Question
Nitric acid, \(HNO_{3}\) can be made by reacting nitrogen dioxide with water.
The enthalpy change for the reaction can be measured indirectly using a Hess’ cycle.
$3 \mathrm{NO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) \stackrel{\Delta H_{\mathrm{r}}}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{HNO}_3(\mathrm{l})+\mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})$
(a) Explain what is meant by the term enthalpy change of formation.
(b) Complete the Hess’ cycle using the values given in the table and hence calculate the enthalpy change, $\Delta H_r$, for this reaction. Show your working.
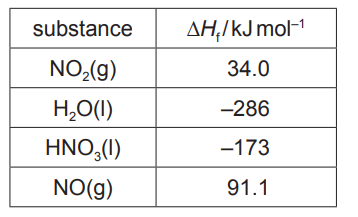
$3 \mathrm{NO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{I}) \stackrel{\Delta H_{\mathrm{r}}}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{HNO}_3(\mathrm{I})+\mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})$
$\Delta H_r=$ $\mathrm{kJmol}^{-1}$ [3]
(c) Nitrogen and oxygen do not react at normal atmospheric temperatures. Explain why.[5]
Nitrogen oxides can be formed naturally in the Earth’s atmosphere from nitrogen and oxygen in the air.
(d) State one way that nitrogen oxides are produced naturally.[1]
(e) Nitrogen dioxide, $\mathrm{NO}_2$, acts as a homogeneous catalyst in the oxidation of atmospheric sulfur dioxide.
(i) Explain why $\mathrm{NO}_2$ is described as a homogeneous catalyst. [3]
(ii) Write equations which describe the two reactions occurring when $\mathrm{NO}_2$ acts as a catalyst in the formation of sulfur trioxide from sulfur dioxide. [2] [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) M1 (enthalpy / energy change) when one mole of a compound/substance is formed
M2 from its elements in their standard states
(b)
M1 use of correct stoichiometry in calculation $3 x \Delta H_f \mathrm{NO}_2 \quad 1 \mathrm{x}-\Delta \mathrm{H}_f \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \quad 2 \mathrm{x} \Delta \mathrm{H}_f \mathrm{HNO}_3 \quad 1 \mathrm{x} \Delta \mathrm{H}_f \mathrm{NO}$
M2 correct signs associated with the appropriate $\Delta H_f$ values/terms used for the calculation of $\Delta \mathrm{H}_{\text {reaction }}$ M3 $\Delta \mathrm{H}_{\text {reaction }}=-(102-286)+(-346+91.1)=-70.9 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$
(c) M1 nitrogen has a triple bond
M2 EITHER
high energy is needed to break the bond
OR
at normal temperatures there is not enough energy to break the bond / to overcome the activation energy
(d) lightning
(e)(i) M1 define homogeneous
(homogeneous catalyst is) in the same phase / state as the reactants
M2 and M3 Define catalyst
All 3 points scores 2 marks. Any 2 points scores 1 mark
increase the rate
AND
lowers the activation energy
AND
without being chemically altered at the end of the reaction / are regenerated at the end of the reaction
(e)(ii)$\begin{aligned} & \text { M1 NO } \mathrm{N}_2+\mathrm{SO}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{SO}_3 \\ & \text { M2 NO }+1 / 2 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}_2\end{aligned}$
