Question
Water leaves the end of a hose pipe at point P with a horizontal velocity of 6.6m/s, as shown in fig.2.1
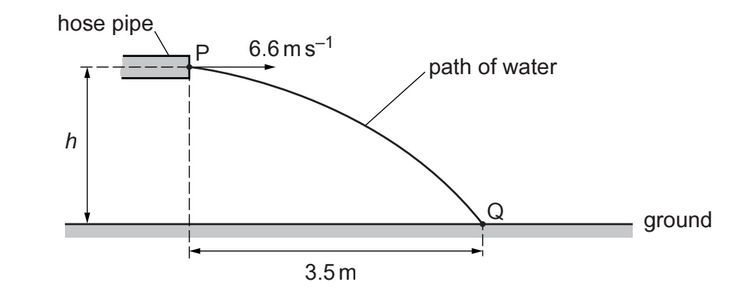
Point P is at height h above the ground. The water hits the ground at point Q. The horizontal distance from P to Q is 3.5m. Air resistance is negligible. Assume that the water between P and Q consists of non-interacting droplets of water and that the only force acting on each droplet is its weight.
(a) Explain, briefly, why the horizontal component of the velocity of a droplet of water remains constant as it moves from P to Q.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Show that the time taken for a droplet of water to move from P to Q is 0.53s.[1]
(c) Calculate height h.
h = ………………………………………………m [2]
(d) For the movement of a droplet of water from P to Q, state and explain whether the
displacement of the droplet is less than, more than or the same as the distance along its path.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(e) Calculate the magnitude of the displacement of a droplet of water that moves from P to Q.
displacement = ………………………………………………m [2] [Total: 7]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) force (on droplet of water) in horizontal direction is zero.
(b) (time taken =) 3.5 / 6.6 = 0.53 (s)
(c) s = ut + 1⁄2\(at^ 2\)
s = 1⁄2× 9.81× 0.532 \(\rightarrow h = 1.4 m\)
(d) displacement is straight-line distance (from P to Q) so less (than distance along path)
or
displacement is the shortest distance (from P to Q).
(e) \((displacement)^2 = 3.5^2 + 1.4^2\)
displacement = 3.8 m
Question
(a) Complete Table 1.1 by stating whether each of the quantities is a vector or a scalar.
(b) The variation with time t of the velocity v of an object is shown in Fig. 1.1.
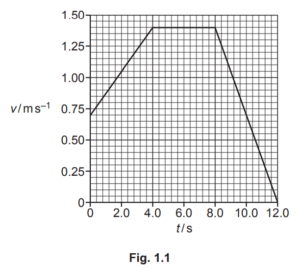
(i) Determine the acceleration of the object from time t = 0 to time t = 4.0s.
acceleration = ………………………………………… ms−2 [2]
(ii) Determine the distance moved by the object from time t = 0 to time t = 4.0s.
distance = …………………………………………….. m [2]
(c) (i) Define force. [1]
(ii) The motion represented in Fig. 1.1 is caused by a resultant force F acting on the object.
On Fig. 1.2, sketch the variation of F with time t from t = 0 to t = 12.0s. Numerical values of F are not required.
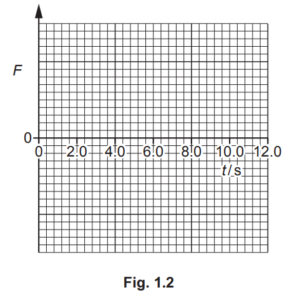
[3]
[Total: 10]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) acceleration: vector
work: scalar
power: scalar
Three correct scores 2 marks. Two correct scores 1 mark.
(b) (i) a = (v –u) / t or a = gradient or a =Δv / (Δ)t
e.g. a = (1.40 – 0.70) / 4.0
= 0.18 ms–2
(b) (ii) distance = 0.5× (0.70 + 1.40)× 4.0
or
(0.70× 4.0) + (0.5× 0.70× 4.0)
= 4.2 m
(c) (i) (force equal to) rate of change of momentum
(c) (ii) horizontal line starting from t = 0 and ending at t = 4.0 s at a positive value of F
horizontal line starting from t = 4.0 s and ending
at t = 8.0 s at F = 0
horizontal line starting from t = 8.0 s and ending at t = 12.0 s at a negative value of F and the magnitude of F is larger than
from t = 0 to 4.0 s
