and can be compressed.
C A solid has no fixed shape and cannot be compressed.
D A gas takes the shape of the container it is in and can be compressed.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
1. Solids have a fixed shape and are generally incompressible (A and C are incorrect).
2. Liquids take the shape of their container but are nearly incompressible (B is incorrect).
3. Gases take the shape of their container and are highly compressible (D is correct).
Thus, only statement D accurately describes the properties of a gas.
In which state does 1 \(dm^{3}\) of methane contain the most particles?
A) gas at \(100^{\circ}\)C
B) gas at room temperature
C) liquid
D) solid
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In the solid state, particles are tightly packed, resulting in the highest density. For the same volume (\(1 \, dm^3\)), solid methane contains more particles than liquid or gas because the number of particles is proportional to mass (via \(n = \frac{m}{M}\)), and solids have the highest mass per unit volume. Gases, being less dense, have far fewer particles in the same volume.
Nitrogen is heated in a balloon, which expands slightly.
Which statements about the molecules of nitrogen are correct?
1 They move further apart.
2 They move more quickly.
3 They remain the same distance apart.
4 Their speed remains unchanged.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
When nitrogen gas is heated in a balloon:
1. The molecules gain kinetic energy and move further apart as the balloon expands (statement 1 is correct).
2. The increased temperature causes molecules to move more quickly (statement 2 is correct).
3. The distance between molecules increases with expansion (statement 3 is wrong).
4. Speed increases with temperature (statement 4 is wrong).
Thus, only statements 1 and 2 are correct.
What happens to the average speed of gas particles when pressure and temperature are increased?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
From the kinetic theory of gases, the average speed (\(v_{avg}\)) of gas particles depends on temperature (\(T\)) as \(v_{avg} \propto \sqrt{T}\). Thus, increasing temperature increases the average speed.
Pressure (\(P\)) and speed are related indirectly—if temperature is held constant, increasing pressure (by reducing volume) does not change the average speed. However, if both pressure and temperature increase, the temperature effect dominates, leading to higher particle speeds.
Therefore, the average speed of gas particles increases when both pressure and temperature are increased.
In which changes do the particles move further apart?

A) W and X B) W and Z C) X and Y D) Y and Z
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Particles move further apart when a substance changes from:
1. Solid to Liquid (Y) – Particles gain energy and break free from fixed positions, increasing separation.
2. Liquid to Gas (Z) – Particles spread out significantly, moving independently with large gaps.
In contrast, W (Gas to Liquid) and X (Liquid to Solid) involve particles coming closer. Thus, the correct answer is D (Y and Z).
Which row describes the arrangement and movement of particles in a liquid?
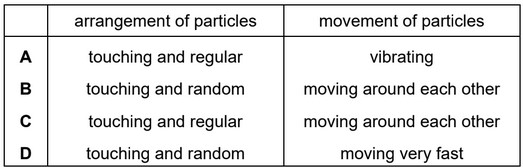
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In a liquid:
1. Arrangement: Particles are close but not in a fixed pattern (disordered, unlike solids).
2. Movement: Particles slide past each other, exhibiting fluidity but with some cohesion.
Row B correctly describes this behavior—particles are not rigidly arranged (unlike A and C) and are not widely spaced (unlike D).
Which row represents the particles of a gas colliding most frequently?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The frequency of gas particle collisions depends on their speed and density. In the given image, Row A shows:
- High particle density (more particles per unit volume).
- Fast-moving particles (indicated by longer motion trails).
Since collision frequency increases with both speed and particle concentration, Row A represents the highest collision rate. Temperature (which governs speed) and pressure (which affects density) are maximized in this case.
Sodium chloride is a liquid at 900 °C. How are the particles arranged and how do the particles move in sodium chloride at 900 °C?
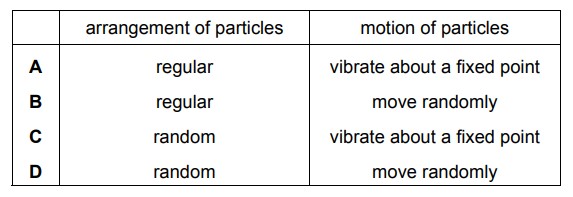
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
At 900 °C, sodium chloride is in the liquid state:
1. Arrangement: The particles (Na+ and Cl− ions) are closely packed but disordered, with no fixed lattice structure.
2. Movement: The ions move randomly, sliding past each other due to sufficient kinetic energy, allowing fluidity.
3. Forces: Ionic bonds are weakened but not broken, maintaining cohesion while permitting mobility.
Thus, the correct description is D (Particles are close together and arranged randomly; particles move around each other).
An attempt was made to compress a gas and a solid using the apparatus shown.
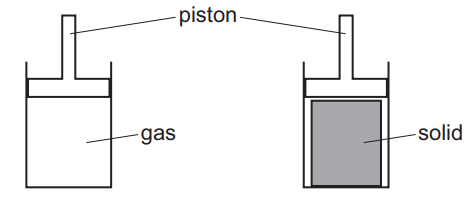
Which substance would be compressed and what is the reason for this?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Gas Compression: Gases can be compressed because their particles are far apart with empty space between them. Applying force (via the piston) reduces this space.
2. Solid Incompressibility: Solids cannot be compressed because their particles are already tightly packed in a fixed arrangement.
Thus, only the gas (option B) meets both criteria—compressibility due to large interparticle spaces.
