(a) M reacts to form R by the addition of one reagent, as shown in Fig. 5.1.
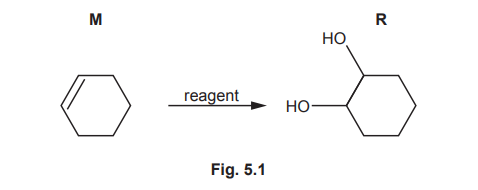
Identify the reagent and conditions for this reaction.
(b) R is also made from M by two steps, as shown in Fig. 5.2.
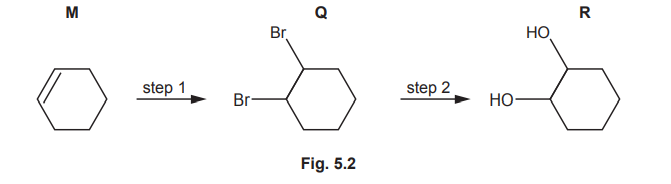
(i) Identify the reagents and conditions for steps 1 and 2 in Fig. 5.2.
(ii) Name the mechanism for step 1 in Fig. 5.2.
(c) The infrared spectrum of R is shown in Fig. 5.3.

Use the absorptions in the region above \(1500cm^{–1}\) in Table 5.1 when answering this question.
• Add F to Fig. 5.3 to identify the peak that is present in an infrared spectrum of both Q and R. Identify the bond that corresponds to the absorption for F.
• Add G to Fig. 5.3 to identify the peak that is not present in an infrared spectrum of Q. Identify the bond that corresponds to the absorption for G.
(d) Y is made from Q in a three-step reaction.
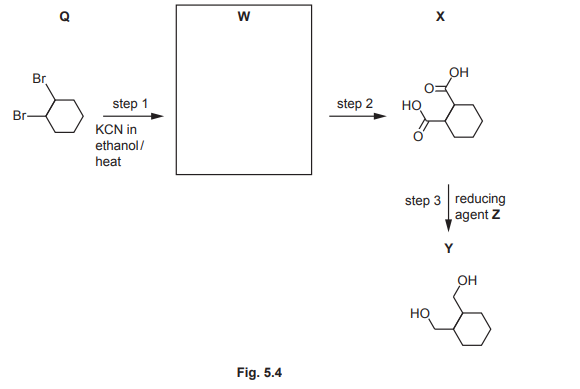
(i) Draw the structure of W in the box in Fig. 5.4. [1]
(ii) In step 2, W is heated with HCl (aq) to produce X and an inorganic product. Identify the formula of the inorganic product.
(iii) In step 3, X reacts with reducing agent Z to produce Y. Complete the equation for the reaction of X with Z. Use a molecular formula to represent the organic product. Use [H] to represent one atom of hydrogen from Z.
…… \(C_8H_{12}O_4 + ……[H]\)
(iv) Identify Z
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) The reagent is cold dilute \(KMnO_4\) (potassium manganate(VII)).
Explanation: Cold dilute \(KMnO_4\) oxidizes alkenes to diols (e.g., M to R) without breaking the C=C bond further.
(b)(i)
• Step 1: \(Br_2\) (in the dark).
• Step 2: NaOH(aq) + heat.
Explanation: Step 1 involves electrophilic addition of bromine to form a dibromoalkane. Step 2 uses NaOH(aq) under heat to substitute Br with OH via nucleophilic substitution.
(b)(ii) The mechanism for step 1 is electrophilic addition.
Explanation: Bromine (\(Br_2\)) acts as an electrophile, adding across the C=C double bond.
(c)
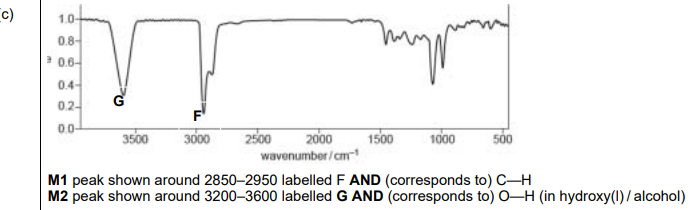
Explanation:
• F: The peak at ~2900 cm\(^{-1}\) corresponds to C-H bonds (present in both Q and R).
• G: The peak at ~3400 cm\(^{-1}\) corresponds to O-H bonds (absent in Q but present in R due to the diol group).
(d)(i) W =  (Note: Replace with actual structure if available).
(Note: Replace with actual structure if available).
(d)(ii) The inorganic product is NH₄Cl.
Explanation: Hydrolysis of W (amide) with HCl produces a carboxylic acid (X) and ammonium chloride.
(d)(iii) The balanced equation is:
\[ C_8H_{12}O_4 + 8[H] \rightarrow C_8H_{16}O_2 + 2H_2O \]
Explanation: Reducing agent Z adds hydrogen atoms to X, converting the carboxylic acid groups to alcohols (Y).
(d)(iv) Z is LiAlH₄ (lithium aluminium hydride).
Explanation: LiAlH₄ is a strong reducing agent capable of reducing carboxylic acids to primary alcohols.
