Question
Fumaric acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid.
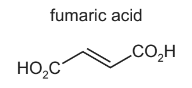
(a) Identify the products of the reaction between fumaric acid and an excess of hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII).
(b) Fumaric acid can form addition and condensation polymers.
(i) Draw the repeat unit of the addition polymer poly(fumaric acid).
(ii) Draw the repeat unit of the polyester formed when fumaric acid reacts with ethane-1,2-diol,
(CH2OH)2.
The ester bond should be shown fully displayed.
(iii) Explain why polyesters normally biodegrade more readily than polyalkenes.
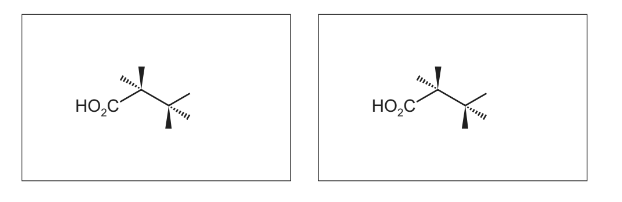
(c) Fumaric acid reacts with cold, dilute, acidified manganate(VII) to form compound P.
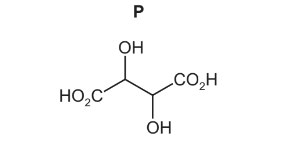
Only three stereoisomers of P exist. One of the stereoisomers is shown.
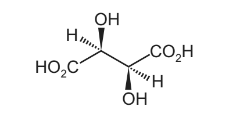
Complete the three-dimensional diagrams in the boxes to show the other two stereoisomers of P.
(d) The enzyme fumarase catalyses the reaction of fumarate ions, C4H2O42-, with water to form malate ions, C4H4O52-.
\(C_{4}H_{2}O_{4}^{2-} + H_{2}O \rightleftharpoons C_{4}H_{4}O_{5}^{2-}\)
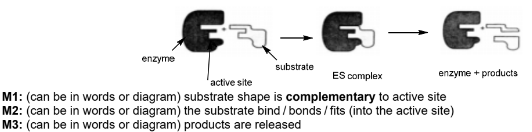
Describe, with the aid of a suitably labelled diagram, how an enzyme such as fumarase can catalyse a reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) CO2 and H2O / in words
(b)(i) 
(b)(ii) 
(b)(iii) C—C bonds are non-polar / polyalkenes cannot be hydrolysed
OR polyesters / they can be broken down by hydrolysis
(c) 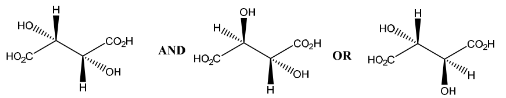
(d)