Question
(a) The oxidation of nitrogen(II) oxide is shown in the equation.
$
2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NO}_2(\mathrm{~g})
$
The initial rate of this reaction was measured, starting with different concentrations of the two reactants. The following results were obtained.
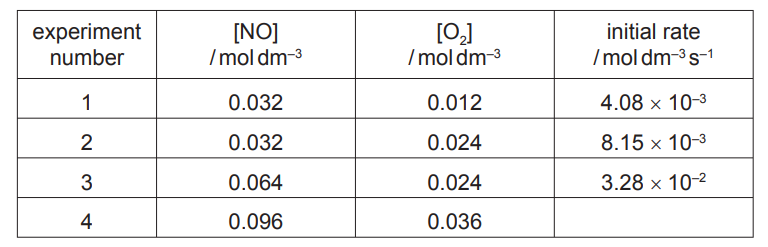
(i) Use the data in the table to determine the order with respect to each reactant. Show your reasoning.
(ii) Calculate the initial rate in experiment 4. Give your answer to two significant figures.
initial rate $=$ $\mathrm{moldm}^{-3} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$
(iii) Write the rate equation for this reaction.
(iv) Use the results of experiment 1 to calculate the rate constant, $k$, for this reaction. Include the units of $k$.
rate constant, $k=$ units $[6]$
(b) (i) On the following axes
- draw two Boltzmann distribution curves, at two different temperatures, $T_1$ and $T_2\left(T_2>T_1\right)$,
- label the curves and the axes.

(ii) State and explain, using your diagram, the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of reaction. [5]
(c) The compound nitrosyl fluoride, NOF, can be formed by the following reaction.
$
2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{F}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightleftharpoons 2 \mathrm{NOF}(\mathrm{g})
$
The rate is first order with respect to $\mathrm{NO}$ and $\mathrm{F}_2$. The reaction mechanism has two steps.
Suggest equations for the two steps of this mechanism, stating which is the rate determining slower step. [2] [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) $[\mathrm{NO}] 2^{\text {nd }}$ order and the concentration is $\times 2$, rate $\times 4$
$\left[\mathrm{O}_2\right] \quad 1^{\text {st }}$ order and evidence of using expt $1 \& 2$ when the concentration is $\times 2$, rate doubles
(ii) $\quad(0.00408 \times 27)$
rate $=\underline{0.11}\left(\mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}^{-3} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}\right)$ to $2 \mathbf{s f}$
(iii) (Rate $=) k\left[\mathrm{O}_2\right][\mathrm{NO}]^2$
(iv) $k=332(.03125)$
$\mathrm{mol}^{-2} \mathrm{dm}^6 \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$
(b) (i) labelled axes $x$-axis: energy (KE) and $y$-axis: molecules or particles two curves: starts origin; not touching $x$-axis again; no levelling out; curves only intersecting once curves labelled and $\mathrm{T} 2$ is to the right and lower max than T1
(ii) rate increases and energy of the particles increases more particles have $E_{\mathrm{a}}$
(c) 1 mole of $F_2$ and 1 mole NO reacting in the slow step a balanced mechanism consistent with overall equation
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{F}_2+\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow \mathrm{NOF}+\mathrm{F} \\
& \mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{F} \rightarrow \mathrm{NOF}
\end{aligned}
$
OR
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{F}_2+\mathrm{NO} \rightarrow \mathrm{NOF}_2 \\
& \mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{NOF}_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NOF}
\end{aligned}
$
