Question
A student is testing the kinematic equations for uniformly accelerated motion by measuring the time it takes for light-weight plastic balls to fall to the floor from a height of 3 m in the lab. The student predicts the time to fall using g as\( 9.80 m/s^2 \)but finds the measured time to be 35% greater. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the large percent error?
(A) The acceleration due to gravity is 70% greater than\( 9.80 m/s^2\) at this location.
(B) The acceleration due to gravity is 70% less than\( 9.80 m/s^2\) at this location.
(C) Air resistance increases the downward acceleration.
(D) The acceleration of the plastic balls is not uniform.
(E) The plastic balls are not truly spherical.
Answer/Explanation
Question
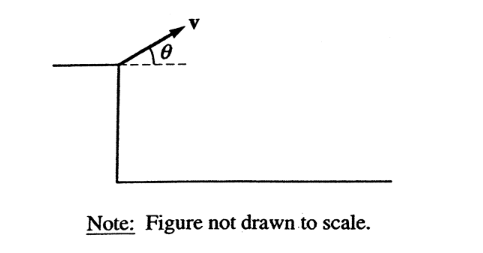
An object is thrown with velocity v from the edge of a cliff above level ground. Neglect air resistance. In order for the object to travel a maximum horizontal distance from the cliff before hitting the ground, the throw should be at an angle with respect to the horizontal of
(A) greater than 60° above the horizontal
(B) greater than 45° but less than 60° above the horizontal
(C) greater than zero but less than 45° above the horizontal
D) zero
Answer/Explanation
Question
An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on Earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 6 s of its fall?
(A) 30 m
(B) 60 m
(C) 120 m
(D) 180 m
(E) 360 m
Answer/Explanation
Question
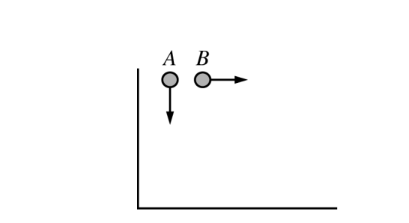
Two stones, represented in the figure above, are thrown from the same height with the same initial speed. Stone A is thrown vertically downward and stone B is thrown horizontally. If the stones are thrown at the same time and air resistance is negligible, which of the following is true?
(A) The two stones will reach the ground at the same time with the same speed.
(B) The two stones will reach the ground at the same time but with different speeds.
(C) Stone A will reach the ground first, but stone B will have the greater speed just before hitting the ground.
(D) Stone A will reach the ground first, but the two stones will have the same speed just before they hit the ground.
(E) Stone A will reach the ground first, and will have the greater speed just before hitting the ground.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Both stone A and stone B initially have the same potential energy \(U_i \)and kinetic energy . \(K_i \)Both stones therefore have the same\( K _f \)at ground level, when 0.\( U_f \)= Substituting into conservation of energy to solve for the speeds of the stones when
\( U_i+K_i=U_f+K_f\)
they reach the ground yields \(mgh+\frac{1}{2}mv^2_0=0+\frac{1}{2}mv^2_{f}\);thus , \(v_f=\sqrt{v^2_{0}+2gh}\)
Question
A rock is dropped off a cliff and falls the first half of the distance to the ground in \(t_1\) seconds. If it falls the second half of the distance in \(t_2\) seconds, what is the value of \(t_2 /t_1\)? (Ignore air resistance.)
(A) \(1/(2\sqrt{2})\)
(B) \(1/\sqrt{2}\)
(C) 1/32
(D) \(1-(1/\sqrt{2})\)
(E) \(\sqrt{2}-1\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: E
Let y denote the total distance that the rock falls and let T
denote the total time of the fall. Then \(\frac{1}{2} y = \frac{1}{2} gt_1^2\) and \(y=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(gT^2\), so
