Question
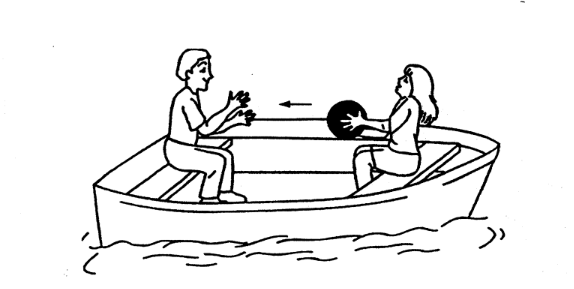
As shown above, two students sit at opposite ends of a boat that is initially at rest. The student in the front throws a heavy ball to the student in the back. What is the motion of the boat at the time immedi- ately after the ball is thrown and, later, after the ball is caught? (Assume that air and water friction are negligible.) Immediately
After the Throw After the Catch
(A) Boat moves forward forward Boat moves
(B) Boat moves forward Boat moves backward
(C) Boat moves forward Boat does not move
(D) Boat moves backward Boat does not move
(E) Boat moves backward Boat moves forward
Answer/Explanation
Question

In order to model the motion of an extinct ape, scientists measure its hand and arm bones. From shoulder to wrist, the arm bones are 0.60 m long and their mass is 4.0 kg. From wrist to the tip of
the fingers, the hand bones are 0.10 m long and their mass is 1.0 kg. In the model above, each bone is assumed to have a uniform density.
When the arm and hand hang straight down, the distance from the shoulder to the center of mass of the arm-hand system is most nearly
(A) 0.25 m
(B) 0.35 m
(C) 0.37 m
(D) 0.50 m
(E) 0.93 m
Answer/Explanation
Question
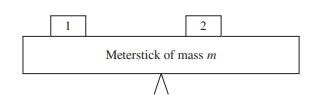
A meterstick of nonnegligible mass m is pivoted at its center, as shown. Two blocks, block 1 and block 2, are placed on top of the meterstick. When the meterstick is released from the rest at the position shown, it begins to rotate clockwise. Which of the following statements about the masses of the two blocks is correct?
(A) It cannot be determined which block has greater mass, because the lever arms associated with the torques provided by each block are different.
(B) The blocks are of equal mass, because the magnitude of the angular acceleration of each block is the same.
(C) Block 1 has greater mass, because the lever arm associated with the torque it provides is larger than that of block 2.
(D) Block 2 has greater mass, because more torque is provided by block 2 with a smaller lever arm.
(E) The blocks are of equal mass, because the meterstick’s mass is not negligible.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
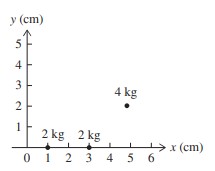
Three objects, of mass 2 kg, 2 kg, and 4 kg, are arranged as shown in the diagram. Which of the following is closest to the y-coordinate of the three objects’ center of mass?
(A) 2.0 cm
(B) 3.5 cm
(C) 1.5 cm
(D) 0.5 cm
(E) 1.0 cm
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
E
Question
A projectile is launched on level ground in a parabolic path so that its range would normally be 500 m. When the projectile is at the peak of its flight, the projectile breaks into two pieces of equal mass. One of these pieces falls straight down, with no further horizontal motion. How far away from the launch point does the other piece land?
(A) 250 m
(B) 375 m
(C) 500 m
(D) 750 m
(E) 1000 m
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
