Question
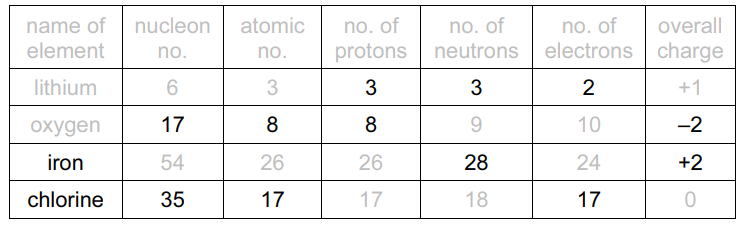
(a) Complete the table to show the composition and identity of some atoms and ions
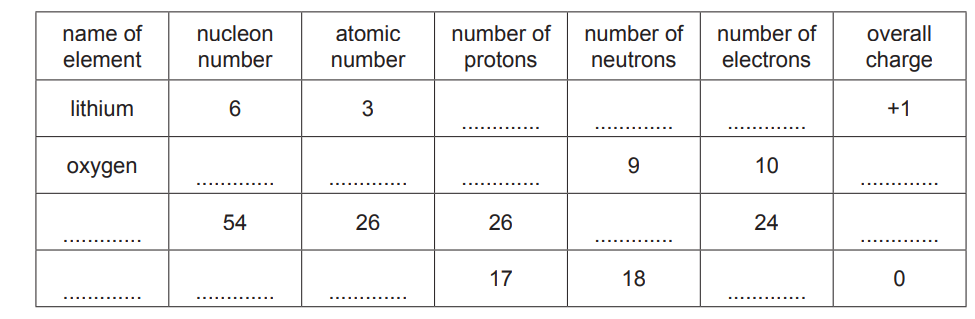
(b) Beams of protons, neutrons and electrons behave differently in an electric field due to their differing properties.
The diagram shows the path of a beam of electrons in an electric field.
Add and label lines to represent the paths of beams of protons and neutrons in the same field.
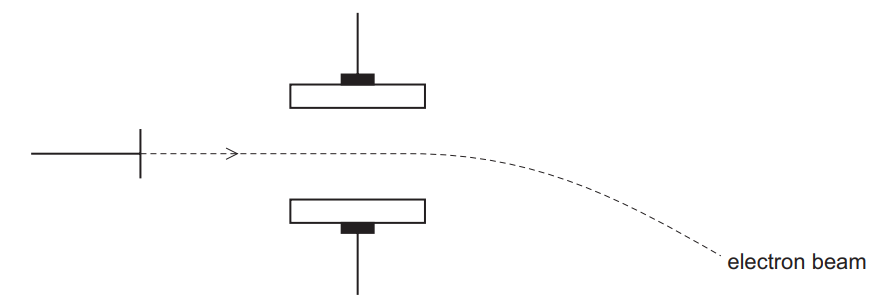
(c) The fifth to eighth ionisation energies of three elements in the third period of the Periodic Table are given. The symbols used for reference are not the actual symbols of the elements.
(i) State and explain the group number of element Y.
group number ………………………….
explanation ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[1]
(ii) State and explain the general trend in first ionisation energies across the third period………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(iii) Explain why the first ionisation energy of element Y is less than that of element X………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(iv) Complete the electronic configuration of element Z.
$1s^{2}$ ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(d) A sample of strontium exists as a mixture of four isotopes. Information about three of these isotopes is given in the table.
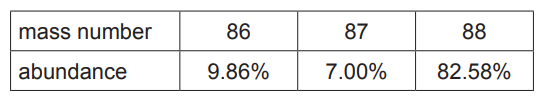
abundance 9.86% 7.00% 82.58%
(i) Calculate the abundance of the fourth isotope
abundance = ……………………….. % [1]
(ii) The relative atomic mass of this sample of strontium is 87.71.
Calculate the mass number of the fourth isotope.
mass number = ……………………….. [2] [Total: 16]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a)
(b) line straight on labelled ‘neutrons’
line (curving) up labelled ‘protons’
proton line clearly shows less (overall) deflection than electron curve
(c) (i) Group 16/6/VI
AND
Big (owtte) increase/big difference/ big gap/ big jump/ jump in increase/ jump in difference after 6th IE
(ii) increases (across period) due to increasing attraction (of nucleus for electrons)
due to increasing nuclear charge/ atomic / proton number AND
constant/similar shielding/ same (outer/ number of) shell/ energy level
(iii) electron (pair) repulsion
(Y has a) pair of electrons in a (3)p orbital/ a (3)p orbital is full ORA
(iv) $\quad\left(1 s^2\right) 2 s^2 2 p^6 3 s^2 3 p^5$
(d) (i) 0.56(%)
(ii)
$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{(A \times 0.56)+(86 \times 9.86)+(87 \times 7.00)+(88 \times 82.58)}{100}=87.71 \\
& A=84
\end{aligned}
$
