Question
(a) State an experimental phenomenon that provides evidence for:
(i) the particulate nature of electromagnetic radiation
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) the wave nature of matter.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(b) A particle of matter moves with momentum p.
(i) State the equation that gives the effective wavelength λ of the particle. State the name of any other symbols used. [2]
(ii) State the name given to the wavelength of the moving particle.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) Electrons are accelerated from rest through a potential difference (p.d.) of 4.8kV.
(i) Show that the final speed of the electrons is 4.1 × 107ms–1. [2]
(ii) Calculate the effective wavelength of a beam of electrons moving at the speed in (c)(i).
wavelength = …………………………………………….. m [2] [Total: 9]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) photoelectric effect
(a) (ii) electron diffraction
(b) (i) λ = h / p
h is the Planck constant
(b) (ii) de Broglie (wavelength)
(c )(i) ½mv2 = eV
½ × 9.11 × 10–31 × v2 = 1.60 × 10–19 × 4800 so v = 4.1 × 107 m s–1
(c) (ii) λ = h / mv = 6.63 × 10–34 / (9.11 × 10–31 × 4.1 × 107)
= 1.8 × 10–11
Question
Electrons, travelling at speed v in a vacuum, are incident on a very thin carbon film, as illustrated in Fig. 7.1.
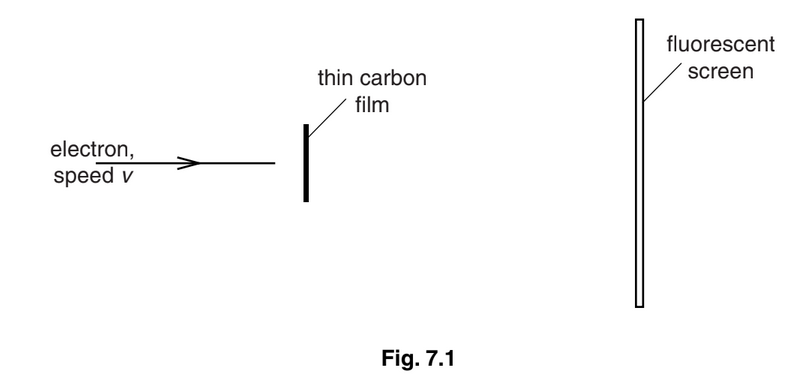
The emergent electrons are incident on a fluorescent screen. A series of concentric rings is observed on the screen.
(a) Suggest why the observed rings provide evidence for the wave nature of particles.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(b) The initial speed of the electrons is increased. State and explain the effect, if any, on the radii of the rings observed on the screen.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[3]
(c) A proton and an electron are each accelerated from rest through the same potential difference.
Determine the ratio
ratio = …………………………………………..[4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) either if light passes through suitable film / cork dust etc.
either diffraction occurs and similar pattern observed
or concentric circles are evidence of diffraction
or diffraction is a wave property
(b) (speed increases so) momentum increases
\(λ = h/p\) so λ decreases
hence radii decrease
(special case: wavelength decreases so radii decreases – scores 1/3)
or
(speed increases so) energy increases
\(λ = h / √(2Em)\) so λ decreases
hence radii decrease
(c) electron and proton have same (kinetic) energy
either \(E = p^2/ 2m\) or \(p = √(2Em) \)
ratio \(= p_e / p_p = √(m_e / m_p)\)
ratio \(= \sqrt{\frac{(9.1 × 10^{–31})} { (1.67 × 10^{–27})}\)
