In the diagram, X is the Boltzmann distribution for the energies of the particles in a reaction and \(E_{A1}\) is the activation energy for that reaction.

Which statement is correct?
A. \(E_{A2}\) is the activation energy at a higher temperature.
B. \(E_{A2}\) is the activation energy at a lower temperature.
C. Y is the Boltzmann distribution at a lower temperature.
D. Z is the Boltzmann distribution at a higher temperature.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
At a lower temperature, the Boltzmann distribution (Y) shifts to the left, showing fewer particles with high energy. The activation energy (\(E_{A1}\)) remains unchanged, but the fraction of particles exceeding it decreases. Thus, Y represents the distribution at a lower temperature, making option C correct. Options A, B, and D are incorrect because \(E_{A2}\) is not a valid activation energy, and Z represents a higher temperature distribution, not Y.
In the high temperatures of car engines, nitrogen reacts with oxygen to produce nitrogen monoxide.

This reaction has activation energy \(E_a\). Which reaction pathway diagram correctly represents this reaction? 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The reaction \(\text{N}_2 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{NO}\) is endothermic, meaning the products have higher energy than the reactants. The correct pathway diagram (C) shows the reactants at a lower energy level, followed by an activation energy barrier (\(E_a\)), and the products at a higher energy level. This matches the thermodynamic and kinetic behavior of the reaction.
The graph shows the boiling points of the hydrogen compounds of Group 16 elements.
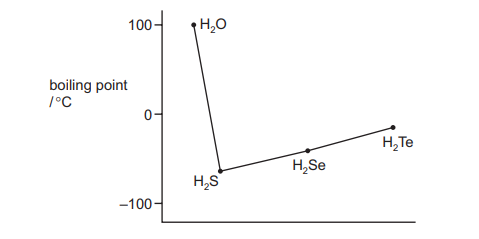
Which statement correctly explains why water does not fit the trend of the other compounds?
A. There are fewer electrons in the oxygen atoms so there is less shielding of the nuclear charge.
B. There are strong hydrogen bonds in water but not in the other compounds.
C. The covalent bonds in water are much stronger than in the other compounds.
D. The water molecules are smaller and so have stronger van der Waals’ forces.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Water (\(H_2O\)) has an anomalously high boiling point compared to other Group 16 hydrogen compounds (\(H_2S\), \(H_2Se\), \(H_2Te\)) due to hydrogen bonding. Oxygen’s high electronegativity allows for strong dipole-dipole interactions (hydrogen bonds) between water molecules, which are absent in the other compounds. This explains why water deviates from the trend.
Hydrated cobalt(II) sulfate loses water when heated to give anhydrous cobalt(II) sulfate. All the water of crystallisation is lost to the atmosphere as steam. When 3.10 g of hydrated cobalt(II) sulfate, \(CoSO_4•xH_2O\), is heated to constant mass the loss in mass is 1.39 g. What is the value of x, to the nearest whole number?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The mass of anhydrous \(\ce{CoSO4}\) is the initial mass minus the mass of water lost: \(3.10\, \pu{g} – 1.39\, \pu{g} = 1.71\, \pu{g}\). The molar mass of \(\ce{CoSO4}\) is \(59 + 32 + (4 \times 16) = 155\, \pu{g mol^{-1}}\). The number of moles of \(\ce{CoSO4}\) is \(\frac{1.71}{155} = 0.01103\, \pu{mol}\). The number of moles of \(\ce{H2O}\) lost is \(\frac{1.39}{18} = 0.07722\, \pu{mol}\). The ratio \(x = \frac{\text{moles of } \ce{H2O}}{\text{moles of } \ce{CoSO4}} = \frac{0.07722}{0.01103} \approx 7.00\), which is 7 to the nearest whole number.
