A reaction scheme is shown in Fig. 7.1. The reagents needed for reaction 2 and reaction 3 are stated. Reaction 5 takes place when \(C_2H_5NH_2\) is mixed with compound V. No special conditions are required.
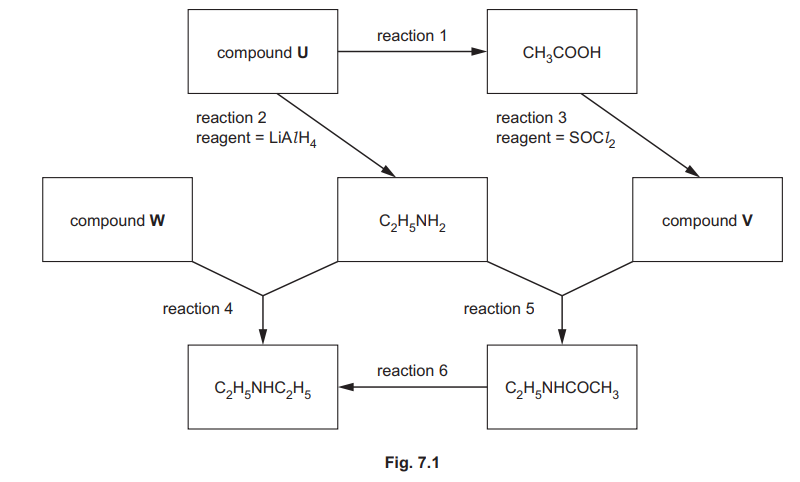
(a) Identify compound U which contains only three elements.
(b) Describe the reagents and conditions for reaction 1.
(c) Identify compound V.
(d) Complete the equation for reaction 3.
\(CH_3COOH + SOCl_2 \to …………..\)
(e) Identify compound W.
(f) Describe the conditions for reaction 4.
(g) Suggest the reagent needed for reaction 6.
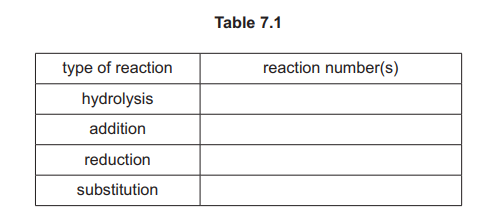
(h) Complete Table 7.1 by adding the reaction numbers, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, to the right-hand column. Use the reaction numbers given in Fig. 7.1. Each of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 should be used once only.
(i) Compare the basicities of \(C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\), \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5\), and \(NH_3\). Explain your answer. 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) CH₃CN / ethanenitrile
Explanation: Compound U contains only three elements (C, H, N) and is derived from the nitrile group (–CN) in the reaction scheme.
(b) dilute acid / HCl (aq) AND hot / heat
Explanation: Hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids requires dilute acid (e.g., HCl) and heating to facilitate the reaction.
(c) CH₃COCl / ethanoyl chloride
Explanation: Compound V reacts with \(C_2H_5NH_2\) to form an amide, indicating it is an acyl chloride (ethanoyl chloride).
(d) \(CH_3COCl + SO_2 + HCl\)
Explanation: The reaction of acetic acid (\(CH_3COOH\)) with thionyl chloride (\(SOCl_2\)) produces ethanoyl chloride (\(CH_3COCl\)), sulfur dioxide (\(SO_2\)), and hydrogen chloride (\(HCl\)).
(e) \(C_2H_5Br / C_2H_5Cl\) / bromoethane / chloroethane
Explanation: Compound W is a haloalkane (bromoethane or chloroethane) used in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
(f) heat in ethanol AND under pressure / in sealed tube
Explanation: Reaction 4 involves nucleophilic substitution, requiring heat in ethanol and high pressure (sealed tube) for completion.
(g) LiAlH₄ / lithium aluminium hydride
Explanation: Reduction of amides to amines is achieved using a strong reducing agent like lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH₄).
(h)

Explanation: The reaction numbers are matched based on the transformations: 1 (hydrolysis), 2 (reduction), 3 (acyl chloride formation), 4 (nucleophilic substitution), 5 (amide formation), and 6 (reduction).
(i) \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5 > NH_3 > C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\)
Explanation: Basicity decreases with electron-withdrawing groups (e.g., –COCH₃ in \(C_2H_5NHCOCH_3\)) and increases with electron-donating groups (e.g., –C₂H₅ in \(C_2H_5NHC_2H_5\)). Ammonia (\(NH_3\)) has intermediate basicity.
