Pre AP Chemistry -1.2C Particle Attractions and Phase Changes- MCQ Exam Style Questions -New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.2C Particle Attractions and Phase Changes- MCQ Exam Style Questions – New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.2C Particle Attractions and Phase Changes- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Pre AP Chemistry – per latest Pre AP Chemistry Syllabus.
A compound, X, has a melting point of 71°C and a boiling point of 375°C.
Which statement about X is correct?
A) It is a liquid at 52°C and a gas at 175°C.
B) It is a liquid at 69°C and a gas at 380°C.
C) It is a liquid at 75°C and a gas at 350°C.
D) It is a liquid at 80°C and a gas at 400°C.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To determine the state of a substance at different temperatures, we compare the given temperature to its melting and boiling points:
- Below melting point: solid
- Between melting and boiling points: liquid
- Above boiling point: gas
Analyzing each option:
A) 52°C is below melting point (should be solid), 175°C is below boiling point (should be liquid). Incorrect.
B) 69°C is below melting point (should be solid), 380°C is just above boiling point (correct for gas). Partially correct but not fully.
C) 75°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), but 350°C is below boiling point (should be liquid, not gas). Incorrect.
D) 80°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), 400°C is above boiling point (correct for gas). Fully correct.
Four processes are listed.
- Brownian motion
- condensation
- diffusion
- evaporation
Which processes involve a change of state?
A 1 and 2 B 1 and 3 C 2 and 4 D 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Processes involving a change of state are those where matter transitions between solid, liquid, and gas phases. Here:
- Condensation (2): Gas → Liquid
- Evaporation (4): Liquid → Gas
Brownian motion (1) and diffusion (3) describe particle movement within a state (e.g., gas or liquid) and do not involve phase changes. Thus, the correct pair is 2 and 4 (Option C).
The diagram shows how the arrangement of particles changes when a substance changes state.
Which change of state is shown?
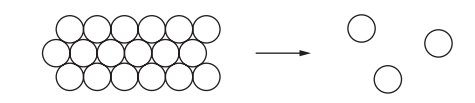
A) boiling
B) condensation
C) evaporation
D) sublimation
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The diagram shows a direct transition from a solid (where particles are tightly packed in a fixed arrangement) to a gas (where particles are widely spaced and move freely). This bypasses the liquid phase entirely.
Sublimation is the process where a solid turns directly into a gas without becoming a liquid first. Examples include dry ice (solid CO₂) or iodine crystals. Since the change matches this description, the correct answer is D (sublimation).
The diagram shows some changes of state.
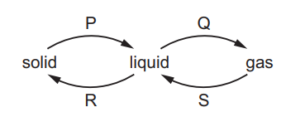
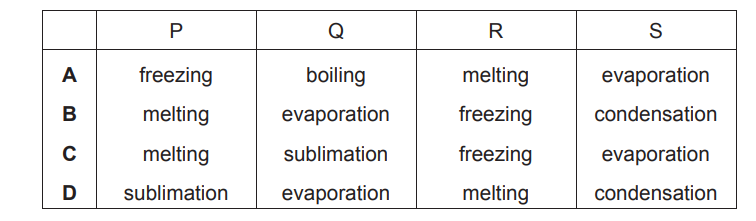
Which words describe the changes of state, P, Q, R and S?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
P (Melting): Solid → Liquid. Heat is absorbed, breaking intermolecular forces.
Q (Evaporation): Liquid → Gas. High-energy particles escape the liquid phase.
R (Freezing): Liquid → Solid. Heat is released, forming an ordered structure.
S (Condensation): Gas → Liquid. Particles lose energy and coalesce.
Thus, the correct sequence is B (P-Melting, Q-Evaporation, R-Freezing, S-Condensation).
The changes that occur when a substance changes state are shown below.
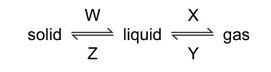
Which process, W, X, Y or Z, is occurring in the following four situations?
- Butter melts on a warm day.
- Water condenses on a cold surface.
- The volume of liquid ethanol in an open beaker reduces.
- Ice forms inside a freezer.
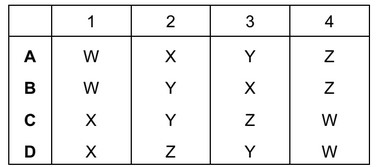
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Butter melting (W): Solid to liquid transition (melting).
2. Water condensing (Y): Gas to liquid transition (condensation).
3. Ethanol evaporating (X): Liquid to gas transition (evaporation).
4. Ice forming (Z): Liquid to solid transition (freezing).
The correct sequence is W, Y, X, Z, matching option B.
What are the processes W, X, Y and Z in the following diagram?
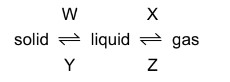
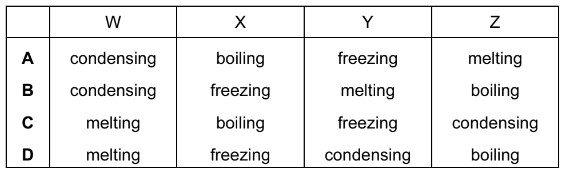
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The diagram shows phase changes between solid, liquid, and gas states:
- W (Solid → Liquid): Melting – Particles gain energy to overcome fixed positions.
- X (Liquid → Gas): Boiling/Evaporation – High-energy particles escape as gas.
- Y (Liquid → Solid): Freezing – Particles lose energy and form ordered structure.
- Z (Gas → Liquid): Condensation – Gas particles cool and coalesce into liquid.
Thus, the correct sequence is W: melting, X: boiling, Y: freezing, Z: condensing, matching option C.
Which row explains how increasing the surface area of a fixed volume of liquid water and blowing air over the surface speeds up evaporation?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Increasing surface area:
- More water molecules are exposed at the surface.
- More molecules can escape per second.
Blowing air over the surface:
- Removes water vapour above the surface.
- Prevents saturation of air near the surface.
- Maintains a high evaporation rate.
The correct row is the one that includes:
- More molecules escaping due to larger surface area.
- Removal of vapour by moving air.
Ans: D
A quantity of water is boiled to form the same mass of steam.
Which row shows how the volume and density of the water change?
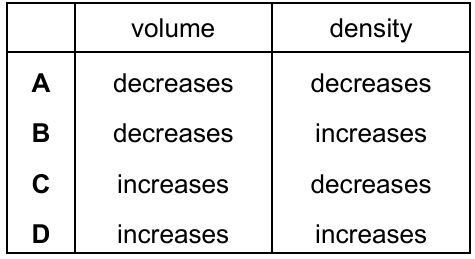
▶️ Answer/Explanation
When water boils to form steam:
- The mass remains the same.
- The volume increases greatly (gas particles are much further apart).
Density is given by:
\( \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} \)
Since mass stays the same but volume increases:
- Density decreases.
Therefore:
Volume increases, density decreases.
Ans: C
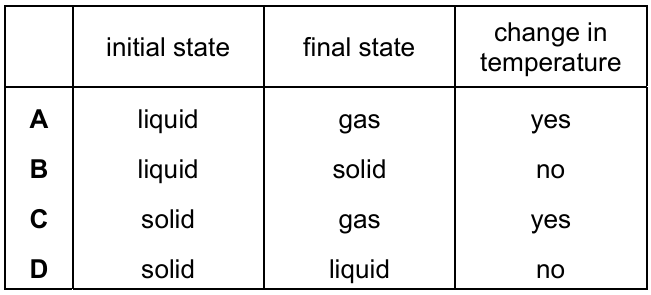
Which row describes the process of melting?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
During melting:
- The substance changes from solid to liquid.
- Energy is absorbed (latent heat of fusion).
- The temperature remains constant at the melting point.
- Particles change from vibrating in fixed positions to moving past each other.
The correct row describing these features is:
Ans: D
Which name is given to the change of state when steam at 100° C changes to water at 100° C?
A) boiling
B) condensation
C) evaporation
D) melting
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Steam at 100°C changing to water at 100°C is a change from gas to liquid.
This process is called condensation.
The temperature remains constant during this change of state.
Ans: B
A textbook gives the description of a thermal process as:
‘More-energetic molecules escape from the surface of a liquid which causes the liquid to cool.’
Which process is being described?
A boiling
B Brownian motion
C condensation
D evaporation
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In evaporation:
- The most energetic molecules escape from the surface.
- The remaining molecules have lower average kinetic energy.
- This causes the liquid to cool.
Therefore, the process described is evaporation.
Ans: D
Some terms describing changes of state are listed.
1 boiling
2 solidification
3 condensation
4 evaporation
Which two terms identify the same change of state?
A 1 and 3
B 1 and 4
C 2 and 3
D 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Boiling and evaporation are both changes from liquid to gas.
Solidification is liquid to solid.
Condensation is gas to liquid.
Therefore, the two terms describing the same change of state are:
1 and 4
Ans: B
The diagram shows four labelled changes of state between solid, liquid and gas.
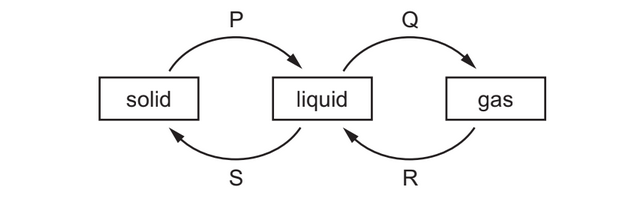
Which changes need an energy input?
A P and Q
B Q and R
C R and S
D S and P
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Changes that require energy input (endothermic processes) are:
- Melting (solid → liquid)
- Boiling / evaporation (liquid → gas)
These processes require energy to overcome intermolecular forces.
From the diagram, these correspond to P and Q.
Ans: A
The melting point of a substance is –78 °C and its boiling point is 23 °C.
Which row gives the correct state of matter of the substance at the given temperatures?
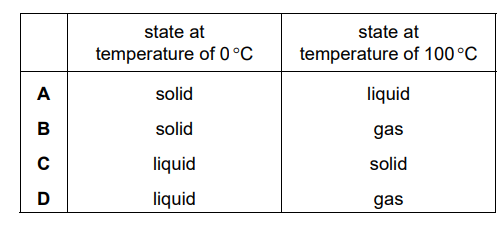
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Rules:
- Below melting point → solid
- Between melting and boiling point → liquid
- Above boiling point → gas
Given:
- Melting point = –78 °C
- Boiling point = 23 °C
Therefore:
- Temperature below –78 °C → solid
- Between –78 °C and 23 °C → liquid
- Above 23 °C → gas
The row that matches these states is:
Ans: D
The table lists the melting points and the boiling points of four different substances.
Which substance is a liquid at \(0^\circ \mathrm{C}\) ?
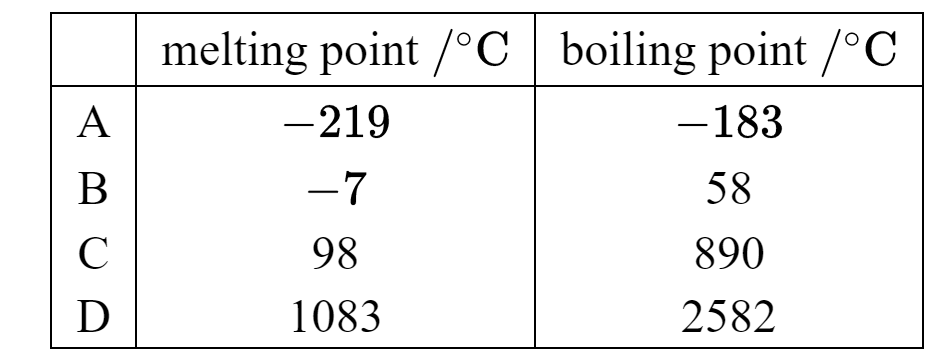
Answer/Explanation
A substance is a liquid when:
- The temperature is above its melting point, and
- The temperature is below its boiling point.
At \(0^\circ \mathrm{C}\), the substance that satisfies:
\[ \text{melting point} < 0^\circ \mathrm{C} < \text{boiling point} \]
is Substance B.
Ans: B
Rods of the same shape and size are inserted through corks into a tank of hot water. Each rod is covered with a layer of solid wax that has a low melting point. After a period of time, some wax melts.
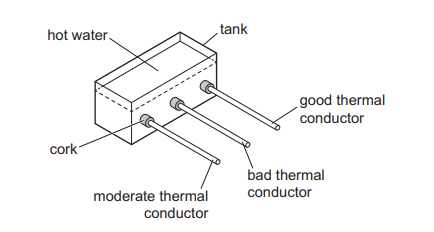
On which rod will the wax melt first?
- all at the same time
- good thermal conductor
- bad thermal conductor
- moderate thermal conductor
Answer/Explanation
Thermal energy is transferred along the rod by conduction.
A good thermal conductor transfers heat more quickly from the hot water to the wax.
Therefore, the wax on the good conductor reaches its melting point first.
Ans: B
It is a warm and humid day. A glass contains an iced drink. Water starts to form on the outside of the glass.

What is the name of the effect by which the water forms?
- condensation
- conduction
- convection
- evaporation
Answer/Explanation
The cold glass cools the air around it.
Water vapour in the warm air loses thermal energy and changes from gas to liquid on the surface of the glass.
This change of state is called condensation.
Ans: A
A substance loses thermal energy (heat) to the surroundings at a steady rate.
The graph shows how the temperature of the substance changes with time.
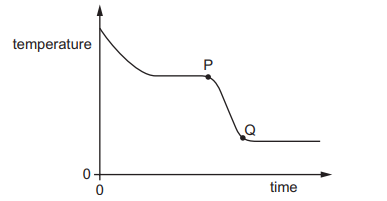
What could the portion PQ of the graph represent?
- gas condensing
- gas cooling
- liquid cooling
- liquid solidifying
Answer/Explanation
During PQ, the temperature is decreasing.
This means the substance is cooling and not undergoing a change of state (since temperature would remain constant during a phase change).
Therefore, PQ represents a substance cooling in a single state.
The correct option is:
liquid cooling
Ans: C
The liquid level in a thermometer rises when the thermometer is placed in hot water. What causes this?
A The liquid contracts.
B The liquid evaporates.
C The liquid expands.
D The liquid freezes.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
When the thermometer is placed in hot water, the temperature of the liquid inside increases.
As temperature increases, the liquid expands.
This expansion causes the liquid level to rise in the narrow tube.
Ans: C
An ice cube is placed in a beaker and is heated. The ice melts to form water, which evaporates at first and then boils. The steam condenses on a cold window in the room.
Which process involves a transfer of energy from the ice, water or steam to the surroundings?
A melting
B evaporating
C boiling
D condensing
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Melting, evaporation and boiling all require an input of energy (they absorb energy from the surroundings).
Condensation is the reverse process of evaporation. During condensation, steam changes into liquid water and releases energy to the surroundings.
Therefore, the process involving transfer of energy to the surroundings is:
Ans: D (condensing)
A man puts some ice into a glass of water on a warm day. After a short time, he notices that the ice disappears and that water droplets appear on the outside of the glass.
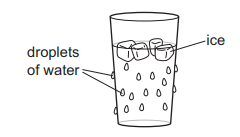
Which two changes of state are taking place?
A condensation and freezing
B condensation and melting
C boiling and melting
D freezing and evaporation
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The ice disappears because it changes from solid to liquid. This process is melting.
The water droplets on the outside of the glass form because water vapour in the warm air cools and changes from gas to liquid. This process is condensation.
Therefore, the two changes of state are:
condensation and melting
Ans: B
An ice cube is placed in a beaker and is heated. The ice melts to form water, which evaporates at first and then boils. The steam condenses on a cold window in the room.
Which process involves a transfer of energy from the ice, water or steam to the surroundings?
A melting
B evaporating
C boiling
D condensing
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Melting, evaporation and boiling require an input of energy (they absorb energy from the surroundings).
Condensation is the reverse of evaporation. When steam condenses into water, it releases thermal energy to the surroundings.
Therefore, the process involving energy transfer to the surroundings is:
Ans: D (condensing)
An ice cube is placed in a beaker and is heated. The ice melts to form water, which evaporates at first and then boils. The steam condenses on a cold window in the room.
Which process involves a transfer of energy from the ice, water or steam to the surroundings?
A melting
B evaporating
C boiling
D condensing
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Melting, evaporation and boiling all require an input of energy (they absorb energy from the surroundings).
Condensation is the reverse process of evaporation. When steam changes back into liquid water, it releases thermal energy to the surroundings.
Therefore, the process involving energy transfer to the surroundings is:
Ans: D (condensing)
Equal masses of two different liquids are put into identical beakers.
Liquid 1 is heated for 100 s and liquid 2 is heated for 200 s by heaters of the same power.
Each liquid has the same rise in temperature.
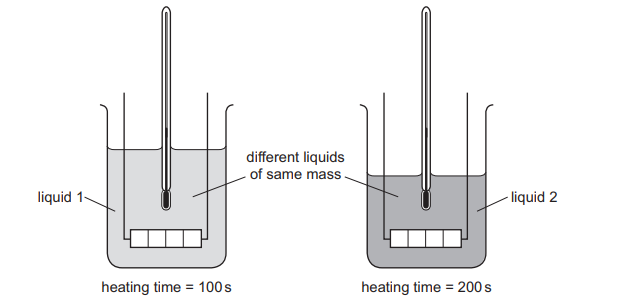
Which statement is correct?
A. Each beaker of liquid has the same thermal capacity.
B. Each beaker of liquid receives the same energy.
C. Liquid 1 receives more energy than liquid 2.
D. The thermal capacity of liquid 1 is less than the thermal capacity of liquid 2.
Answer/Explanation
Energy supplied by a heater:
\( E = P \times t \)
Since both heaters have the same power:
- Liquid 1 is heated for 100 s → receives \( P \times 100 \)
- Liquid 2 is heated for 200 s → receives \( P \times 200 \)
So liquid 2 receives twice as much energy as liquid 1.
Both liquids have the same temperature rise, so using
\( E = C \Delta T \)
For the same \( \Delta T \), the liquid that requires more energy has a larger thermal capacity.
Therefore, liquid 2 has a larger thermal capacity than liquid 1.
Ans: D
A solid is heated from room temperature.
The graph shows how its temperature changes with time as it is heated constantly.
At which time has it just become completely liquid?
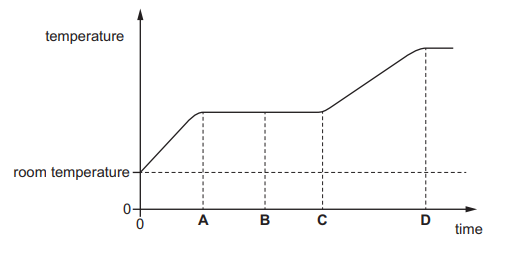
Answer/Explanation
When a solid is heated:
- Temperature increases while it is solid.
- Temperature stays constant during melting (change of state).
- After melting is complete, temperature rises again as a liquid.
The substance is completely liquid at the end of the flat (constant temperature) section of the graph.
This corresponds to time:
Ans: C
What are the correct terms for each change of state?
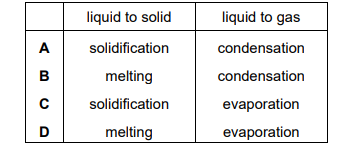
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Changes of state:
- Solid → Liquid = Melting
- Liquid → Gas = Evaporation / Boiling
- Gas → Liquid = Condensation
- Liquid → Solid = Freezing / Solidification
The row that correctly matches these processes is:
Ans: C
Which statement correctly describes a change of state?
A A gas condenses to form a liquid.
B A liquid melts to form a solid.
C A solid condenses to form a liquid.
D A solid boils to form a gas.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Correct changes of state:
- Gas → Liquid = Condensation
- Solid → Liquid = Melting
- Liquid → Solid = Freezing
- Liquid → Gas = Boiling / Evaporation
Only option A correctly describes a real change of state.
Ans: A
Gases can be compressed, but liquids cannot.
Which statement explains this difference?
A. Each molecule in a gas is more compressible than each molecule in a liquid.
B. Molecules in a gas are further apart than molecules in a liquid.
C. Molecules in a gas attract each other more strongly than molecules in a liquid.
D. Molecules in a gas move more slowly than molecules in a liquid.
Answer/Explanation
Gas molecules are much further apart than liquid molecules.
This means there is a lot of empty space between gas molecules, so they can be pushed closer together (compressed).
In liquids, molecules are already close together, so they cannot be compressed easily.
Ans: B
At –39 °C, liquid mercury solidifies without a change of temperature.
Which row shows whether the mercury absorbs or releases energy and what happens to the bonds between the mercury atoms?
| energy | bonds between atoms | |
| A | absorbed | stronger |
| B | absorbed | weaker |
| C | released | stronger |
| D | released | weaker |
Answer/Explanation
Solidification (freezing) occurs at constant temperature.
During freezing:
- The substance releases energy to the surroundings.
- Particles become more ordered.
- Bonds between atoms become stronger.
Ans: C
Two states of matter are described as follows.
State 1: The molecules are very far apart. They move about very quickly at random in straight lines until they hit something.
State 2: The molecules are quite closely packed together. They move about at random. They do not have fixed positions.
What is state 1 and what is state 2?
| state 1 | state 2 | |
| A | gas | liquid |
| B | gas | solid |
| C | liquid | gas |
| D | solid | liquid |
Answer/Explanation
State 1: Molecules are far apart and move rapidly in straight lines → this describes a gas.
State 2: Molecules are close together but can move around and do not have fixed positions → this describes a liquid.
Ans: A
Some ice is slowly heated and its temperature is measured. A graph is plotted of temperature against time.
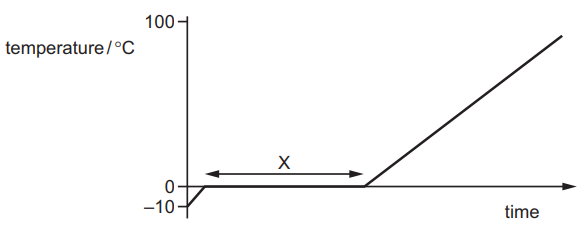
Which row describes what happens to the thermal energy and to the temperature in section X?
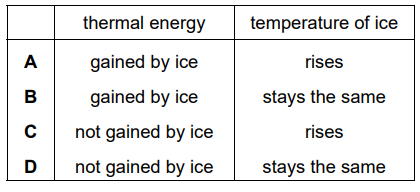
Answer/Explanation
In section X, the graph is flat (constant temperature).
This means the ice is melting.
During melting:
- Thermal energy increases (energy is absorbed).
- Temperature remains constant.
The row that matches this description is:
Ans: B
