Question
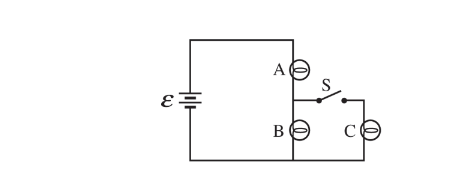
A circuit contains three identical light bulbs and a switch S connected to an ideal battery of\( emf \varepsilon \), as shown in the figure above. The switch is initially open and bulbs A and B have equal brightness, while C is not lit. What happens to the brightness of bulbs A and B when the switch S is closed and bulb C lights up?
Bulb A Bulb B
(A) Remains the same Becomes dimmer
(B) Becomes dimmer Becomes dimmer
(C) Becomes brighter Becomes dimmer
(D) Becomes brighter Not lit
(E) Remains the same Not lit
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Questions
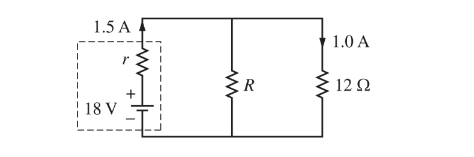
Two resistors of resistances R and \(12 \Omega\) are connected to a battery of emf 18 V, as shown in the figure above. The battery has an internal resistance of r. The current in the battery is 1.5 A, and the current in the \(12 \Omega\) resistor is 1.0 A.
What is the resistance R ?
(A) 7.2 \(\Omega\)
(B) 12 \(\Omega\)
(C) 18\(\Omega\)
(D) 24 \(\Omega\)
(E) 45 \(\Omega\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D The parallel branches must all have the same voltage, and the current flowing through R must be 0.5A. Therefore,
Eqn1 : 18V -(1.5A)r ( 1.0A )(12Ω)
Eqn2 : 18V-( 1.5A)r ( 0.5A)R
Eqn1- Eqn2: 0 = (1.0A)(122) – (0.5A)R
\( R=\frac{(1.0A)(12\Omega )}{(0.5A)}\)
\( R=24\Omega\)
Question
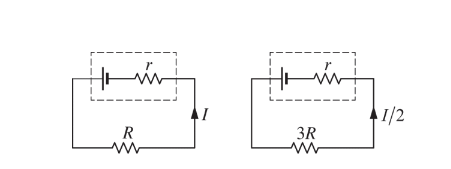
When a battery is connected to an external resistance R, as shown above on the left, there is a current I in the circuit. When the external resistance is changed to 3R, the current changes to I /2 , as shown above on the right. What is the internal resistance r of the battery?
(A) R /4
(B) R /2
(C) R
(D) 2R
(E) 4R
Answer/Explanation
Question
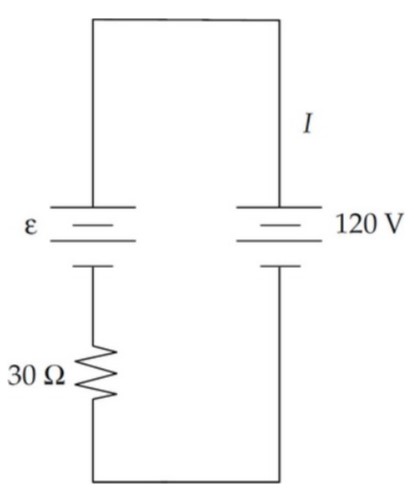
A battery with emf ε and internal resistance of 30 Ω is being recharged by connecting it to an outlet with a potential difference of 120 Vas shown above. While it is being recharged, 3 A flows through the battery. Determine the emf of the battery.
(A) 210V
(B) 150 V
(C) 90V
(D) 30V
(E) 9V
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The potential difference around the loop must be zero according to Kirchhoff sloop rule. The current in the circuit is going counterclockwise if the battery is being charged by the 120 V outlet. A counterclockwise loop starting right below the 120 V outlet will produce the following, 120 – ε – (3)(30) = o. Therefore, ε = 30 V.
