Ethene reacts with steam in the presence of sulfuric acid.
\(C_2H_4 + H_2O \to CH_3CH_2OH\)
Which type of reaction is this?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Reaction Analysis: The reaction involves ethene (\( C_2H_4 \)) combining with water (\( H_2O \)) to form ethanol (\( CH_3CH_2OH \)).
2. Type of Reaction: This is an addition reaction because the double bond in ethene breaks, and water adds across the bond without eliminating any byproducts.
3. Elimination of Other Options: – A (acid-base): No proton transfer occurs. – C (hydrolysis): Typically involves breaking bonds using water, not forming new ones. – D (substitution): No atom/group is replaced; instead, water is added.
Thus, the correct answer is B (addition).
The diagram shows the structural formula of a hydrocarbon molecule Q.
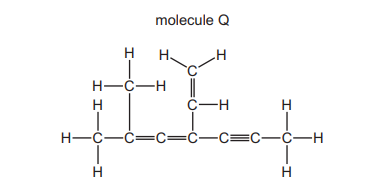
How many of the carbon atoms in molecule Q are \(sp^2\) hybridised?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. **Identify \(sp^2\) Hybridized Carbons**: In organic chemistry, carbon atoms with double bonds (alkenes, carbonyls, etc.) are \(sp^2\) hybridized, while single-bonded carbons (alkanes) are \(sp^3\) hybridized.
2. **Analyze the Structure**: The given hydrocarbon (Q) contains a benzene ring (6 carbons) and an additional double bond. In the benzene ring, all 6 carbons are \(sp^2\) hybridized due to the alternating double bonds. However, the side chain may introduce variability.
3. **Count \(sp^2\) Carbons**: Based on the structure, only 4 carbons are confirmed to be \(sp^2\) hybridized (typically the ones directly involved in double bonds or aromatic systems).
4. **Conclusion**: The correct count is **4 \(sp^2\) hybridized carbons**, making option B correct.
Ethene reacts with steam in the presence of sulfuric acid.
\(C_2H_4 + H_2O \to CH_3CH_2OH\)
Which type of reaction is this?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
This is an addition reaction because water (\(H_2O\)) adds across the double bond of ethene (\(C_2H_4\)) to form ethanol (\(CH_3CH_2OH\)). The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst. Addition reactions are characteristic of alkenes, where the π bond breaks and new atoms are added without any byproducts.
When heated with KOH dissolved in ethanol, halogenoalkanes can undergo an elimination reaction to form alkenes. What are the possible elimination products when 2-bromobutane is heated with KOH dissolved in ethanol?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The elimination reaction of 2-bromobutane (CH₃CHBrCH₂CH₃) with KOH/ethanol follows Zaitsev’s rule, producing a mixture of alkenes:
- But-2-ene (CH₃CH=CHCH₃) – Major product (more substituted alkene).
- But-1-ene (CH₃CH₂CH=CH₂) – Minor product (less substituted alkene).
Option D is incorrect because CH₂=CHCH=CH₂ (buta-1,3-diene) is not formed in this reaction. Thus, the correct answer is C.
