A reaction scheme is shown in Fig. 7.1. The reagents needed for reaction 2 and reaction 3 are stated. Reaction 5 takes place when \(C_2H_5NH_2\) is mixed with compound V. No special conditions are required.
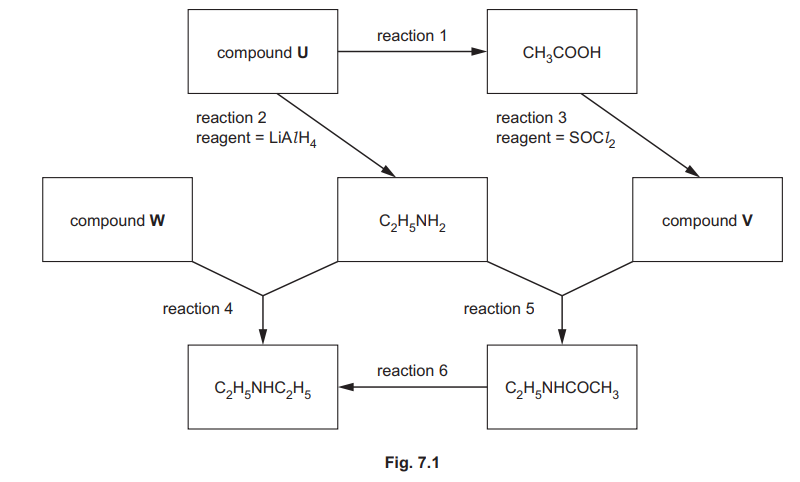
(a) Identify compound U which contains only three elements.
(b) Describe the reagents and conditions for reaction 1.
(c) Identify compound V.
(d) Complete the equation for reaction 3.
\(CH_3COOH + SOCl_2 \to …………..\)
(e) Identify compound W.
(f) Describe the conditions for reaction 4.
(g) Suggest the reagent needed for reaction 6.
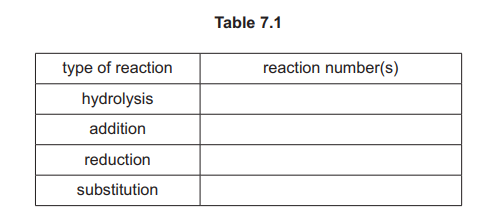
(h) Complete Table 7.1 by adding the reaction numbers, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, to the right-hand column. Use the reaction numbers given in Fig. 7.1. Each of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 should be used once only.
(i) Compare the basicities of \(C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\), \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5\), and \(NH_3\). Explain your answer. 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) CH₃CN / ethanenitrile
Explanation: Compound U must contain only C, H, and N. The nitrile group (–CN) in the reaction scheme confirms it as ethanenitrile (CH₃CN).
(b) dilute HCl (aq) and heat
Explanation: Hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids requires acidic conditions (dilute HCl) and heating to break the strong C≡N bond.
(c) CH₃COCl / ethanoyl chloride
Explanation: Compound V reacts with ethylamine to form an amide, indicating it is an acyl chloride (ethanoyl chloride).
(d) \(CH_3COCl + SO_2 + HCl\)
Explanation: Thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) converts carboxylic acids to acyl chlorides, with byproducts of SO₂ and HCl gas.
(e) \(C_2H_5Br\) / bromoethane
Explanation: Compound W is a haloalkane (bromoethane) used to alkylate amines in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
(f) Heat in ethanol under pressure (sealed tube)
Explanation: Nucleophilic substitution of amines with haloalkanes requires heating in a solvent (ethanol) and pressurized conditions.
(g) LiAlH₄ / lithium aluminium hydride
Explanation: Reduction of amides to amines is achieved using the strong reducing agent LiAlH₄.
(h)

Explanation: The reactions are matched as: 1 (nitrile hydrolysis), 2 (reduction), 3 (acyl chloride formation), 4 (alkylation), 5 (amide formation), and 6 (amide reduction).
(i) Basicity order: \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5 > NH_3 > C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\)
Explanation: – \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5\) is most basic due to two electron-donating ethyl groups. – \(NH_3\) has intermediate basicity. – \(C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\) is least basic due to the electron-withdrawing carbonyl group.
