\(Ni^{2+}\) ions form a number of different complex ions, including \([Ni(H_2O)_6]^{2+}\), \([Ni(NH_3)_6]^{2+}\) and \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\). The abbreviation en represents 1,2-diaminoethane. The numerical values of two stability constants, \(K_{stab}\), are given in Table 5.1.
(a) Complete the expression for the \(K_{stab}\) of [Ni(en)₃]²⁺.
(b) A solution of [Ni(H₂O)₆]²⁺ is added to a solution that contains 0.10 mol/dm³ NH₃ and 0.10 mol/dm³ en.
(i) Predict which complex ion, \([Ni(NH_3)_6]^{2+}\) or \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\), is present in the resulting mixture in the highest concentration. Explain your answer.
(ii) Complete the equation for the ligand exchange reaction occurring in (i).
Complete Fig. 5.1 to show the three-dimensional structures of the two isomers of [Ni(en)₃]²⁺.
Use 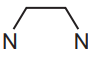 to represent the en ligand. Name the type of isomerism shown.
to represent the en ligand. Name the type of isomerism shown.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) The stability constant expression for \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\) is:
\[ K_{stab} = \frac{[[Ni(en)_3]^{2+}]}{[Ni^{2+}][en]^3} \]
Explanation: The stability constant (\(K_{stab}\)) is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the complex ion to the product of the concentrations of the free metal ion and the ligand raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients.
(b)(i) The complex ion present in the largest concentration is \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\).
Explanation: From Table 5.1, \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\) has a larger stability constant (\(K_{stab} = 10^{18}\)) compared to \([Ni(NH_3)_6]^{2+}\) (\(K_{stab} = 10^8\)). A higher \(K_{stab}\) indicates greater stability, so \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\) predominates.
(b)(ii) The ligand exchange reaction is:
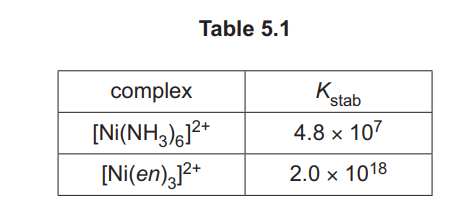
\[ [Ni(H_2O)_6]^{2+} + 3en \rightarrow [Ni(en)_3]^{2+} + 6H_2O \]
Explanation: Water ligands are replaced by en (1,2-diaminoethane) due to the higher stability of the \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\) complex.
![Isomers of [Ni(en)₃]²⁺](https://www.iitianacademy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Screenshot-2025-01-25-090025.png)
Type of isomerism shown: Optical isomerism.
Explanation: The two isomers of \([Ni(en)_3]^{2+}\) are non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers), characteristic of optical isomerism.
