Question
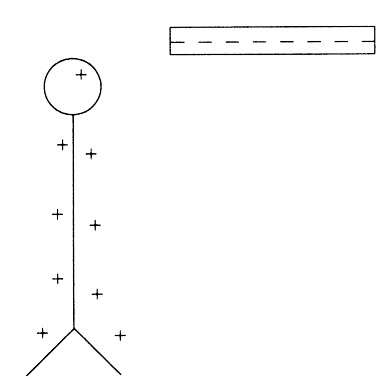
The diagram above shows a leaf electroscope that has been charged positively by a negatively charged rod. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) The electroscope was charged by conduction.
(B) The electroscope was charged by contact.
(C) If the rod is brought closer, protons will move to the top of the electroscope.
(D) If the rod is brought closer, electrons will be repelled from the top of the electroscope.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(D)
The electroscope was charged by induction since it is oppositely charged. Bringing the negative charges closer will drive electrons down toward the leaves as protons are not free to move.
Question
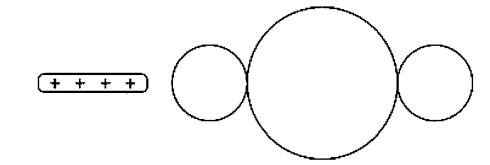
A positively charged rod is brought near to but not touching three metal spheres that are in contact with each other, as shown in the figure. Which is the best representation of the charge arrangement inside the three spheres?
(A) 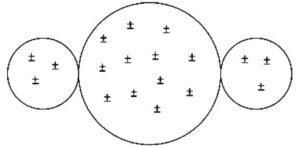
(B) 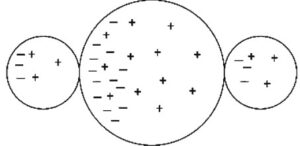
(C) 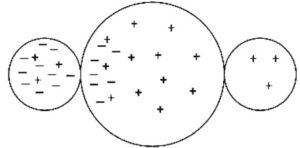
(D) 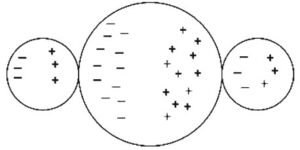
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Only electrons can move in the metal spheres. Protons (positive charges) are stuck in the nuclei of atoms and cannot move. In the presence of the positively charged rod, the three-sphere system will polarize with excess electrons moving toward the positively charged rod. Answer choice A shows no charge polarization. Choice B shows each individual sphere polarized, which cannot happen since the conductors are in contact and act as one system. Choice D shows protons moving, which also cannot happen.
Question
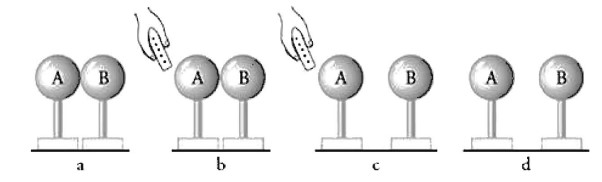
Two neutral metal spheres on insulating stands are placed so they touch, as shown in figure a. A positive rod is brought close to sphere A, as shown in figure b. Sphere B is moved to the right, as shown in figure c. The positive rod is then removed, as shown in figure d. Which of the following correctly describes the situation after the rod is removed? (Select two answers.)
(A) The net charge of the system that includes both spheres remains neutral.
(B) The net charge of sphere B is negative.
(C) Spheres A and B attract each other.
(D) The electric field between the spheres points to the right.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A and C
Sphere A is negative, and sphere Bis positive. The rod polarizes the system that consists of the two spheres, pulling excess electrons to the left and leaving the right side with an excess positive charge of equal magnitude.
Question
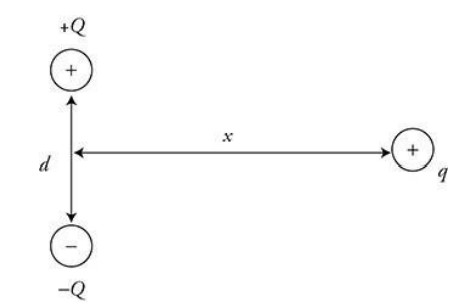
Two spheres with charges +Q and -Q of equal magnitude are placed a vertical distance d apart on the y-axis as shown in the figure. A third charge +q is brought from a distance x, where x >> d, horizontally toward the midpoint between +Q and-Q. The net force on +q as it is moved to the left along the x-axis:
(A) increases and remains in the same direction
(B) increases and changes direction
(C) remains the same magnitude and in the same direction
(D) remains in the same direction but decreases to zero
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A—In its original location x, the two electrostatic forces on +q add as shown in the figure.
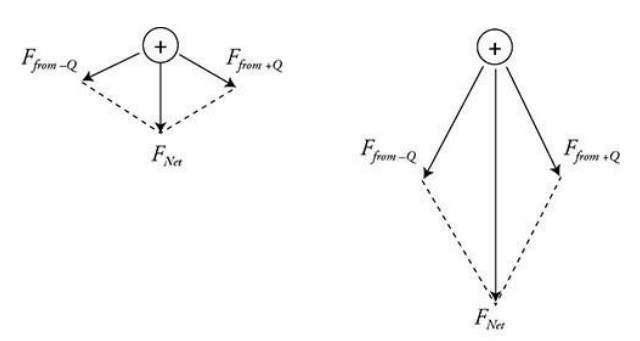
As the charge +q is moved toward +Q and —Q, the electrostatic forces increase in strength, and their direction also shifts as shown in the figure. Thus, the net force increases in strength, but continues to point directly downward due to the symmetry of the charge arrangement.
Question
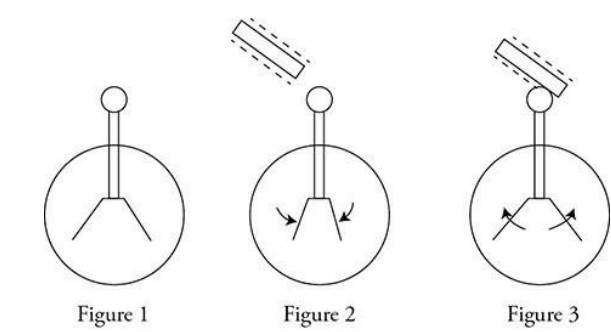
An electroscope is shown with its movable metal leaves in a sequence of events. Originally the electroscope is in a position with the leaves at an outward angle as shown in Figure 1. A negatively charged rod is brought close to the electroscope and the leaves swing downward as shown in Figure 2. Finally, the rod touches the electroscope and the leaves spring outward as shown in Figure 3. Which of the following statements correctly describe this behavior? (Select two answers.)
(A) In Figure 1, the electroscope has a net positive charge.
(B) In Figure 2, the leaves move closer together because the rod discharges the electroscope.
(C) In Figure 2, negative charges are pushed toward the leaves at the bottom of the electroscope.
(D) In Figure 3, positive charges from the electroscope migrate onto the rod, leaving the electroscope negatively charged.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A and C—The electroscope is initially charged in Figure 1 because the leaves repel each other. When the negatively charged rod is brought close, but not in contact with the electroscope, it repels electrons toward the bottom of the electroscope. Since this brings the leaves closer together, the original charge must have been positive. Note that the rod cannot “discharge” the electroscope without touching it. Positive charge carriers do not move through solid objects, because they are buried in the nucleus.
