Pre AP Chemistry -1.3A Gas Pressure and Particle Collisions- MCQ Exam Style Questions -New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.3A Gas Pressure and Particle Collisions- MCQ Exam Style Questions – New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -1.3A Gas Pressure and Particle Collisions- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Pre AP Chemistry – per latest Pre AP Chemistry Syllabus.
Which statement describes what happens as ice at 0 °C melts to become water?
A. Energy is absorbed and the temperature remains constant.
B. Energy is absorbed and the temperature rises.
C. Energy is released and the temperature remains constant.
D. Energy is released and the temperature rises.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Understand melting
Melting is a change of state from solid to liquid.
Step 2: Energy transfer
During melting, energy is absorbed to break intermolecular bonds.
Step 3: Temperature behaviour
While melting occurs at 0 °C, the temperature remains constant until all the ice has melted. The absorbed energy is used as latent heat, not to increase temperature.
Ans: A
Brownian motion of particles is observed. Which statements describe the movement of the particles?
1. The particles all travel along a curved path.
2. The particles move randomly.
3. The particles all travel in the same direction.
A. 1 and 3
B. 1 only
C. 2 and 3
D. 2 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Understand Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random movement of small particles suspended in a fluid, caused by collisions with fast-moving molecules of the fluid.
Step 2: Analyse each statement
- Statement 1: Not correct. The path is irregular and zig-zag, not a smooth curved path.
- Statement 2: Correct. The motion is random.
- Statement 3: Incorrect. The particles do not all move in the same direction.
Therefore, only statement 2 is correct.
Ans: D
A piece of solid metal melts to become a liquid. How do the particles of metal or their behaviour change?
A. They increase in size.
B. They move around each other.
C. They move much further apart.
D. They vibrate more about their fixed positions.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Particle model of a solid
In a solid, particles are closely packed and vibrate about fixed positions.
Step 2: Particle model of a liquid
In a liquid, particles are still close together but are free to move around each other.
Step 3: Analyse the options
- A: Incorrect – particle size does not change.
- B: Correct – particles can move around each other in a liquid.
- C: Incorrect – particles do not move much further apart (that happens during boiling).
- D: Incorrect – vibrating about fixed positions describes a solid.
Ans: B
Smoke particles, illuminated by a bright lamp, are seen through a microscope. They move about randomly.
What causes this motion?
A. Attraction between the smoke particles and the molecules of the air
B. Collisions between the smoke particles and the molecules of the air
C. Evaporation of the faster-moving smoke particles
D. Warming of the smoke particles by the lamp
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the phenomenon
The random movement of smoke particles is called Brownian motion.
Step 2: Cause of Brownian motion
Air molecules are constantly moving at high speeds. They collide unevenly with the smoke particles.
Step 3: Effect of collisions
These uneven collisions cause the smoke particles to move randomly.
Therefore, the motion is caused by collisions between smoke particles and air molecules.
Ans: B
What is a basic assumption of the kinetic theory, as applied to an ideal gas?
A. Collisions between gas molecules are elastic.
B. Each gas molecule occupies a finite volume.
C. Gases consist of particles that experience the force of gravity.
D. Gas molecules attract each other with weak intermolecular forces.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Recall assumptions of the kinetic theory for an ideal gas
- Gas particles are in constant random motion.
- Collisions between particles and with the walls are perfectly elastic.
- The volume of the particles themselves is negligible compared to the container volume.
- There are no intermolecular forces between particles (except during collisions).
Step 2: Analyse the options
- A: Correct – collisions are elastic (kinetic energy is conserved).
- B: Incorrect – ideal gas particles are assumed to have negligible volume.
- C: Incorrect – gravity is ignored in the basic model.
- D: Incorrect – ideal gas particles do not attract each other.
Ans: A
In an experiment, smoke particles are suspended in air and viewed through a microscope.
The smoke particles move about with short random movements. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Air particles have large masses compared to smoke particles and they move in one direction only.
B. Air particles have large masses compared to smoke particles and they move in random directions.
C. Air particles move at high speeds compared to smoke particles and they move in one direction only.
D. Air particles move at high speeds compared to smoke particles and they move in random directions.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the phenomenon
The random movement of smoke particles is called Brownian motion.
Step 2: Cause of motion
Air molecules are very small and move at high speeds. They collide randomly with the larger smoke particles.
Step 3: Analyse the options
- A and B are incorrect because air particles are much smaller and lighter than smoke particles.
- C is incorrect because air particles do not move in one direction only; they move randomly.
- D is correct because air particles move at high speeds and in random directions.
Ans: D
Which row describes the forces between the molecules and the motion of the molecules in a gas?
| Forces between molecules | Motion of molecules | |
|---|---|---|
| A | strong | move freely |
| B | strong | vibrate only |
| C | weak | move freely |
| D | weak | vibrate only |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Recall properties of gases
- Molecules are far apart.
- Intermolecular forces are very weak (negligible).
- Molecules move freely in random directions.
Step 2: Compare with options
The correct combination is:
Weak forces + Move freely
This corresponds to C.
Ans: C
A gas is heated in a sealed container.
The volume of the container does not change.
What happens to the molecules of the gas?
A. The average distance between molecules increases.
B. The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases.
C. The mass of each molecule increases.
D. The volume of each molecule increases.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Understand heating at constant volume
The container is sealed, so the volume and number of molecules remain constant.
Step 2: Effect of increasing temperature
Temperature is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of gas molecules.
When the gas is heated, molecules move faster.
Step 3: Analyse options
- A: Incorrect – volume is constant, so average spacing does not significantly change.
- B: Correct – kinetic energy increases when temperature increases.
- C: Incorrect – mass of molecules does not change.
- D: Incorrect – size of molecules does not change.
Ans: B
A stationary smoke particle is hit by a fast-moving nitrogen molecule.
Which row describes the motion of the smoke particle and of the nitrogen molecule after the collision?
| Smoke particle | Nitrogen molecule | |
|---|---|---|
| A | moves | rebounds |
| B | moves | stops |
| C | remains stationary | rebounds |
| D | remains stationary | stops |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Apply kinetic theory
Collisions between molecules are elastic, meaning momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
Step 2: After collision
- The nitrogen molecule does not stop; it rebounds after the collision.
- The smoke particle gains momentum and begins to move.
Therefore:
Smoke particle → moves
Nitrogen molecule → rebounds
Ans: A
Brownian motion is observed when looking at smoke particles in air using a microscope.
What causes the smoke particles to move at random?
A. Smoke particles are hit by air molecules.
B. Smoke particles are moved by convection currents in the air.
C. Smoke particles have different weights and fall at different speeds.
D. Smoke particles hit the walls of the container.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the phenomenon
Brownian motion is the random motion of tiny particles suspended in a fluid.
Step 2: Cause of motion
Air molecules move rapidly and randomly. They collide unevenly with the larger smoke particles.
Step 3: Effect of collisions
These continuous random collisions cause the smoke particles to move randomly.
Ans: A
The molecules of a substance become more closely packed and move more quickly.
What is happening to the substance?
A. A gas is being heated and compressed.
B. A gas is being heated and is expanding.
C. A liquid is boiling.
D. A liquid is evaporating at room temperature.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Interpret “move more quickly”
This means the temperature is increasing (kinetic energy increases).
Step 2: Interpret “more closely packed”
This means the substance is being compressed (volume decreases).
Step 3: Analyse the options
- A: Gas heated → molecules move faster. Gas compressed → molecules become closer together. ✔
- B: Expanding gas → molecules move further apart. ✘
- C and D: During boiling or evaporation, particles move further apart, not closer. ✘
Ans: A
Brownian motion is observed when using a microscope to look at smoke particles in air.
What causes the smoke particles to move at random?
A. Smoke particles are hit by air molecules.
B. Smoke particles are moved by convection currents in the air.
C. Smoke particles have different weights and fall at different speeds.
D. Smoke particles hit the walls of the container.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the phenomenon
Brownian motion is the random motion of tiny particles suspended in a fluid.
Step 2: Cause of motion
Air molecules move rapidly and randomly. They collide unevenly with the larger smoke particles.
Step 3: Result
These continuous random collisions cause the smoke particles to move in a zig-zag random path.
Ans: A
The diagram shows a sealed jar containing a gas.
Which statement about the gas in the jar is correct?
A. The gas molecules collide with the inside of the jar more often as the temperature increases.
B. The gas molecules move more slowly as the temperature increases.
C. The pressure of the gas decreases as the temperature increases.
D. The pressure of the gas is higher at the top of the jar than at the bottom of the jar.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Effect of temperature on gas molecules
When temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of gas molecules increases.
Step 2: What this means
- Molecules move faster.
- They collide with the container walls more frequently and with greater force.
- In a sealed container (constant volume), pressure increases.
Step 3: Analyse options
- A: Correct – collisions with the walls occur more often.
- B: Incorrect – molecules move faster, not slower.
- C: Incorrect – pressure increases, not decreases.
- D: Incorrect – gas pressure is the same throughout the jar.
Ans: A
A student places his thumb firmly on the outlet of a bicycle pump, to stop the air coming out.
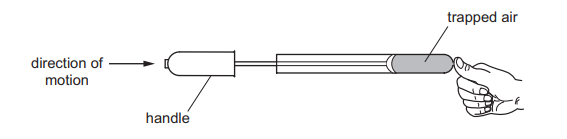
What happens to the pressure and what happens to the volume of the trapped air as the pump handle is pushed in?
| Pressure | Volume | |
|---|---|---|
| A | decreases | decreases |
| B | decreases | remains the same |
| C | increases | decreases |
| D | increases | remains the same |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the situation
The air is trapped because the outlet is blocked.
Step 2: Effect of pushing the handle
Pushing the handle reduces the volume of the trapped air.
Step 3: Apply Boyle’s Law
At constant temperature:
\( P \propto \frac{1}{V} \)
If volume decreases, pressure increases.
Conclusion:
Pressure increases and volume decreases.
Ans: C
A gas is stored in a sealed container of constant volume. The temperature of the gas increases.
This causes the pressure of the gas to increase.
What happens to the gas molecules during this pressure increase?
A. The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases.
B. The average separation of the molecules decreases.
C. The average separation of the molecules increases.
D. The volume of each molecule increases.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Volume is constant
Since the container is sealed and rigid, the volume does not change.
Step 2: Effect of increasing temperature
Temperature is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of gas molecules.
When temperature increases, molecules move faster.
Step 3: Why pressure increases
Faster molecules collide with the walls more frequently and with greater force, increasing pressure.
Analyse options:
- A: Correct – kinetic energy increases.
- B and C: Incorrect – average separation stays the same because volume is constant.
- D: Incorrect – size of molecules does not change.
Ans: A
Extremely small pollen grains in water are viewed through a microscope. The grains are seen to move continually and randomly.
What is the reason for this random movement?
A. The grains are moved by randomly moving water molecules.
B. The grains are moved by random convection currents in the water.
C. The grains are moved by random rays of light reflecting off them.
D. The grains are moved by the random motion of their own atoms.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify the phenomenon
The continual random movement of tiny particles suspended in a fluid is called Brownian motion.
Step 2: Cause of Brownian motion
Water molecules are constantly moving randomly and collide unevenly with the pollen grains.
Step 3: Result
These random collisions cause the pollen grains to move in a random zig-zag motion.
Ans: A
When a microscope is used to look at smoke particles in air, Brownian motion is observed.
What causes the smoke particles to move at random?
A. Smoke particles are hit by air molecules.
B. Smoke particles are moved by convection currents in the air.
C. Smoke particles have different weights and fall at different speeds.
D. Smoke particles hit the walls of the container.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Identify Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random movement of tiny particles suspended in a fluid.
Step 2: Cause of the motion
Air molecules move rapidly and randomly. They collide unevenly with the larger smoke particles.
Step 3: Result
These constant random collisions cause the smoke particles to move in a random zig-zag pattern.
Ans: A
