Question
(a) [MnCl 4]2- is a complex ion.
(i) Deduce the oxidation state of manganese in [MnCl 4]2-.
(ii) The [MnCl 4]2- complex does not contain any 180° bond angles.
Draw a three-dimensional diagram to show the shape of the [MnCl 4]2- complex. State one bond angle on your diagram.
(b) A solution of cobalt(II) sulfate contains the complex ion [Co(H2O)6]2+.
A solution containing [Co(H2O)6]2+ is reacted separately with an excess of each of NaOH(aq), NH3(aq) and NaCl(aq).
Write an equation for each of these reactions. State one observation that can be made immediately after the reaction, include the colour and state of the cobalt-containing product.
(i) [Co(H2O)6]2+ and an excess of NaOH(aq)
(ii) [Co(H2O)6]2+ and an excess of NH3(aq)
(iii) [Co(H2O)6]2+ and an excess of NaCl(aq)
(iv) Name the type of reaction that occurs in (b)(iii).
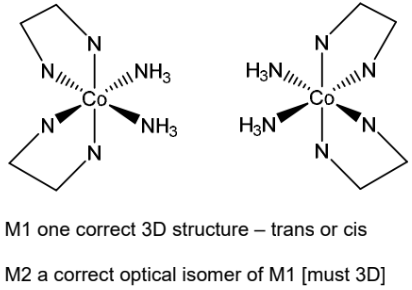
(c) Cobalt forms the complex ion [Co(NH3)2(en)2]2+. The abbreviation en is used for the bidentate ligand 1,2-diaminoethane, H2NCH2CH2NH2. The complex ion shows both geometrical and optical isomerism.
(i) Define the term bidentate ligand.
(ii) Draw three-dimensional diagrams for the two optical isomers of [Co(NH3)2(en)2]2+.
Each en ligand can be represented using 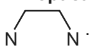
Answer/Explanation
Answer (a)(i) +2 (a)(ii)
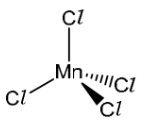
bond angle labelled 109.5°.
(b)(i) [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH– → Co(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2H2O OR [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 2OH– → Co(OH)2 + 6H2O blue precipitate
(b)(ii) [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 6NH3 → [Co(NH3)6]2+ + 6H2O
yellow / brown / straw solution
(b)(iii) [Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl – → [CoCl4]2– + 6H2O
blue solution
(b)(iv) ligand exchange
(c)(i) (a species) that donates two lone pairs to form two dative bonds
to a (transition) metal atom / metal ion
(c)(ii)