Question
Which of the following experiments could be used to determine the inertial mass of a block?
A Place the block on a rough horizontal surface. Lift one end of the surface up and measure the angle the surface makes with the horizontal at the moment the block begins to slide.
B Drop the block from different heights and measure the time of fall from each height.
C Place the block on a rough horizontal surface. Give the block an initial velocity and then let it come to rest. Measure the initial velocity and the distance the block moves in coming to rest.
D Use a spring scale to exert a force on the block. Measure the acceleration of the block and the applied force.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The inertial mass can be determined using Newton’s second law: \(a=\frac{F}{m}\).
Question
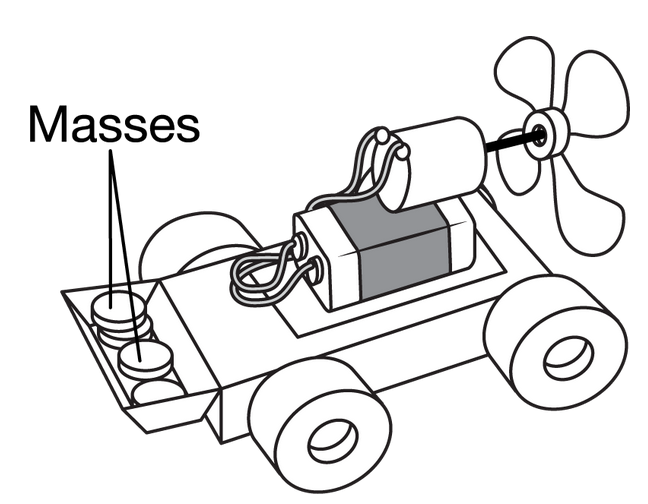
A toy car has a battery-powered fan attached to it such that the fan creates a constant force that is exerted on the car so that it is propelled in the opposite direction in which the fan blows air. The car has a carriage that allows a student to attach objects of different masses, as shown above. The fan has only one speed setting. All frictional forces are considered to be negligible. Which of the following procedures could be used to determine how the mass of the fan-car-object system affects the acceleration of the system?
A. Measure the mass of the system using a balance, activate the fan, measure the distance traveled by the system at a known time by using a stopwatch, and repeat the experiment for several trials with different objects added to the carriage.
B. Measure the mass of the system using a balance, activate the fan, use a meterstick and stopwatch to measure the initial and final speeds of the system, and repeat the experiment for several trials with different objects added to the carriage.
C. Measure the mass of the system using a balance, connect a spring scale to the back of the car, measure the amount of force required to hold the system at rest, and repeat the experiment for several trials with different objects added to the carriage.
D. Measure the mass of the system using a balance, activate the fan, use a stopwatch to record the time it takes for the system to travel before the battery of the fan no longer works, and repeat the experiment for several trials with different objects added to the carriage.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The mass of the fan-car-object system can be found by using a mass balance. The fan will propel the car forward with a constant force in all trials of the experiment. The meterstick can be used to measure the displacement of the toy car after a stopwatch is used to record a time in which the system travels. The following equation can be used to determine the acceleration of the system: \(x=x_0+v_{xo}t+\frac{1}{2}a_xt^2\) (with the initial speed of the system equal to zero). Newton’s second law of motion equation could be applied to determine the relationship between the three quantities within the equation: \(ΣF_x=ma_x\).
Question
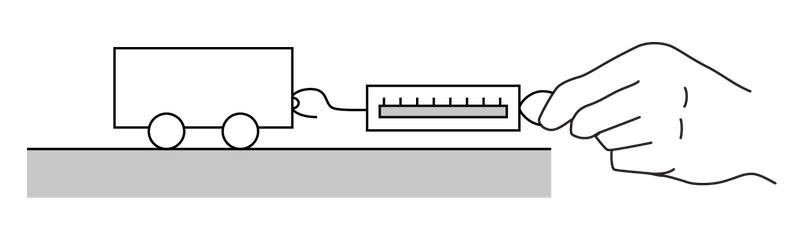
A student sets up an experiment to determine the inertial mass of a cart. The student has access to the following measurement equipment: a spring scale, a meterstick, and a stopwatch. The student uses the spring scale to pull the cart starting from rest along a horizontal surface such that the reading on the spring scale is always constant. All frictional forces are negligible. In addition to the spring-scale reading, which two of the following quantities could the student measure with the available equipment and then use to determine the inertial mass of the cart? Select two answers.
A The total distance traveled by the cart after it has been in motion
B The average speed of the cart while in motion
C The acceleration of the cart while in motion
D The time during which the cart is in motion
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The meterstick can be used to measure the total distance traveled by the cart. The distance and time can be used to determine the acceleration of the cart by using the equation \(x=x_0+v_{0x}t+\frac{1}{2}a_xt^2\) , where the initial velocity \(v_{0x}\) is zero. Once the acceleration of the cart has been determined, it can be used with the spring-scale reading and the equation for Newton’s second law of motion a⃗ \(=\frac{Σ\vec{F}}{ m}\) to determine the inertial mass of the cart.
The stopwatch can be used to measure the time during which the cart is in motion. This time and distance traveled by the cart can be used to determine the acceleration of the cart by using the equation \(x=x_0+v_{0x}t+\frac{1}{2}a_xt^2\), where the initial velocity v0x is zero. Once the acceleration of the cart has been determined, it can be used with the spring-scale reading and the equation for Newton’s second law of motion a⃗ \(=\frac{Σ\vec{F}}{ m}\) to determine the inertial mass of the cart.
