Pre AP Chemistry -1.2A Thermal Energy and Heat Capacity- MCQ Exam Style Questions -New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.2A Thermal Energy and Heat Capacity- MCQ Exam Style Questions – New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.2A Thermal Energy and Heat Capacity- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Pre AP Chemistry – per latest Pre AP Chemistry Syllabus.
The temperature of the water at the bottom of a waterfall is greater than the temperature of the water at the top. The energy in the gravitational potential store of the water at the top is transferred to the thermal store at the bottom.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 \( \mathrm{J/(kg\,^\circ C)} \).
What is the temperature difference for a waterfall of height 21 m?
A 0.0050 \( ^\circ C \)
B 0.049 \( ^\circ C \)
C 20 \( ^\circ C \)
D 200 \( ^\circ C \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Loss in gravitational potential energy = gain in thermal energy.
\( mgh = mc\Delta T \)
Cancel \( m \):
\( gh = c\Delta T \)
\( \Delta T = \frac{gh}{c} \)
Substitute values:
\( \Delta T = \frac{(9.8)(21)}{4200} \)
\( \Delta T = \frac{205.8}{4200} \approx 0.049 ^\circ C \)
Ans: B
A thermometer has a low thermal capacity. Why is this an advantage?
A The thermometer does not absorb much thermal energy to raise its own temperature.
B The thermometer does not conduct much thermal energy to the surroundings.
C The thermometer does not melt when it gets hot.
D The thermometer does not radiate much thermal energy to the surroundings.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Thermal capacity is the amount of thermal energy required to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C.
If a thermometer has low thermal capacity:
- It needs only a small amount of energy to change its temperature.
- It does not significantly cool the object being measured.
- It responds quickly to temperature changes.
Therefore, it does not absorb much thermal energy to raise its own temperature.
Ans: A
Extremely small pollen grains in water are viewed through a microscope. The grains are seen to move continually and randomly.
What is the reason for this random movement?
A The grains are moved by randomly moving water molecules.
B The grains are moved by random convection currents in the water.
C The grains are moved by random rays of light reflecting off them.
D The grains are moved by the random motion of their own atoms.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
This is an example of Brownian motion.
Water molecules are constantly moving randomly and collide unevenly with the pollen grains.
These random collisions cause the grains to move in a continuous zig-zag motion.
Ans: A
The diagram shows the apparatus needed for an experiment to determine the specific heat capacity of the material from which an object is made.
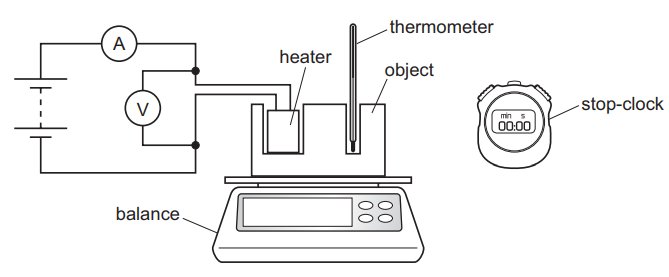
Which piece of apparatus could be omitted if the purpose of the experiment is to determine the thermal capacity of the object?
A ammeter
B balance
C stop-clock
D thermometer
▶️ Answer/Explanation
To determine specific heat capacity, we use:
\( E = mc\Delta T \)
This requires measuring:
- mass (balance)
- temperature change (thermometer)
- electrical energy supplied (ammeter + time)
However, to determine thermal capacity:
\( E = C\Delta T \)
Mass is not required.
Therefore, the balance can be omitted.
Ans: B
One end of a rod of copper is placed in hot water. Thermal energy travels along the rod to make the other end warmer.
What is the behaviour of the copper at an atomic level that accounts for most of the transfer of thermal energy from one end to the other?
A Atoms at the hot end gain kinetic energy and move towards the other end.
B Atoms at the hot end expand, colliding with other atoms and transferring energy.
C Free electrons at the hot end gain energy and move towards the other end, colliding with atoms along the rod.
D Free electrons at the hot end gain energy from the hot water and move directly to the other end.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Copper is a metal and contains free electrons.
When the hot end is heated:
- Free electrons gain kinetic energy.
- They move through the metal.
- They collide with ions/atoms in the lattice and transfer energy.
This is the main mechanism of thermal conduction in metals.
Ans: C
The diagrams show four blocks of steel. The blocks are all drawn to the same scale.
The same quantity of thermal energy is given to each block.
Which block shows the greatest rise in temperature?
A 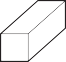
B 
C 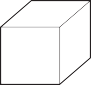
D 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
For thermal energy:
\( Q = mc\Delta T \)
Since all blocks are made of steel, \( c \) is the same.
Given the same energy \( Q \):
\( \Delta T = \frac{Q}{mc} \)
This shows:
- Smaller mass → larger temperature rise
- Larger mass → smaller temperature rise
Block A has the smallest volume (and therefore smallest mass).
So it experiences the greatest rise in temperature.
Ans: A
The specific heat capacities of aluminium, iron, ethanol and water are given.
| Substance | Specific heat capacity (J/kg°C) |
|---|---|
| Aluminium | 900 |
| Iron | 450 |
| Ethanol | 2400 |
| Water | 4200 |
1 kg of each metal is put into 5 kg of each liquid.
The starting temperature of each metal is 60°C. The starting temperature of each liquid is 10°C.
Which example has the highest final temperature?
A aluminium + ethanol
B iron + ethanol
C aluminium + water
D iron + water
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Heat lost by metal = Heat gained by liquid
\( m_m c_m (60 – T) = m_l c_l (T – 10) \)
The final temperature will be higher when:
- The metal has large heat capacity (large \( c_m \))
- The liquid has small heat capacity (small \( c_l \))
Compare options:
- Aluminium (900) gives more heat than iron (450).
- Ethanol (2400) absorbs less heat than water (4200).
So the combination giving the highest final temperature is:
Aluminium + Ethanol
Ans: A
A block of copper has a mass of 2.0 kg.
The block of copper absorbs 12 000 J of thermal energy.
The specific heat capacity of copper is 385 J / (kg °C).
What is the temperature rise of the copper?
A 15.6 °C
B 31.2 °C
C 46.8 °C
D 62.4 °C
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Use the formula:
\( Q = mc\Delta T \)
Rearrange for temperature rise:
\( \Delta T = \frac{Q}{mc} \)
Substitute values:
\( \Delta T = \frac{12000}{(2.0)(385)} \)
\( \Delta T = \frac{12000}{770} \)
\( \Delta T = 15.6 ^\circ C \)
Ans: A
Which quantity gives the thermal capacity of a solid object?
A. the energy lost by radiation from the object in 1.0 s
B. the energy needed to melt the object
C. the energy needed to raise the temperature of the object by 1.0 °C
D. the total amount of thermal energy in the object
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Thermal capacity is defined as the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of an object by 1°C (or 1 K).
Mathematically:
\( C = \frac{Q}{\Delta T} \)
So when \( \Delta T = 1^\circ C \), the energy required equals the thermal capacity.
Ans: C
A metal has a specific heat capacity of 360 J / (kg °C). An object made of this metal has a mass of 2.0 kg.
What is the thermal capacity (heat capacity) of the object?
A 180 J / °C
B 180 J / kg
C 720 J / °C
D 720 J / kg
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Thermal capacity is given by:
\( C = mc \)
Substitute values:
\( C = (2.0)(360) \)
\( C = 720 \text{ J/°C} \)
Ans: C
A night storage heater contains a large block of material that is heated electrically during the night. During the day the block cools down, releasing thermal energy into the room.

Which thermal capacity and which night-time temperature increase will cause the most energy to be stored by the block?
| thermal capacity of block | night-time temperature increase | |
| A | large | large |
| B | large | small |
| C | small | large |
| D | small | small |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The energy stored is given by:
\( E = C \Delta T \)
To maximise stored energy:
- Thermal capacity \( C \) must be large.
- Temperature increase \( \Delta T \) must be large.
Therefore, the correct combination is:
large thermal capacity and large temperature increase
Ans: A
The diagram shows the equipment used in an experiment on the heating of aluminium.
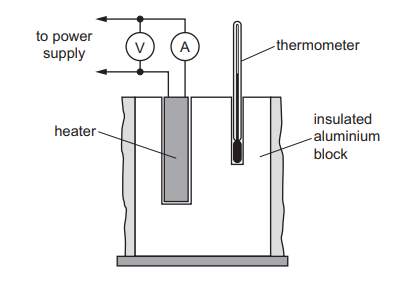
The table gives the results for the experiment.
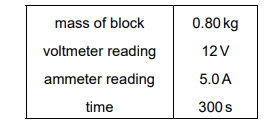
The specific heat capacity of aluminium is \(900 \text{ J/(kg °C)}\).
What is the maximum possible temperature rise in the block?
A \(9^\circ C\)
B \(20^\circ C\)
C \(25^\circ C\)
D \(225^\circ C\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Given:
\( m = 0.80 \text{ kg} \)
\( V = 12 \text{ V} \)
\( I = 5.0 \text{ A} \)
\( t = 300 \text{ s} \)
\( c = 900 \text{ J/(kg °C)} \)
Step 1: Electrical energy supplied
\( E = VIt \)
\( E = 12 \times 5.0 \times 300 \)
\( E = 18000 \text{ J} \)
Step 2: Use heat equation
\( E = mc\Delta T \)
\( \Delta T = \dfrac{E}{mc} \)
\( \Delta T = \dfrac{18000}{0.80 \times 900} \)
\( \Delta T = \dfrac{18000}{720} \)
\( \Delta T = 25^\circ C \)
Ans: C
