Question
(a) Chlorobenzene and phenol both show a lack of reactivity towards reactants that cause the breaking of the C–X bond (X = Cl or OH).
Explain why.
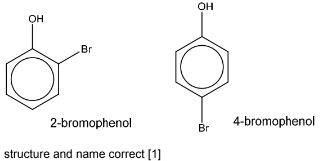
(b) When phenol is reacted with bromine dissolved in an inert solvent, two isomeric bromophenols, C6H4BrOH, are formed.
Suggest structures for these products. Name each compound.
(c) A student suggested that phenol can be prepared from benzene by the method shown.
step 4 ___________________________________
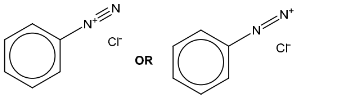
(ii) Deduce the structure for K and draw its structural formula in the box.
(iii) Name the mechanism for step 1.
(iv) Write an equation for step 2. Use [H] for the reducing agent in this equation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) M1 C-X / C-Cl / C-O bond is stronger (in chlorobenzene / phenol) [1]
M2 p-orbital / lone pair on Cl / O(H) / X (in chlorobenzene / phenol) [1]
M3 electrons of the (Cl / O / electronegative atom) AND overlap / delocalise with π-electron cloud / delocalise into ring [1]
(b)
(c)(i) step 1 conc. HNO3 + H2SO4 (and temperare 50–55 °C) [1]
step 2 Sn + HCl AND one of conc.HCl + heat [1]
step 4 H2O warm / heat [1]
(c)(ii)
(c)(iii) step 1 electrophilic substitution
(c)(iv) C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
