The diagram shows a section of a polymer molecule.
–CH₂–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH=CH–CH₂–
Which monomer will produce this polymer?
A. CH₂=CH₂
B. CH₃CH=CH₂
C. CH₃CH=CHCH₃
D. CH₂=CH–CH=CH₂
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The polymer segment contains a repeating unit of \( \ce{-CH2-CH=CH-CH2-} \). This pattern arises from the addition polymerization of a conjugated diene monomer, where the double bonds open up to form the polymer chain. The monomer 1,3-butadiene (\( \ce{CH2=CH-CH=CH2} \)) undergoes 1,4-addition polymerization. In this process, the central single bond in the monomer becomes the double bond in the polymer, and the terminal double bonds form the new single bonds that link the repeating units, perfectly matching the given polymer structure.
Question
The diagrams show the structures of lycopene and \(\beta \)-carotene.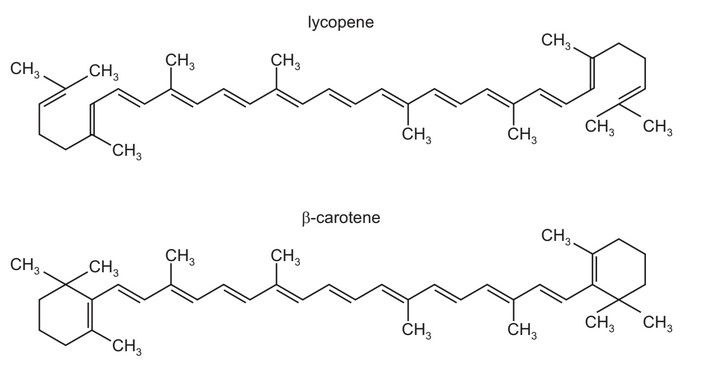
When lycopene is converted into β-carotene, what is the gain or loss of hydrogen atoms per
molecule?
A 4 gained
B 2 gained
C no change
D 2 lost
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
