Solutions X and Y both have a concentration of 0.10 mol dm–3. A fixed volume of solution X is added to a conical flask, and solution Y is added from a burette to the conical flask. A titration is performed.
The diagram shows the pH titration curve for the acid–base reaction between the solutions.
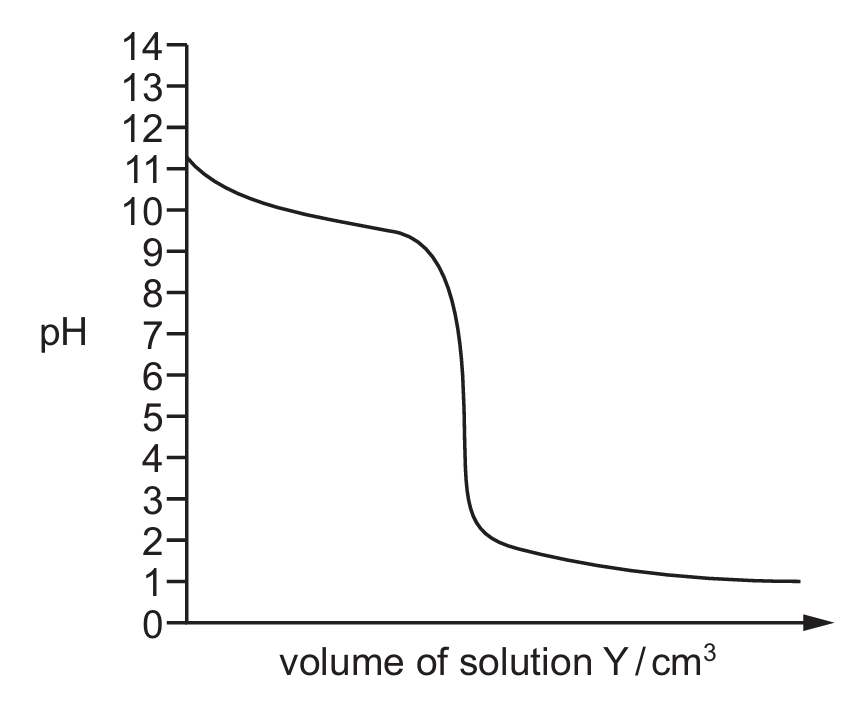
What are solutions X and Y?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The curve starts at a high pH (~11-13), indicating the solution in the flask (X) is a base. The steep drop at the equivalence point is characteristic of a strong acid-strong base titration. Ammonia is a weak base and nitric acid is a strong acid. The initial high pH and the shape of the curve match the titration of a weak base (ammonia) with a strong acid (nitric acid).
Which emission from an internal combustion engine contributes to the erosion of marble statues?
A. carbon monoxide
B. nitrogen
C. nitrogen dioxide
D. unburnt hydrocarbons
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Marble statues are primarily composed of calcium carbonate (\(CaCO_3\)). Nitrogen dioxide (\(NO_2\)) from engine emissions reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere to form nitric acid (\(HNO_3\)), a strong acid. This acid then reacts with the calcium carbonate, dissolving it in a process called acid erosion: \(CaCO_3(s) + 2HNO_3(aq) \rightarrow Ca(NO_3)_2(aq) + CO_2(g) + H_2O(l)\).
Question
The catalytic converters fitted to cars remove pollutants from the exhaust gases. Some of the
reactions that occur involve oxygen, which comes from the air.
Which pollutants in the exhaust gases will react with oxygen on the surface of the catalytic
converter?
A NO_{2}
B unburnt fuel
C CO
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question:
Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc
\(1HC \imath(aq)~+~Zn(s)\rightarrow ZnC\imath_{2}(aq)~+~H_{2}g\)
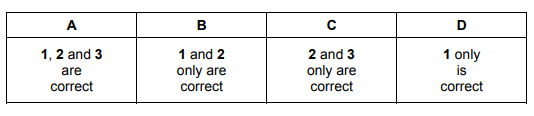
What will increase the rate of this reaction but will not change the Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies?
1 addition of a suitable catalyst
2 an increase in concentration of hydrochloric acid
3 an increase in temperature of hydrochloric acid

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
