The table shows three sets of reagents and reaction conditions.
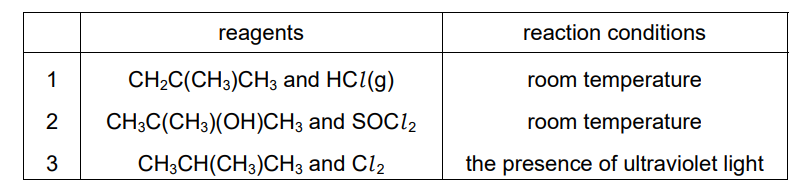
Which sets of reagents and conditions can be used to produce 2-chloro-2-methylpropane as one of the organic products?
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2 and 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To produce 2-chloro-2-methylpropane (\((CH_3)_3CCl\)) from 2-methylpropene (\((CH_3)_2C=CH_2\)):
- Set 1 (HCl gas): Electrophilic addition of HCl to the alkene forms the tertiary alkyl halide via Markovnikov addition.
- Set 2 (Cl₂ in UV light): Free-radical substitution replaces a hydrogen on the tertiary carbon with chlorine.
- Set 3 (NaCl(aq) + H₂SO₄): The acid protonates the alkene to form a carbocation, which reacts with Cl⁻ to yield the product.
All three methods can produce 2-chloro-2-methylpropane, making A (1, 2, and 3) correct.
When X is added to NaOH(aq) and heated under reflux, pentan-2-ol is made. Which organic product is made when X is heated with a solution of KCN dissolved in ethanol?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Since X produces pentan-2-ol (\( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH(OH)CH}_3 \)) with NaOH, X must be 2-chloropentane (\( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH(Cl)CH}_3 \)). When heated with KCN/ethanol, a nucleophilic substitution occurs, replacing Cl with CN to form 2-cyanopentane (\( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH(CN)CH}_3 \)), corresponding to option D.
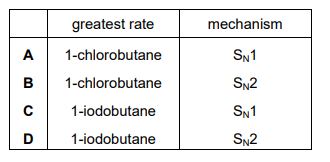
1-chlorobutane and 1-iodobutane both react with aqueous sodium hydroxide by a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. Which reaction has the greatest rate under the same conditions and which mechanism is followed by this reaction?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In nucleophilic substitution reactions:
- Reactivity: The C-I bond in 1-iodobutane is weaker than the C-Cl bond in 1-chlorobutane, making it react faster with NaOH.
- Mechanism: Since 1-iodobutane is a primary haloalkane, it undergoes an \(S_N2\) mechanism (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution).
Thus, the correct answer is D: 1-iodobutane reacts fastest by an \(S_N2\) mechanism.
(CH₃)₃CCN reacts to form alcohol Y via the reaction sequence shown.
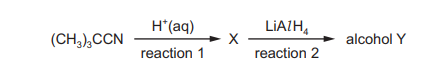
Which row names the molecule X and the class of alcohol Y?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Step 1: Hydrolysis of nitrile
(CH₃)₃CCN undergoes hydrolysis to form (CH₃)₃CCOOH (2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid). This is molecule X.
Step 2: Reduction of carboxylic acid
(CH₃)₃CCOOH is reduced using LiAlH₄ to form (CH₃)₃CCH₂OH (2,2-dimethylpropan-1-ol). This is alcohol Y.
Classification of alcohol Y
(CH₃)₃CCH₂OH is a primary alcohol because the –OH group is attached to a carbon that is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Thus, the correct combination is:
X: 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid
Y: primary alcohol
Matching row C in the given options.
