Question
(a) Define the term electron affinity.
(b) Write an equation for the process corresponding to the second ionisation energy of calcium.
Include state symbols.
Some data relating to calcium and oxygen are listed. Select relevant data from this list for your answers to parts (c), (d) and (e).
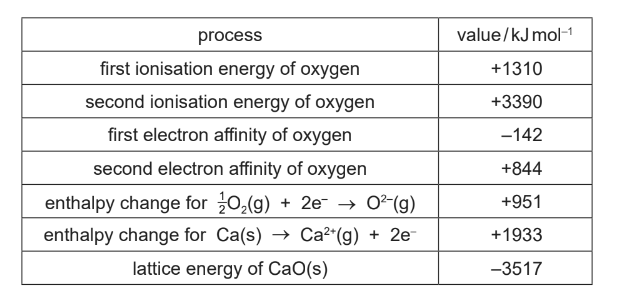
Show all your working.
(d) (i) Suggest why the first electron affinity of oxygen is negative.
(ii) Suggest why the second electron affinity of oxygen is positive.
(e) Calculate the enthalpy of formation of calcium oxide, CaO(s).
(f) The lattice energy of lithium fluoride, LiF(s), is –1022kJmol-1.
Identify the factor that causes the lattice energy of calcium oxide to be more exothermic than
that of lithium fluoride. Explain why this factor causes the difference in lattice energies.
Answer/Explanation
Answer (a) • enthalpy/energy change
• one mole of electrons gained
• by one mole of atoms
• gaseous (atoms)
(b) Ca+(g) → Ca2+(g) + e–
(c) M1: selecting correct data 951, 844, 142 only
M2: evaluation to give 249 (ΔHatom)
OR 2(951) = BE – 2(142) + 2(844)
M3: evaluation to 498 (2 × 249) ecf M2
951 =ΔHatom –142 + 844
ΔHatom = 249
BE = 498 (kJ mol–1)
(d)(i) attraction between nucleus / protons / nuclear charge
and electron
(d)(ii) repulsion between 1– ion / electrons of O–
and electron
(e) M1: selecting correct data 951, 1933, 3517 only (ignore signs)
M2: evaluation to give –633 (Δ Hf) ecf
ΔHf = 951 + 1933 – 3517 = –633 (kJ mol–1)
(f) ionic charge / charge density (of the ions)
greater (attractive) force between the ions
