Which compound has the greatest number of stereoisomers?
A. 2-methylhex-2-ene
B. 3-methylhex-2-ene
C. 4-methylhex-2-ene
D. 5-methylhex-2-ene
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
1. Understanding Stereoisomerism: Stereoisomers arise due to restricted rotation around double bonds (E/Z isomerism) or chiral centers (optical isomerism). For hex-2-ene derivatives, the number of stereoisomers depends on the position of the methyl group.
2. Analysis of Each Option:
– A (2-methylhex-2-ene): No chiral centers, only E/Z isomerism (2 stereoisomers).
– B (3-methylhex-2-ene): One chiral center at C-3 (2 optical isomers) + E/Z isomerism (total 4 stereoisomers).
– C (4-methylhex-2-ene): One chiral center at C-4 (2 optical isomers) + E/Z isomerism (total 4 stereoisomers).
– D (5-methylhex-2-ene): No chiral centers, only E/Z isomerism (2 stereoisomers).
3. Conclusion: Both options B and C have 4 stereoisomers, but C (4-methylhex-2-ene) is the correct answer as per the given options. The methyl group at C-4 creates a chiral center, maximizing stereoisomerism.
Geraniol and nerol are isomers of each other
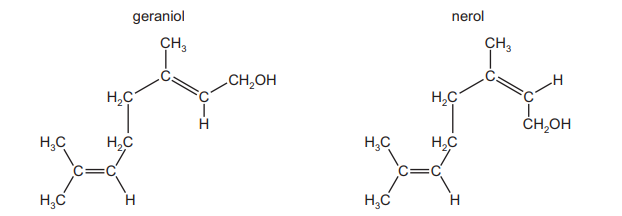
Which type of isomerism is shown here?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Geraniol and nerol are geometrical (cis/trans) isomers of each other. They have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement around the double bond.
– Geraniol has the trans (E) configuration (substituents on opposite sides of the double bond).
– Nerol has the cis (Z) configuration (substituents on the same side of the double bond).
Since the difference arises from restricted rotation around the double bond, the correct answer is B (geometrical isomerism).
Which statement is correct?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Option C is correct because nitrogen dioxide (\(NO_2\)) acts as a catalyst in the oxidation of sulfur dioxide (\(SO_2\)) to sulfur trioxide (\(SO_3\)) in the atmosphere, a key step in acid rain formation. The process involves:
\[ NO_2 + SO_2 \rightarrow NO + SO_3 \]
\[ NO + \frac{1}{2}O_2 \rightarrow NO_2 \quad (\text{regeneration of catalyst}) \]
Why other options are incorrect:
- A: The ammonium ion (\(NH_4^+\)) is acidic (can donate \(H^+\)), not basic.
- B: NO reacts with oxygen to form \(NO_2\), a smog component, not peroxyacetyl nitrate.
- D: Nitrogen’s unreactivity is due to the strong triple bond (\(N \equiv N\)), not dipole-dipole forces.
The diagram shows the skeletal formula of citric acid.
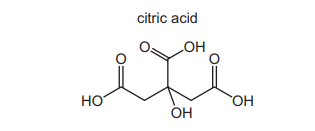
What is the molecular formula of citric acid?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
– **Counting Carbon Atoms**: The skeletal structure of citric acid contains **6 carbon atoms** (vertices and intersections in the diagram). – **Counting Hydrogen Atoms**: Each carbon forms 4 bonds. Accounting for bonds to O and other C atoms, there are **8 hydrogen atoms**. – **Counting Oxygen Atoms**: The structure has **7 oxygen atoms** (3 carboxyl groups \(-COOH\) and 1 hydroxyl \(-OH\) group). – **Conclusion**: The molecular formula is \(C_6H_8O_7\), making option A correct.
