Which solid has a simple molecular lattice?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
A simple molecular lattice consists of molecules held together by weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces). Sulfur (S8) forms such a lattice, as it exists as discrete S8 molecules. Calcium fluoride (ionic), nickel (metallic), and silicon(IV) oxide (giant covalent) do not have simple molecular structures, making option D correct.
The element tin exists in two forms, grey tin and white tin. Some properties of grey tin and white tin are shown.

Which structural change might take place when grey tin changes to white tin?
A. giant covalent to giant ionic
B. giant covalent to giant metallic
C. giant ionic to giant covalent
D. giant ionic to giant metallic
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Grey tin has a diamond-like giant covalent structure (similar to carbon), while white tin has a giant metallic structure. The transition from grey tin to white tin involves breaking covalent bonds and forming a metallic lattice, making option B correct.
Which oxide is insoluble in aqueous sodium hydroxide?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
MgO (Magnesium oxide) is a basic oxide that does not react with NaOH (a strong base). In contrast, \(Al_2O_3\) (amphoteric) dissolves in NaOH, \(P_4O_{10}\) (acidic) forms phosphates, and \(SO_2\) (acidic) forms sulfites. Thus, MgO is the only insoluble oxide among the options.
V and W are two compounds. Each one contains a different Group 2 element. A sample of each solid is added to water, shaken, and the pH of the resulting solution is measured.
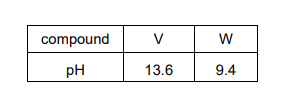
Which row could identify V and W? 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Group 2 oxides (e.g., MgO, CaO) react with water to form hydroxides, increasing pH (strongly alkaline). The solubility of hydroxides increases down the group, so Ba(OH)₂ (from BaO) gives a higher pH than Mg(OH)₂ (from MgO). Thus, V = MgO (pH 10) and W = BaO (pH 13), matching option C.
