Which statement about the properties associated with the different types of bonding involved is correct?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Ionic compounds conduct electricity only in molten or aqueous states due to free-moving ions, whereas metals conduct in solid state via delocalized electrons. Thus, statement C is correct. Option A is incorrect as not all O-H containing compounds form H-bonds (e.g., \( \text{H}_2\text{O}_2 \)). Option B is false (e.g., \( \text{NH}_4\text{Cl} \) has both bonds). Option D is incorrect since covalent networks (e.g., diamond) have high melting points without H-bonds.
V and Z are both elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table. Each element forms one stable ion that does not contain another element. The atomic radius of each element and the ionic radius of the ion described above is shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. Ions of V and Z have the same number of full electron shells.
B. Ions of Z are positively charged.
C. Z has a greater electronegativity than V.
D. V has more outer electrons than Z
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The data shows Z has a smaller atomic radius than V, and its ionic radius is larger than its atomic radius. This pattern is characteristic of a non-metal forming an anion (e.g., \( \ce{Cl} \) forming \( \ce{Cl-} \)), while V, whose ionic radius is smaller than its atomic radius, is a metal forming a cation (e.g., \( \ce{Na} \) forming \( \ce{Na+} \)). Electronegativity increases across a period, so Z (a non-metal) has a greater electronegativity than V (a metal).
Ammonia reacts with acids to form the ammonium ion.
\[ \text{NH}_3 + \text{H}^+ \rightleftharpoons \text{NH}_4^+ \]
Which row is correct?
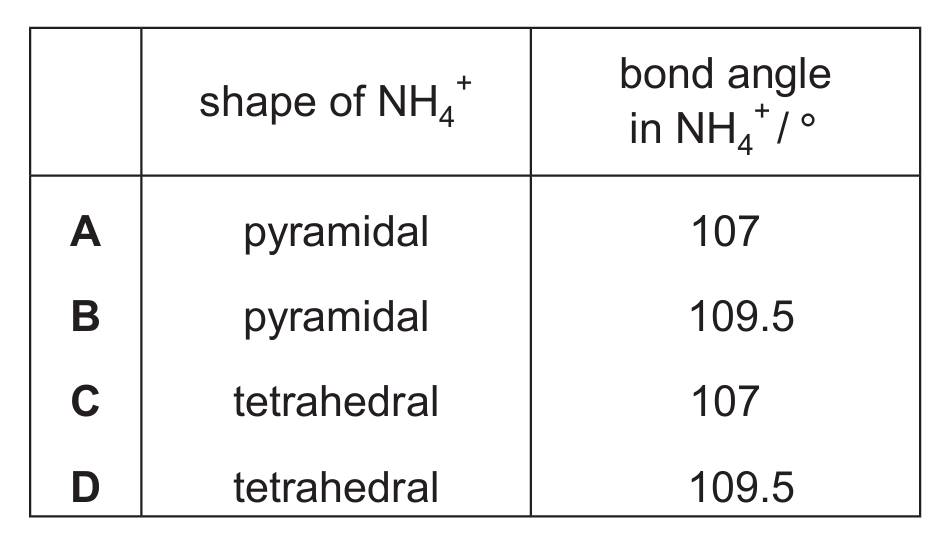
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) has 4 bonding pairs and no lone pairs around the central N atom. This gives a tetrahedral electron pair geometry and a tetrahedral molecular shape. The bond angle in a perfect tetrahedron is 109.5°.
The boiling points of Br₂, ICl and IBr are given in the table.

Which row explains:
• why the boiling point of ICl is greater than Br₂?
• why the boiling point of IBr is greater than ICl ? 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
ICl has a higher boiling point than Br₂ because ICl is a polar molecule with permanent dipole-dipole forces, whereas Br₂ is non-polar and only has weaker London (dispersion) forces. IBr has a higher boiling point than ICl because IBr has a greater number of electrons (IBr: 198; ICl: 178), resulting in stronger London forces. The difference in electronegativity for both ICl and IBr is similar (approx. 0.5), so the polarity is comparable, making the difference in electron count and the resulting London forces the dominant factor for the second comparison.
