1-chlorobutane and 1-iodobutane both react with aqueous sodium hydroxide by a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. Which reaction has the greatest rate under the same conditions and which mechanism is followed by this reaction?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In nucleophilic substitution reactions:
- Reactivity: 1-iodobutane reacts faster than 1-chlorobutane because the C-I bond is weaker than the C-Cl bond (lower bond enthalpy), making it easier to break.
- Mechanism: The reaction follows an \( S_N2 \) mechanism, where the nucleophile (\( \text{OH}^- \)) attacks the carbon from the opposite side of the leaving group (I⁻ or Cl⁻), resulting in inversion of configuration.
Thus, 1-iodobutane has the greatest rate and follows the \( S_N2 \) mechanism, corresponding to option D.
Compound X is found in cell walls of some bacteria. Its structural formula is shown.
compound X
\(CH_3(CH_2)_{17}CH=CH(CH_2)_{17}CH(OH)CH(CH_3)CO_2H\)
How many stereoisomers are there with this structural formula?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Compound X has three stereocenters:
- The carbon-carbon double bond (\(CH=CH\)) exhibits E/Z (cis-trans) isomerism (2 configurations).
- The chiral carbon (\(CH(OH)\)) has 2 configurations (R/S).
- The carbon (\(CH(CH_3)\)) adjacent to the carboxyl group is also chiral (2 configurations).
Total stereoisomers = \(2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8\). Thus, the correct answer is D (8).
Structural isomerism only should be considered when answering this question. How many straight-chain isomers are there with molecular formula C4H8Cl2?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
For the straight-chain molecule C4H8Cl2, the two chlorine atoms can be placed on different carbon atoms, leading to structural isomers. The possible combinations are:
- 1,1-dichlorobutane
- 1,2-dichlorobutane
- 1,3-dichlorobutane
- 1,4-dichlorobutane
- 2,2-dichlorobutane
- 2,3-dichlorobutane
Thus, there are 6 distinct structural isomers, making option A correct.
Compound Z has the molecular formula \(C_4H_8O_2\). Compound Z reacts with propan-1-ol in the presence of concentrated H₂SO₄. The diagram shows the skeletal formulae of three compounds, S, T and U.
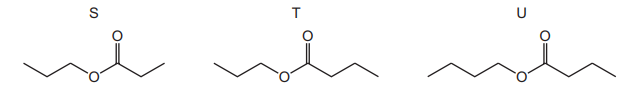
What are the possible skeletal formulae of the products of the reaction between compound Z and propan-1-ol?
A. S and T
B. U only
C. S and U
D. T only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Compound Z (\(C_4H_8O_2\)) is likely a carboxylic acid or ester. When it reacts with propan-1-ol (\(C_3H_7OH\)) under acidic conditions, an esterification occurs, forming an ester. The product T is the ester \(C_3H_7COOCH_2CH_2CH_3\) (propyl propanoate), which matches the reaction. Neither S (a ketone) nor U (an ether) can form from this reaction, making D (T only) the correct answer.
