Cobalt, rhodium and iridium are metals in the same group of the Periodic Table.
(a) The shorthand electronic configuration of cobalt is \([Ar]3d^74s^2\).
(i) Identify what is meant by [Ar] by giving its full electronic configuration.
(ii) The lowest-energy electrons in cobalt are in the 1s orbital. Draw the shape of a 1s orbital.
(iii) Deduce the number of unpaired electrons in a cobalt atom.
(b) Table 1.1 gives some details of the stable naturally occurring isotopes of rhodium and iridium.
Complete Table 1.1.
(c) Table 1.2 shows the relative abundances of isotopes in a sample of an alloy containing rhodium and iridium only.
(i) Define relative isotopic mass.
(ii) Use Table 1.2 to calculate the relative atomic mass, \(A_r\), of iridium in the alloy. Give your answer to two decimal places.
(d) Hydrated rhodium(III) chloride, RhCl₃•xH₂O, catalyses the conversion of ethene to but-2-ene. Both stereoisomers of but-2-ene are formed in the reaction.
(i) Hydrated rhodium(III) chloride contains 20.5% by mass of water of crystallisation. Deduce the integer value of x in RhCl₃•xH₂O. Show your working.
(ii) Define stereoisomers.
(iii) Explain how the conversion of ethene to but-2-ene can be described as an addition reaction.
(iv) Draw the two stereoisomers of but-2-ene.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) \([Ar]\) represents the electronic configuration of argon: \(1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^6\).
Explanation: The noble gas notation \([Ar]\) is shorthand for the full configuration of argon, which is the core electron arrangement for cobalt.
(a)(ii) The 1s orbital is spherical in shape.
Explanation: The 1s orbital is the simplest atomic orbital, with a spherical electron density distribution centered around the nucleus.
(a)(iii) There are 3 unpaired electrons in a cobalt atom.
Explanation: The \(3d^7\) configuration has 3 unpaired electrons (Hund’s rule: electrons occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing).
(b) Completed Table 1.1:
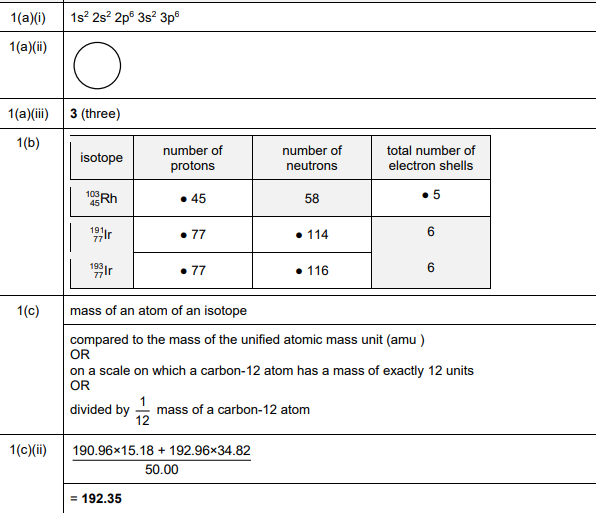
Explanation: The missing values are filled based on the given isotopic data, ensuring mass numbers and proton/neutron counts are consistent.
(c)(i) Relative isotopic mass is the mass of an isotope relative to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Explanation: It is a dimensionless quantity comparing the mass of an isotope to the standard carbon-12 scale.
(c)(ii) The relative atomic mass of iridium is \(192.22\).
Explanation: Calculation: \((191 \times 0.373) + (193 \times 0.627) = 192.22\).
(d)(i) The integer value of \(x\) is 3.
Explanation: Using the given % mass of water, the molar mass ratio gives \(x = 3\) (detailed working shown in the answer image).
(d)(ii) Stereoisomers are compounds with the same structural formula but different spatial arrangements of atoms.
Explanation: They differ in the orientation of groups around a double bond or chiral center.
(d)(iii) The reaction combines two ethene molecules to form but-2-ene, adding atoms without losing any.
Explanation: Addition reactions involve the combination of molecules to form a single product.
(d)(iv) The two stereoisomers of but-2-ene are cis-but-2-ene and trans-but-2-ene.

Explanation: The cis isomer has both methyl groups on the same side, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides.
