Pre AP Chemistry -3.2A Chemical Transformations and Conservation of Atoms- MCQ Exam Style Questions -New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -3.2A Chemical Transformations and Conservation of Atoms- MCQ Exam Style Questions – New Syllabus 2025-2026
Pre AP Chemistry -3.2A Chemical Transformations and Conservation of Atoms- MCQ Exam Style Questions – Pre AP Chemistry – per latest Pre AP Chemistry Syllabus.
Which diagram represents a chemical change?
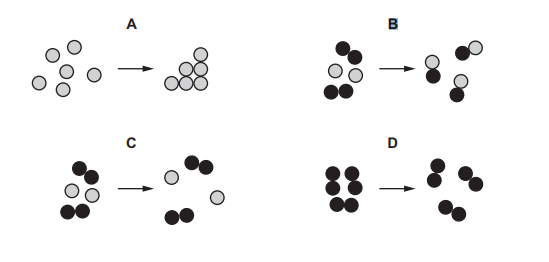
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Chemical changes involve formation of new substances with different properties.
2. In diagram B, the original substances (red and blue particles) combine to form a new compound (purple particles), indicating a chemical reaction.
3. Other diagrams (A, C, D) show physical changes like state changes or mixing without new substance formation.
Thus, only B represents a chemical change.
A sequence of changes involving sulfur is shown.
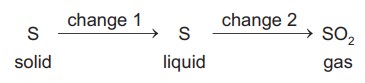
Which row describes the changes?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The sequence involves two distinct changes:
- Change 1 (Ssolid → Sliquid): A physical change (melting) where only the state changes from solid to liquid, with no alteration in chemical composition.
- Change 2 (Sliquid → SO2): A chemical change where sulfur reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide, resulting in new substances with different properties.
Therefore, the correct description is:
- Change 1: Physical
- Change 2: Chemical
This matches Option C in the table.
Which diagram represents a chemical change?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Chemical changes involve the formation of new substances with different properties. Analyzing the diagrams:
- A-C: Show physical changes (melting, dissolving, mixing) where the original substances remain chemically unchanged.
- D: Shows a clear chemical reaction where new substances are formed (evidenced by color change and gas production).
Key indicators in Diagram D:
- Bubbles indicate gas formation (new substance)
- Color change suggests a chemical reaction occurred
- The final product is chemically different from the reactants
Therefore, D is the correct answer as it represents a true chemical change.
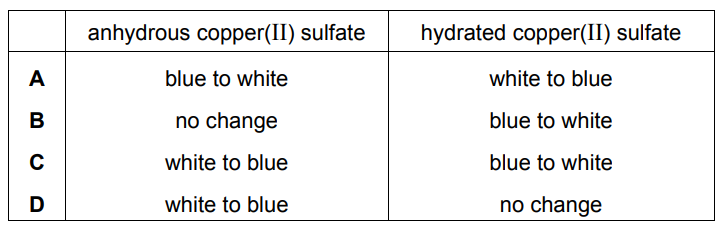
Separate samples of anhydrous copper(II) sulfate and hydrated copper(II) sulfate are heated.
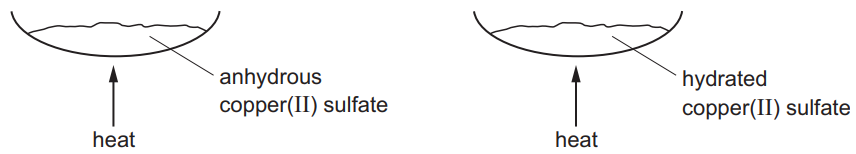
Which row shows the correct colour changes?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Key Observations:
- Anhydrous CuSO4 (white powder):
- Remains white when heated (no water to lose)
- No chemical change occurs
- Hydrated CuSO4·5H2O (blue crystals):
- Loses water of crystallization when heated
- Turns from blue to white/grayish-white (anhydrous form)
- This is a reversible physical change
The correct combination is:
- Anhydrous: no change (white → white)
- Hydrated: blue → white
This matches Option B in the table.
Silicon(IV) oxide reacts with chlorine and carbon to form liquid silicon(IV) chloride, SiCl4, and carbon dioxide gas.
If the reaction is carried out at r.t.p., which symbol equation represents this reaction?
A) SiO2(l) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
B) SiO2(l) + 2Cl2(g) + C(g) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
C) SiO2(s) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(g) + CO2(g)
D) SiO2(s) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The correct equation must account for the physical states: SiO2 is solid (s), Cl2 is gas (g), carbon is solid (s), SiCl4 is liquid (l) at r.t.p., and CO2 is gas (g). Therefore, option D is correct. Option A incorrectly shows SiO2 as liquid, B shows carbon as gas (unlikely at r.t.p.), and C shows SiCl4 as gas when it should be liquid.
The incomplete equation for photosynthesis is shown.
![]()
Compound P is a product of the reaction. Which row describes the values of w, x and y and gives the empirical formula of compound P?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The balanced equation for photosynthesis is:
\[ 6CO_2 + 6H_2O \rightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 \]
Here, \( w = 6 \), \( x = 6 \), and \( y = 6 \). The empirical formula of glucose (\( C_6H_{12}O_6 \)) simplifies to \( CH_2O \). Thus, the correct row is:
w = 6, x = 6, y = 6, Empirical formula of P = CH2O (Option A).
The equation for the reaction between barium chloride and dilute sulfuric acid is shown.
BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Which row shows the state symbols for this equation?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
1. Barium chloride (\(\text{BaCl}_2\)) is typically in aqueous solution (\(\text{aq}\)) when reacting with dilute sulfuric acid.
2. Sulfuric acid (\(\text{H}_2\text{SO}_4\)) is also in aqueous form (\(\text{aq}\)) as it is dilute.
3. Barium sulfate (\(\text{BaSO}_4\)) forms a white precipitate, so it is solid (\(\text{s}\)).
4. Hydrochloric acid (\(\text{HCl}\)) remains in aqueous solution (\(\text{aq}\)) as it is soluble.
Thus, the correct state symbols are \(\text{BaCl}_2(\text{aq}) + \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4(\text{aq}) \rightarrow \text{BaSO}_4(\text{s}) + 2\text{HCl}(\text{aq})\), which matches option A.
Sodium nitride contains the nitride ion, \(N^{3-}\). Sodium nitride is unstable and decomposes into its elements. What is the equation for the decomposition of sodium nitride?
A) \(2NaN_{3}\rightarrow 2Na+3N_{2}\)
B) \(2Na_{3}N\rightarrow 6Na+N_{2}\)
C) \(2NaN_{3}\rightarrow Na_{2}+3N_{2}\)
D) \(2Na_{3}N\rightarrow 6Na+2N\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Sodium nitride has the formula \(Na_3N\) (since sodium is \(+1\) and nitride is \(-3\)). When it decomposes, it forms sodium (\(Na\)) and nitrogen gas (\(N_2\)). The balanced equation is:
\(2Na_3N \rightarrow 6Na + N_2\).
Option A and C involve \(NaN_3\) (sodium azide), which is incorrect. Option D is unbalanced and forms nitrogen atoms instead of \(N_2\). Thus, the correct answer is B.
Aluminium reacts with fluorine.
\[ xAl(s) + yF_2(g) \rightarrow zAlF_3(s) \]
Which values of x, y and z balance the equation?
| x | y | z | |
| A B C D | 1 2 3 4 | 2 3 2 3 | 1 2 3 4 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To balance the equation:
1. Aluminium (Al): Ensure the number of Al atoms is equal on both sides. If \( z = 2 \), then \( x = 2 \).
2. Fluorine (F): Since \( F_2 \) is diatomic, \( y = 3 \) ensures \( 6F \) atoms, matching \( 2AlF_3 \) (which also requires \( 6F \)).
Thus, the balanced equation is:
\[ 2Al(s) + 3F_2(g) \rightarrow 2AlF_3(s) \]
This corresponds to Option B (\( x = 2 \), \( y = 3 \), \( z = 2 \)).
